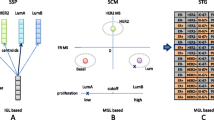
Abstract
Pooling of microarray datasets seems to be a reasonable approach to increase sample size when a heterogeneous disease like breast cancer is concerned. Different methods for the adaption of datasets have been used in the literature. We have analyzed influences of these strategies using a pool of 3,030 Affymetrix U133A microarrays from breast cancer samples. We present data on the resulting concordance with biochemical assays of well known parameters and highlight critical pitfalls. We further propose a method for the inference of cutoff values directly from the data without prior knowledge of the true result. The cutoffs derived by this method displayed high specificity and sensitivity. Markers with a bimodal distribution like ER, PgR, and HER2 discriminate different biological subtypes of disease with distinct clinical courses. In contrast, markers displaying a continuous distribution like proliferation markers as Ki67 rather describe the composition of the mixture of cells in the tumor.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coates A, Goldhirsch A, Gelber R, International Breast Cancer Study Group (2002) Overhauling the breast cancer overview: are subsets subversive? Lancet Oncol 3(9):525–526. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(02)00842-2
Cole BF, Gelber RD, Gelber S, Coates AS, Goldhirsch A (2001) Polychemotherapy for early breast cancer: an overview of the randomised clinical trials with quality-adjusted survival analysis. Lancet 358(9278):277–286. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(01)05483-6
Sylvester R, Collette L, Duchateau L (2000) The role of meta-analyses in assessing cancer treatments. Eur J Cancer 36(11):1351–1358. doi:10.1016/S0959-8049(00)00125-8
Ein-Dor L, Zuk O, Domany E (2006) Thousands of samples are needed to generate a robust gene list for predicting outcome in cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(15):5923–5928. doi:10.1073/pnas.0601231103
Cheadle C, Vawter MP, Freed WJ, Becker KG (2003) Analysis of microarray data using Z score transformation. J Mol Diagn 5(2):73–81
Eisen MB, Spellman PT, Brown PO, Botstein D (1998) Cluster analysis and display of genome-wide expression patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(25):14863–14868. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.25.14863
Getz G, Levine E, Domany E (2000) Coupled two-way clustering analysis of gene microarray data. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(22):12079–12084. doi:10.1073/pnas.210134797
Gong Y, Yan K, Lin F, Anderson K, Sotiriou C, Andre F, Holmes FA, Valero V, Booser D, Pippen JE Jr, Vukelja S, Gomez H, Mejia J, Barajas LJ, Hess KR, Sneige N, Hortobagyi GN, Pusztai L, Symmans WF (2007) Determination of oestrogen-receptor status and ERBB2 status of breast carcinoma: a gene-expression profiling study. Lancet Oncol 8(3):203–211. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(07)70042-6
Ahr A, Karn T, Solbach C, Seiter T, Strebhardt K, Holtrich U, Kaufmann M (2002) Identification of high risk breast-cancer patients by gene expression profiling. Lancet 359(9301):131–132. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07337-3
Rody A, Holtrich U, Gaetje R, Gehrmann M, Engels K, von Minckwitz G, Loibl S, Diallo-Danebrock R, Ruckhäberle E, Metzler D, Ahr A, Solbach C, Karn T, Kaufmann M (2007) Poor outcome in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancers predicted by loss of Plexin B1. Clin Cancer Res 13(4):1115–1122. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2433
Rody A, Karn T, Ruckhäberle E, Hanker L, Metzler D, Müller V, Solbach C, Ahr A, Gätje R, Holtrich U, Kaufmann M (2009) Loss of Plexin B1 is highly prognostic in low proliferating ER positive breast cancers—results of a large scale microarray analysis. Eur J Cancer 45(3):405–413
Ruckhäberle E, Rody A, Engels K, Gaetje R, von Minckwitz G, Schiffmann S, Grösch S, Geisslinger G, Holtrich U, Karn T, Kaufmann M (2008) Microarray analysis of altered sphingolipid metabolism reveals prognostic significance of sphingosine kinase 1 in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 112(1):41–52. doi:10.1007/s10549-007-9836-9
