Abstract
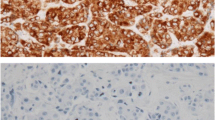
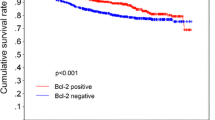
Background This study was undertaken to evaluate the prognostic significance of Bcl-2, a apoptosis-related protein, in patients with early stage breast cancer treated with breast conservation treatment (BCT). Methods After obtaining IRB approval, 504 patients with early stage breast cancer treated with BCT were entered in this study. The paraffin specimens were constructed into tissue micro-arrays with two-fold redundancy, processed and stained for Bcl-2 antibody. Bcl-2 expression was correlated with other clinicopathological parameters and clinical outcomes. Results Bcl-2 expression was identified in 116 cases (28%). Bcl-2 expression was positively correlated with both estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor status (P < 0.0001, respectively). Bcl-2 expression was associated with ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence (P = 0.0322, by log-rank test). Multivariate analysis using Cox proportional hazard model showed that Bcl-2 expression still retained significance as an independent prognostic factor for breast recurrence (P = 0.0348). Conclusions Bcl-2 expression is highly associated with an increased risk of local recurrence in patients with early stage breast cancer. Immunohistochemical staining of the primary tumor for Bcl-2 might be useful to select optimal treatment options for these patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fisher B, Anderson S, Bryant J et al (2002) Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized trial comparing total mastectomy, lumpectomy, and lumpectomy plus irradiation for the treatment of invasive breast cancer. N Engl J Med 347(16):1233–1241. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa022152
Fisher B, Jeong JH, Anderson S, Bryant J, Fisher ER, Wolmark N (2002) Twenty-five-year follow-up of a randomized trial comparing radical mastectomy, total mastectomy, and total mastectomy followed by irradiation. N Engl J Med 347(8):567–575. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa020128
Luini A, Gatti G, Zurrida S et al (2007) The evolution of the conservative approach to breast cancer. Breast 16(2):120–129. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2006.11.001
Fisher B, Anderson S, Fisher ER et al (1991) Significance of ipsilateral breast tumour recurrence after lumpectomy. Lancet 338(8763):327–331. doi:10.1016/0140-6736(91)90475-5
Haffty BG, Carter D, Flynn SD et al (1993) Local recurrence versus new primary: clinical analysis of 82 breast relapses and potential applications for genetic fingerprinting. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 27(3):575–583
Fourquet A, Campana F, Zafrani B et al (1989) Prognostic factors of breast recurrence in the conservative management of early breast cancer: a 25-year follow-up. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 17(4):719–725
Kurtz JM, Jacquemier J, Amalric R et al (1990) Risk factors for breast recurrence in premenopausal and postmenopausal patients with ductal cancers treated by conservation therapy. Cancer 65(8):1867–1878. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(19900415)65:8<1867::AID-CNCR2820650833>3.0.CO;2-I
Borger J, Kemperman H, Hart A, Peterse H, van Dongen J, Bartelink H (1994) Risk factors in breast-conservation therapy. J Clin Oncol 12(4):653–660
Schnitt SJ, Connolly JL, Harris JR, Hellman S, Cohen RB (1984) Pathologic predictors of early local recurrence in stage I and II breast cancer treated by primary radiation therapy. Cancer 53(5):1049–1057. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(19840301)53:5<1049::AID-CNCR2820530506>3.0.CO;2-O
Turner BC, Haffty BG, Narayanan L et al (1997) Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor overexpression mediates cellular radioresistance and local breast cancer recurrence after lumpectomy and radiation. Cancer Res 57(15):3079–3083
Haffty BG, Brown F, Carter D, Flynn S (1996) Evaluation of HER-2 neu oncoprotein expression as a prognostic indicator of local recurrence in conservatively treated breast cancer: a case–control study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 35(4):751–757. doi:10.1016/0360-3016(96)00150-2
