Abstract
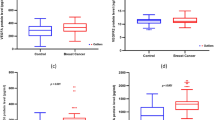
Epidermal growth factor (EGF), a potent mitogenic peptide, plays an important role in the development of cancers, including breast cancer. Previous studies showed that plasma EGF levels may influence the risk of cancer. In the current study, we hypothesized that genetic variants in the promoter region of EGF may influence plasma EGF levels and therefore are associated with breast cancer susceptibility. We genotyped three EGF polymorphisms (G61A, G-1380A, and A-1744G) in the promoter region by PCR-RFLP and measured plasma EGF levels using an enzyme immunoassay in a case–control study of Chinese women. We found that the mean plasma EGF levels in breast cancer patients (249.06 ± 197.54 pg/ml) were significantly lower than those in controls (982.41 ± 375.57 pg/ml, P < 0.001). There was a significant difference of plasma EGF levels among different genotypes carriers of the G-1380A locus in 654 controls (P = 0.007). After adjustment for age, body mass index, family history of cancer, age at menarche, and menopause status, EGF-1380AA carriers had significantly higher plasma EGF levels than -1380GG carriers did (P = 0.003). However, we did not find any significant associations between the three EGF polymorphisms (G61A, G-1380A, and A-1744G) and the risk of breast cancer. These findings indicated that plasma EGF levels served as a protective marker against breast cancer in our study and EGF G-1380A variant might be a modifier on it. Further studies are warranted to verify these findings.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
- PR:
-
Progesterone receptor
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- OR:
-
Odds-ratio
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
References
Smiqal C, Jemal A, Wrad E, Cokkinides V, Smith R, Howe HL, Thun M (2006) Trends in breast cancer by race and ethnicity: update 2006. CA Cancer J Clin 56:168–183
Yang L, Parkin DM, Ferlay J, Li L, Chen Y (2005) Estimates of cancer incidence in China for 2000 and projections for 2005. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14:243–250
Yager JD, Davidson NE (2006) Estrogen Carcinogenesis in breast cancer. N Engl J Med 354:270–282
Sporn MB, Roberts AB (1985) Autocrine growth factors and cancer. Nature 313:745–747
Martinez LI, Dickson RB (1996) Dual regulation of the epidermal growth factor family of growth factors in breast cancer by sex steroids and protein Kinase C. J Steriod Biochem Mol Biol 57:1–11
Levin R (2003) Bidirectional signaling between the estrogen receptor and the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Endocrinol 17:309–317
Yarden Y (2001) The EGFR family and its ligands in human cancer: signalling mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Eur J Cancer 37:S3–S8
Harari PM (2004) Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition strategies in oncology. Endocr Relat Cancer 11:689–708
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX (2001) Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:127–137
Garcia R, Franklin RA, McCubrev JA (2006) EGF induces cell motility and multi-drug resistance gene expression in breast cancer cells. Cell Cycle 5:2820–2826
Salomon DS, Brandt R, Ciardiello F, Normanno N (1995) Epidermal growth factor-related peptides and their receptors in human malignancies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 19:183–232
Tokunaga A, Onda M, Okuda T, Teramoto T, Fujita I, Mizutani T, Kiyama T, Yoshiyuki T, Nishi K, Matsukura N (1995) Clinical significance of epidermal growth factor (EGF), EGF receptor, and c-erbB-2 in human gastric cancer. Cancer 75:1418–1425
Murphy LC, Dotzlaw H, Wong MS, Miller T, Mrockowski B, Gong Y, Murphy LJ (1990) Epidermal growth factor: receptor and ligand expression in human breast cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 1:305–315
Fenton SE,Groce NS, Lee DC (1996) Characterization of the mouse epidermal growth factor promoter and 5′-Flanking region. Role for an atypical TATA sequence. J Biol Chem 271:30870–30878
Mullhaupt B, Feren A, Jones A, Fodor E (2000) DNA sequence and functional characterization of the human and rat epidermal growth factor promoter: regulation by cell growth. Gene 50:191–200
