Abstract
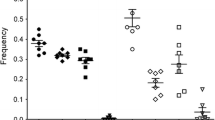
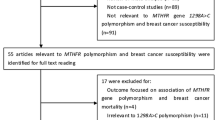
The association between methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene polymorphisms and breast cancer risk has been widely reported, but results were inconsistent and underpowered. To clarify the effects of MTHFR polymorphisms on the risk of breast cancer, an updated meta-analysis of all available studies relating C677T and/or A1298C polymorphisms of MTHFR gene to the risk of breast cancer was conducted. Eligible articles were identified by search of databases including MEDLINE, PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE and Chinese Biomedical Literature database (CBM) for the period up to January 2010. Finally, a total of 41 studies with 16,480 cases and 22,388 controls were included, all for C677T polymorphism and 20 with 12,170 cases and 15,865 controls for A1298C polymorphism. The pooled ORs were performed for the allele contrasts, additive genetic model, dominant genetic model, and recessive genetic model, respectively. Subgroup analyses were also performed by ethnicity and menopausal status. With respect to C677T polymorphism, significantly elevated breast cancer risk was found in overall analysis (T vs. C: OR = 1.041, 95% CI = 1.009–1.073; TT vs. CC: OR = 1.132, 95% CI = 1.019–1.259; TT vs. CC + CT: OR = 1.119, 95% CI = 1.014–1.236); in the subgroup analysis by ethnicity, significantly increased risk was found in East Asian population (T vs. C: OR = 1.121, 95% CI = 1.016–1.237; TT vs. CC: OR = 1.331, 95% CI = 1.073–1.650; TT vs. CC + CT: OR = 1.265, 95% CI = 1.058–1.513) but not in Caucasian population; in the subgroup analysis by menopausal status, no statistically significant association was found. With respect to A1298C polymorphism, no significant association with breast cancer risk was demonstrated in overall, ethnicity- and menopausal status-based population. It can be concluded that potentially functional MTHFR C677T polymorphism may play a low penetrance role in the development of breast cancer.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Larsson SC, Giovannucci E, Wolk A (2007) Folate and risk of breast cancer: a meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst 99(1):64–76. doi:10.1093/jnci/djk006
Rosenblatt DS (2001) Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. Clin Invest Med 24:56–59
Taioli E, Garza MA, Ahn YO, Bishop DT, Bost J, Budai B, Chen K, Gemignani F, Keku T, Lima CS, Le Marchand L, Matsuo K, Moreno V, Plaschke J, Pufulete M, Thomas SB, Toffoli G, Wolf CR, Moore CG, Little J (2009) Meta- and pooled analyses of the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) C677T polymorphism and colorectal cancer: a HuGE-GSEC review. Am J Epidemiol 170:1207–1221. doi:10.1093/aje/kwp275
Boccia S, Hung R, Ricciardi G, Gianfagna F, Ebert MP, Fang JY, Gao CM, Götze T, Graziano F, Lacasaña-Navarro M, Lin D, López-Carrillo L, Qiao YL, Shen H, Stolzenberg-Solomon R, Takezaki T, Weng YR, Zhang FF, van Duijn CM, Boffetta P, Taioli E (2008) Meta- and pooled analyses of the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T and A1298C polymorphisms and gastric cancer risk: a huge-GSEC review. Am J Epidemiol 167:505–516. doi:10.1093/aje/kwm344
Kim YI (2005) 5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase polymorphisms and pharmacogenetics: a new role of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the folate metabolic pathway in human health and disease. Nutr Rev 63:398–407. doi:10.1301/nr.2005.nov.398-407
Goyette P, Pai A, Milos R, Frosst P, Tran P, Chen Z, Chan M, Rozen R (1998) Gene structure of human and mouse methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR). Mamm Genome 9:626–652
De Mattia E, Toffoli G (2009) C677T and A1298C MTHFR polymorphisms, a challenge for antifolate and fluoropyrimidine-based therapy personalisation. Eur J Cancer 45:1333–1351. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2008.12.004
Lissowska J, Gaudet MM, Brinton LA, Chanock SJ, Peplonska B, Welch R, Zatonski W, Szeszenia-Dabrowska N, Park S, Sherman M, Garcia-Closas M (2007) Genetic polymorphisms in the one-carbon metabolism pathway and breast cancer risk: a population-based case-control study and meta-analyses. Int J Cancer 120:2696–2703. doi:10.1002/ijc.22604
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, Moher D, Becker BJ, Sipe TA, Thacker SB (2000) Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 283:2008–2012. doi:10.1001/jama.283.15.2008