Rody A, Karn T, Solbach C, Gaetje R, Munnes M, Kissler S, Ruckhäberle E, Minckwitz GV, Loibl S, Holtrich U, Kaufmann M (2007) The erbB2+ cluster of the intrinsic gene set predicts tumor response of breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy with docetaxel, doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide within the GEPARTRIO trial. Breast 16(3):235–240. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2007.02.006
Wang Y, Klijn JG, Zhang Y, Sieuwerts AM, Look MP, Yang F, Talantov D, Timmermans M, Meijer-van Gelder ME, Yu J, Jatkoe T, Berns EM, Atkins D, Foekens JA (2005) Gene-expression profiles to predict distant metastasis of lymph-node-negative primary breast cancer. Lancet 365(9460):671–679
Minn AJ, Gupta GP, Padua D, Bos P, Nguyen DX, Nuyten D, Kreike B, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Ishwaran H, Foekens JA, van de Vijver M, Massagué J (2007) Lung metastasis genes couple breast tumor size and metastatic spread. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(16):6740–6745. doi:10.1073/pnas.0701138104
Creighton CJ, Kent Osborne C, van de Vijver MJ, Foekens JA, Klijn JG, Horlings HM, Nuyten D, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Chamness GC, Hilsenbeck SG, Lee AV, Schiff R (2009) Molecular profiles of progesterone receptor loss in human breast tumors. Breast Cancer Res Treat 114(2):287–299. doi:10.1007/s10549-008-0017-2
Schmidt M, Böhm D, von Törne C, Steiner E, Puhl A, Pilch H, Lehr HA, Hengstler JG, Kölbl H, Gehrmann M (2008) The humoral immune system has a key prognostic impact in node-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res 68(13):5405–5413. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5206
Desmedt C, Piette F, Loi S, Wang Y, Lallemand F, Haibe-Kains B, Viale G, Delorenzi M, Zhang Y, d’Assignies, Bergh J, Lidereau R, Ellis P, Harris AL, Klijn JG, Foekens JA, Cardoso F, Piccart MJ, Buyse M, Sotiriou C (2007) TRANSBIG Consortium. Strong time dependence of the 76-gene prognostic signature for node-negative breast cancer patients in the TRANSBIG multicenter independent validation series. Clin Cancer Res 13(11):3207–3214
Sotiriou C, Wirapati P, Loi S, Harris A, Fox S, Smeds J, Nordgren H, Farmer P, Praz V, Haibe-Kains B, Desmedt C, Larsimont D, Cardoso F, Peterse H, Nuyten D, Buyse M, Van de Vijver MJ, Bergh J, Piccart M, Delorenzi M (2006) Gene expression profiling in breast cancer: understanding the molecular basis of histologic grade to improve prognosis. J Natl Cancer Inst 98(4):262–272
Loi S, Haibe-Kains B, Desmedt C, Lallemand F, Tutt AM, Gillet C, Ellis P, Harris A, Bergh J, Foekens JA, Klijn JG, Larsimont D, Buyse M, Bontempi G, Delorenzi M, Piccart MJ, Sotiriou C (2007) Definition of clinically distinct molecular subtypes in estrogen receptor-positive breast carcinomas through genomic grade. J Clin Oncol 25(10):1239–1246. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.07.1522
Loi S, Haibe-Kains B, Desmedt C, Wirapati P, Lallemand F, Tutt AM, Gillet C, Ellis P, Ryder K, Reid JF, Daidone MG, Pierotti MA, Berns EM, Jansen MP, Foekens JA, Delorenzi M, Bontempi G, Piccart MJ, Sotiriou C (2008) Predicting prognosis using molecular profiling in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer treated with tamoxifen. BMC Genomics 9:239. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-9-239
Zhang Y, Sieuwerts AM, McGreevy M, Casey G, Cufer T, Paradiso A, Harbeck N, Span PN, Hicks DG, Crowe J, Tubbs RR, Budd GT, Lyons J, Sweep FC, Schmitt M, Schittulli F, Golouh R, Talantov D, Wang Y, Foekens JA (2009) The 76-gene signature defines high-risk patients that benefit from adjuvant tamoxifen therapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat. doi:10.1007/s10549-008-0183-2