Shahbazi M, Pravica V, Nasreen N, Fakhoury H, Fryer AA, Strange RC, Hutchinson PE, Osborne JE, Lear JT, Smith AG, Hutchinson IV (2002) Association between functional polymorphism in EGF gene and malignant melanoma. Lancet 359:397–401
Jin G, Miao R, Deng Y, Hu Z, Zhou Y, Tan Y, Wang J, Hua Z, Ding W, Wang L, Chen W, Shen J, Wang X, Xu Y, Shen H (2007) Variant genotypes and haplotypes of the epidermal growth factor gene promoter are associated with a decreased risk of gastric cancer in a high-risk Chinese population. Cancer Sci 98:864–868
Huo X, Hu Z, Zhai X, Wang Y, Wang S, Wang X, Qin J, Chen W, Jin G, Liu J, Gao J, Wei Q, Wang X, Shen H (2007) Common non-synonymous polymorphisms in the BRCA1 associated RING Domain (BARD1) gene are associated with breast cancer susceptibility: a case–control analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 102:329–337
Stephens M, Donnelly P (2003) A comparison of bayesian methods for haplotype reconstruction from population genotype data. Am J Hum Genet 73:1162–1169
Olayioye MA, Neve RM, Lane HA, Hynes NE (2000) The ErbB signaling network: receptor heterodimerization in development and cancer. EMBO J 19:3159–3167
Normanno N, Luca AD, Bianco C, Strizzi L, Mancino M, Maiello MR, Carotenuto A, Feo GD, Caponigro F, Salomon DS (2006) Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling in cancer. Gene 366:2–16
Tomaszewski J, Miturski R, Kotarski J (1996) Concentration of epidermal growth factor (EGF) in serum of women with endometrial cancer. Ginekol Pol 67:248–253
Pawlikowski M, Cieslak D, Stepien H, Berner J, Rybiński K (1989) Elevated blood serum levels of epidermal growth factor in some patients with gastric cancer. Endokrynol Pol 40:149–153
Navarro MA, Mesia R, Diez-Gibert O, Rueda A, Ojeda B, Alonso MC (1997) Epidermal growth factor in plasma and saliva of patients with active breast cancer and breast cancer patients in follow-up compared with healthy women. Breast Cancer Res Treat 42:83–86
Normanno N, Bianco C, Strizzi L, Mancino M, Maiello MR, De Luca A, Caponigro F, Salomon DS (2005) The ErbB receptors and their ligands in cancer: an overview. Curr Drug Targets 6:243–257
McCarron SL, Bateman AC, Theaker JM, Howell WM (2003) EGF +61 gene polymorphism and susceptibility to and prognostic markers in cutaneous malignant melanoma. Int J Cancer 107:673–675
Bhowmick DA, Zhuang Z, Wait SD, Weil RJ (2004) A functional polymorphism in the EGF gene is found with increased frequency in glioblastoma multiforme patients and is associated with more aggressive disease. Cancer Res 64:1220–1223
Amend KL, Elder JT, Tomsho LP, Bonner JD, Johnson TM, Schwartz J, Berwick M, Gruber SB (2004) EGF gene polymorphism and the risk of incident primary melanoma. Cancer Res 64:2668–2672
Randerson-Moor JA, Gaut R, Turner F, Whitaker L, Barrett JH, Silva Idos S, Swerdlow A, Bishop DT, Bishop JA (2004) The relationship between the epidermal growth factor (EGF) 5′UTR variant A61G and melanoma/nevus susceptibility. J Invest Dermatol 123:755–759
James MR, Hayward NK, Dumenil T, Montgomery GW, Martin NG, Duffy DL (2004) Epidermal growth factor gene (EGF) polymorphism and risk of melanocytic neoplasia. J Invest Dermatol 123:760–762
Hamai Y, Matsumura S, Matsusaki K, Kitadai Y, Yoshida K, Yamaguchi Y, Imai K, Nakachi K, Toge T, Yasui W (2005) A single nucleotide polymorphism in the 5-untranslated region of the EGF gene is associated with occurrence and malignant progression of gastric cancer. Pathobiology 72:133–138
Goto Y, Ando T, Goto H, Hamajima N (2005) No association between EGF gene polymorphism and gastric cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14:2454–2456
Costa BM, Ferreira P, Costa S, Canedo P, Oliveira P, Silva A, Pardal F, Suriano G, Machado JC, Lopes JM, Reis RM (2007) Association between functional EGF+61 polymorphism and glioma risk. Clin Cancer Res 13:2621–2626
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Innovative Key Grant of Department of Education of China (no. 705023); National Key Basic Research Program Grants 2002CB512908, Jiangsu Natural Science Foundation BK2004145.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Tian, T., Hu, Z. et al. EGF promoter SNPs, plasma EGF levels and risk of breast cancer in Chinese women. Breast Cancer Res Treat 111, 321–327 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-007-9784-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-007-9784-4