Turner BC, Gumbs AA, Carter D, Glazer PM, Haffty BG (2000) Cyclin D1 expression and early breast cancer recurrence following lumpectomy and radiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47(5):1169–1176. doi:10.1016/S0360-3016(00)00525-3
Recht A, Houlihan MJ (1995) Conservative surgery without radiotherapy in the treatment of patients with early-stage invasive breast cancer. A review. Ann Surg 222(1):9–18. doi:10.1097/00000658-199507000-00003
Zhou L, Yuan R, Serggio L (2003) Molecular mechanisms of irradiation-induced apoptosis. Front Biosci 8:d9–d19. doi:10.2741/927
Steller H (1995) Mechanisms and genes of cellular suicide. Science 267(5203):1445–1449. doi:10.1126/science.7878463
Thompson CB (1995) Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science 267(5203):1456–1462. doi:10.1126/science.7878464
Hawkins CJ, Vaux DL (1994) Analysis of the role of bcl-2 in apoptosis. Immunol Rev 142:127–139. doi:10.1111/j.1600-065X.1994.tb00886.x
Yang QF, Sakurai T, Yoshimura G et al (2000) Expression of Bcl-2 but not Bax or p53 correlates with in vitro resistance to a series of anticancer drugs in breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat 61(3):211–216. doi:10.1023/A:1006474307180
Yang Q, Sakurai T, Yoshimura G et al (2003) Prognostic value of Bcl-2 in invasive breast cancer receiving chemotherapy and endocrine therapy. Oncol Rep 10(1):121–125
Haffty BG, Yang Q, Reiss M et al (2006) Locoregional relapse and distant metastasis in conservatively managed triple negative early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 24(36):5652–5657. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.06.5664
Haffty BG, Fischer D, Fischer JJ (1990) Regional nodal irradiation in the conservative treatment of breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 19(4):859–865
Pejavar S, Wilson LD, Haffty BG (2006) Regional nodal recurrence in breast cancer patients treated with conservative surgery and radiation therapy (BCS+RT). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 66(5):1320–1327. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.07.1379
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E et al (2006) Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin 56(2):106–130
Fulda S, Debatin KM (2006) Extrinsic versus intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene 25(34):4798–4811. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209608
Haith LR Jr, Patton ML, Goldman WT, McCutchan KM (1993) Diminishing blood loss during operation for burns. Surg Gynecol Obstet 176(2):119–123
Sabourin JC, Martin A, Baruch J, Truc JB, Gompel A, Poitout P (1994) bcl-2 expression in normal breast tissue during the menstrual cycle. Int J Cancer 59(1):1–6. doi:10.1002/ijc.2910590102
McDonnell TJ, Deane N, Platt FM et al (1989) bcl-2-immunoglobulin transgenic mice demonstrate extended B cell survival and follicular lymphoproliferation. Cell 57(1):79–88. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(89)90174-8
McDonnell TJ, Korsmeyer SJ (1991) Progression from lymphoid hyperplasia to high-grade malignant lymphoma in mice transgenic for the t(14; 18). Nature 349(6306):254–256. doi:10.1038/349254a0
Pietenpol JA, Papadopoulos N, Markowitz S, Willson JK, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (1994) Paradoxical inhibition of solid tumor cell growth by bcl2. Cancer Res 54(14):3714–3717
Lin X, Denmeade SR, Isaacs JT (1995) The genetics of programmed (apoptotic) cell death. Cancer Surv 25:173–194
Rupnow BA, Knox SJ (1999) The role of radiation-induced apoptosis as a determinant of tumor responses to radiation therapy. Apoptosis 4(2):115–143. doi:10.1023/A:1009675028784
Daidone MG, Silvestrini R, Luisi A et al (1995) Changes in biological markers after primary chemotherapy for breast cancers. Int J Cancer 61(3):301–305. doi:10.1002/ijc.2910610304
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Yale Cancer Center Swebelius Fund and the Breast Cancer Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Q., Moran, M.S. & Haffty, B.G. Bcl-2 expression predicts local relapse for early-stage breast cancer receiving conserving surgery and radiotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 115, 343–348 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-008-0068-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-008-0068-4