Pawitan Y, Bjohle J, Amler L, Borg AL, Egyhazi S, Hall P, Han X, Holmberg L, Huang F, Klaar S, Liu ET, Miller L, Nordgren H, Ploner A, Sandelin K, Shaw PM, Smeds J, Skoog L, Wedren S, Bergh J (2005) Gene expression profiling spares early breast cancer patients from adjuvant therapy: derived and validated in two population-based cohorts. Breast Cancer Res 7(6):R953–R964. doi:10.1186/bcr1325
Miller LD, Smeds J, George J, Vega VB, Vergara L, Ploner A, Pawitan Y, Hall P, Klaar S, Liu ET, Bergh J (2005) An expression signature for p53 status in human breast cancer predicts mutation status, transcriptional effects, and patient survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(38):13550–13555. doi:10.1073/pnas.0506230102
Ivshina AV, George J, Senko O, Mow B, Putti T, Smeds J, Lindahl T, Pawitan Y, Hall P, Nordgren H, Wong John EL, Liu ET, Bergh J, Kuznetsov VA, Miller LD (2006) Genetic reclassification of histologic grade delineates new clinical subtypes of breast cancer. Cancer Res 66(21):10292–10301. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4414
Chin K, DeVries S, Fridlyand J, Spellman PT, Roydasgupta R, Kuo WL, Lapuk A, Neve RM, Qian Z, Ryder T, Chen F, Feiler H, Tokuyasu T, Kingsley C, Dairkee S, Meng Z, Chew K, Pinkel D, Jain A, Ljung BM, Esserman L, Albertson DG, Waldman FM, Gray JW (2006) Genomic and transcriptional aberrations linked to breast cancer pathophysiologies. Cancer Cell 10(6):529–541. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2006.10.009
Minn AJ, Gupta GP, Siegel PM, Bos PD, Shu W, Giri DD, Viale A, Olshen AB, Gerald WL, Massagué J (2005) Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to lung. Nature 436(7050):518–524. doi:10.1038/nature03799
Hess KR, Anderson K, Symmans WF, Valero V, Ibrahim N, Mejia JA, Booser D, Theriault RL, Buzdar AU, Dempsey PJ, Rouzier R, Sneige N, Ross JS, Vidaurre T, Gómez HL, Hortobagyi GN, Pusztai L (2006) Pharmacogenomic predictor of sensitivity to preoperative chemotherapy with paclitaxel and fluorouracil, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 24(26):4236–4244. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.05.6861
Farmer P, Bonnefoi H, Becette V, Tubiana-Hulin M, Fumoleau P, Larsimont D, Macgrogan G, Bergh J, Cameron D, Goldstein D, Duss S, Nicoulaz AL, Brisken C, Fiche M, Delorenzi M, Iggo R (2005) Identification of molecular apocrine breast tumours by microarray analysis. Oncogene 24(29):4660–4671. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208561
Miller WR, Larionov AA, Renshaw L, Anderson TJ, White S, Murray J, Murray E, Hampton G, Walker JR, Ho S, Krause A, Evans DB, Dixon JM (2007) Changes in breast cancer transcriptional profiles after treatment with the aromatase inhibitor, letrozole. Pharmacogenet Genom 17(10):813–826. doi:10.1097/FPC.0b013e32820b853a
The International Genomics Consortium (IGC) The expO project (Expression Project For Oncology) http://www.intgen.org/
Yu K, Ganesan K, Tan LK, Laban M, Wu J, Zhao XD, Li H, Leung CH, Zhu Y, Wei CL, Hooi SC, Miller L, Tan P (2008) A precisely regulated gene expression cassette potently modulates metastasis and survival in multiple solid cancers. PLoS Genet 4(7):e1000129. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000129
Januario T, Lackner MR (2009) Gene expression profiling of 30 human breast cancers. Gene Expression Omnibus Series GSE12763. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE12763
Richardson AL, Wang ZC, De Nicolo A, Lu X, Brown M, Miron A, Liao X, Iglehart JD, Livingston DM, Ganesan S (2006) X chromosomal abnormalities in basal-like human breast cancer. Cancer Cell 9(2):121–132. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2006.01.013
Klein A, Wessel R, Graessmann M, Jürgens M, Petersen I, Schmutzler R, Niederacher D, Arnold N, Meindl A, Scherneck S, Seitz S, Graessmann A (2007) Comparison of gene expression data from human and mouse breast cancers: identification of a conserved breast tumor gene set. Int J Cancer 121(3):683–688. doi:10.1002/ijc.22630
Marty B, Maire V, Gravier E, Rigaill G, Vincent-Salomon A, Kappler M, Lebigot I, Djelti F, Tourdès A, Gestraud P, Hupé P, Barillot E, Cruzalegui F, Tucker GC, Stern MH, Thiery JP, Hickman JA, Dubois T (2008) Frequent PTEN genomic alterations and activated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway in basal-like breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res 10(6):R101. doi:10.1186/bcr2204
Chen DT, Nasir A, Culhane A, Venkataramu C, Fulp W, Rubio R, Wang T, Agrawal D, McCarthy SM, Gruidl M, Bloom G, Anderson T, White J, Quackenbush J, Yeatman T (2009) Proliferative genes dominate malignancy-risk gene signature in histologically-normal breast tissue. Breast Cancer Res Treat. doi:10.1007/s10549-009-0344-y
Affymetrix (2001) Statistical algorithms reference guide, technical report. Affymetrix
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA (2004) affy–analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level. Bioinformatics 20(3):307–315. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btg405
Gentleman RC, Carey VJ, Bates DM, Bolstad B, Dettling M, Dudoit S, Ellis B, Gautier L, Ge Y, Gentry J, Hornik K, Hothorn T, Huber W, Iacus S, Irizarry R, Leisch F, Li C, Maechler M, Rossini AJ, Sawitzki G, Smith C, Smyth G, Tierney L, Yang JY, Zhang J (2004) Bioconductor: open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol 5(10):R80. doi:10.1186/gb-2004-5-10-r80
Spyratos F, Ferrero-Poüs M, Trassard M, Hacène K, Phillips E, Tubiana-Hulin M, Le Doussal V (2002) Correlation between MIB-1 and other proliferation markers: clinical implications of the MIB-1 cutoff value. Cancer 94(8):2151–2159. doi:10.1002/cncr.10458
de Azambuja E, Cardoso F, de Castro G Jr, Colozza M, Mano MS, Durbecq V, Sotiriou C, Larsimont D, Piccart-Gebhart MJ, Paesmans M (2007) Ki-67 as prognostic marker in early breast cancer: a meta-analysis of published studies involving 12, 155 patients. Br J Cancer 96(10):1504–1513. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6603756
Venables WN, Ripley BD (2002) Modern Applied Statistics with S, chap 16.3, 4th edn. Springer. ISBN 0-387-95457-0
Anderson WF, Chen BE, Jatoi I, Rosenberg PS (2006) Effects of estrogen receptor expression and histopathology on annual hazard rates of death from breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 100(1):121–126. doi:10.1007/s10549-006-9231-y
Jatoi I, Chen BE, Anderson WF, Rosenberg PS (2007) Breast cancer mortality trends in the United States according to estrogen receptor status and age at diagnosis. J Clin Oncol 25(13):1683–1690. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.09.2106
Polyak K (2007) Breast cancer: origins and evolution. J Clin Invest 117(11):3155–3163. doi:10.1172/JCI33295
Collins LC, Botero ML, Schnitt SJ (2005) Bimodal frequency distribution of estrogen receptor immunohistochemical staining results in breast cancer: an analysis of 825 cases. Am J Clin Pathol 123(1):16–20. doi:10.1309/HCF035N9WK40ETJ0
Nadji M, Gomez-Fernandez C, Ganjei-Azar P, Morales AR (2005) Immunohistochemistry of estrogen and progesterone receptors reconsidered: experience with 5, 993 breast cancers. Am J Clin Pathol 123(1):21–27. doi:10.1309/4WV79N2GHJ3X1841
Barnes DM, Millis RR, Beex LV, Thorpe SM, Leake RE (1998) Increased use of immunohistochemistry for oestrogen receptor measurement in mammary carcinoma: the need for quality assurance. Eur J Cancer 34(11):1677–1682. doi:10.1016/S0959-8049(98)00149-X
Ross JS, Symmans WF, Pusztai L, Hortobagyi GN (2007) Standardizing slide-based assays in breast cancer: hormone receptors, HER2, and sentinel lymph nodes. Clin Cancer Res 13(10):2831–2835. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2522
Badve SS, Baehner FL, Gray RP, Childs BH, Maddala T, Liu ML, Rowley SC, Shak S, Perez EA, Shulman LJ, Martino S, Davidson NE, Sledge GW, Goldstein LJ, Sparano JA (2008) Estrogen- and progesterone-receptor status in ECOG 2197: comparison of immunohistochemistry by local and central laboratories and quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction by central laboratory. J Clin Oncol 26(15):2433–2435. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.13.6424
Mann GB, Fahey VD, Feleppa F, Buchanan MR (2005) Reliance on hormone receptor assays of surgical specimens may compromise outcome in patients with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 23(22):5148–5154. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.02.076
Ma XJ, Hilsenbeck SG, Wang W, Ding L, Sgroi DC, Bender RA, Osborne CK, Allred DC, Erlander MG (2006) The HOXB13:IL17BR expression index is a prognostic factor in early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 24(28):4611–4619. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.06.6944
Sørlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Thorsen T, Quist H, Matese JC, Brown PO, Botstein D, Eystein Lønning P, Børresen-Dale AL (2001) Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(19):10869–10874. doi:10.1073/pnas.191367098
Gruvberger S, Ringnér M, Chen Y, Panavally S, Saal LH, Borg A, Fernö M, Peterson C, Meltzer PS (2001) Estrogen receptor status in breast cancer is associated with remarkably distinct gene expression patterns. Cancer Res 61(16):5979–5984
van‘t Veer LJ, Dai H, van de Vijver MJ, He YD, Hart AA, Mao M, Peterse HL, van der Kooy K, Marton MJ, Witteveen AT, Schreiber GJ, Kerkhoven RM, Roberts C, Linsley PS, Bernards R, Friend SH (2002) Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature 415(6871):530–536. doi:10.1038/415530a
Lusa L, McShane LM, Reid JF, De Cecco L, Ambrogi F, Biganzoli E, Gariboldi M, Pierotti MA (2007) Challenges in projecting clustering results across gene expression-profiling datasets. J Natl Cancer Inst 99(22):1715–1723. doi:10.1093/jnci/djm216
Teschendorff AE, Naderi A, Barbosa-Morais NL, Caldas C (2006) PACK: profile analysis using clustering and kurtosis to find molecular classifiers in cancer. Bioinformatics 22(18):2269–2275. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btl174
Ertel A, Tozeren A (2008) Switch-like genes populate cell communication pathways and are enriched for extracellular proteins. BMC Genomics 9:3. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-9-3
Gormley M, Tozeren A (2008) Expression profiles of switch-like genes accurately classify tissue and infectious disease phenotypes in model-based classification. BMC Bioinformatics 9:486. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-9-486
Ertel A, Tozeren A (2008) Human and mouse switch-like genes share common transcriptional regulatory mechanisms for bimodality. BMC Genomics 9(1):628. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-9-628
Sell S, Pierce GB (1994) Maturation arrest of stem cell differentiation is a common pathway for the cellular origin of teratocarcinomas and epithelial cancers. Lab Invest 70(1):6–22
Pardal R, Clarke MF, Morrison SJ (2003) Applying the principles of stem-cell biology to cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 3(12):895–902. doi:10.1038/nrc1232
Sanai N, Alvarez-Buylla A, Berger MS (2005) Neural stem cells and the origin of gliomas. N Engl J Med 353(8):811–822. doi:10.1056/NEJMra043666
Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF, Weissman IL (2001) Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature 414(6859):105–111. doi:10.1038/35102167
Jordan CT, Guzman ML, Noble M (2006) Cancer stem cells. N Engl J Med 355(12):1253–1261. doi:10.1056/NEJMra061808
Acknowledgments
We thank Samira Adel and Katherina Kourtis for expert technical assistance and anonymous reviewers for their insightful suggestions. This work was supported by grants from the Deutsche Krebshilfe, the Margarete Bonifer-Stiftung, Bad Soden, the BANSS-Stiftung, Biedenkopf, and the Dr. Robert Pfleger-Stiftung, Bamberg. The efforts of the IGC and expO [31] are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karn, T., Metzler, D., Ruckhäberle, E. et al. Data driven derivation of cutoffs from a pool of 3,030 Affymetrix arrays to stratify distinct clinical types of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 120, 567–579 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-009-0416-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-009-0416-z