Little J, Bradley L, Bray MS, Clyne M, Dorman J, Ellsworth DL, Hanson J, Khoury M, Lau J, O’Brien TR, Rothman N, Stroup D, Taioli E, Thomas D, Vainio H, Wacholder S, Weinberg C (2002) Reporting, appraising, and integrating data on genotype prevalence and gene-disease associations. Am J Epidemiol 156:300–310. doi:10.1093/aje/kwf054
Ma X, Qi X, Chen C, Lin H, Xiong H, Li Y, Jiang J (2010) Association between CYP19 polymorphisms and breast cancer risk: results from 10592 cases and 11720 controls. Breast Cancer Res Treat. doi:10.1007/s10549-009-0693-6
Ma X, Chen C, Xiong H, Fan J, Li Y, Lin H, Xu R, Huang G, Xu B (2010) No association between SOD2 Val16Ala polymorphism and breast cancer susceptibility: a meta-analysis based on 9,710 cases and 11,041 controls. Breast Cancer Res Treat. doi:10.1007/s10549-009-0725-2
Mantel N, Haenszel W (1959) Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst 22:719–748
DerSimonian R, Kacker R (2007) Random-effects model for meta-analysis of clinical trials: an update. Contemp Clin Trials 28:105–114. doi:10.1016/j.cct.2006.04.004
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7:177–188. doi:10.1016/0197-2456(86)90046-2
Chen J, Gammon MD, Chan W, Palomeque C, Wetmur JG, Kabat GC, Teitelbaum SL, Britton JA, Terry MB, Neugut AI, Santella RM (2005) One-carbon metabolism, MTHFR polymorphisms, and risk of breast cancer. Cancer Res 65:1606–1614
Ericson UC, Ivarsson MI, Sonestedt E, Gullberg B, Carlson J, Olsson H, Wirfält E (2009) Increased breast cancer risk at high plasma folate concentrations among women with the MTHFR 677T allele. Am J Clin Nutr 9:1380–1389. doi:10.3945/ajcn.2009.28064
Gao CM, Kazuo T, Tang JH, Cao HX, Ding JH, Wu JZ, Wang J, Liu YT, Li SP, Su P, Keitaro M, Toshiro T (2009) MTHFR polymorphisms, dietary folate intake and risks to breast cancer. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 43:576–580
Tao MH, Shields PG, Nie J, Marian C, Ambrosone CB, McCann SE, Platek M, Krishnan SS, Xie B, Edge SB, Winston J, Vito D, Trevisan M, Freudenheim JL (2009) DNA promoter methylation in breast tumors: no association with genetic polymorphisms in MTHFR and MTR. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 18:998–1002. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-08-0916
Sharp L, Little J, Schofield AC, Pavlidou E, Cotton SC, Miedzybrodzka Z, Baird JO, Haites NE, Heys SD, Grubb DA (2002) Folate and breast cancer: the role of polymorphisms in methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR). Cancer Lett 181:65–71
Campbell IG, Baxter SW, Eccles DM, Choong DY (2002) Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase polymorphism and susceptibility to breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 4(6):R14. doi:10.1186/bcr457
Semenza JC, Delfino RJ, Ziogas A, Anton-Culver H (2003) Breast cancer risk and methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase polymorphism. Breast Cancer Res Treat 77:217–223
Langsenlehner U, Krippl P, Renner W, Yazdani-Biuki B, Wolf G, Wascher TC, Paulweber B, Weitzer W, Samonigg H (2003) The common 677C > T gene polymorphism of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene is not associated with breast cancer risk. Breast Cancer Res Treat 81:169–172
Ergul E, Sazci A, Utkan Z, Canturk NZ (2003) Polymorphisms in the MTHFR gene are associated with breast cancer. Tumour Biol 24:286–290. doi:10.1159/000076460
Shrubsole MJ, Gao YT, Cai Q, Shu XO, Dai Q, Hebert JR, Jin F, Zheng W (2004) MTHFR polymorphisms, dietary folate intake, and breast cancer risk: results from the Shanghai Breast Cancer Study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 13:190–196
Försti A, Angelini S, Festa F, Sanyal S, Zhang Z, Grzybowska E, Pamula J, Pekala W, Zientek H, Hemminki K, Kumar R (2004) Single nucleotide polymorphisms in breast cancer. Oncol Rep 11:917–922
Lee SA, Kang D, Nishio H, Lee MJ, Kim DH, Han W, Yoo KY, Ahn SH, Choe KJ, Hirvonen A, Noh DY (2004) Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase polymorphism, diet, and breast cancer in Korean women. Exp Mol Med 36:116–121
Grieu F, Powell B, Beilby J, Iacopetta B (2004) Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase and thymidylate synthase polymorphisms are not associated with breast cancer risk or phenotype. Anticancer Res 24:3215–3219
Lin WY, Chou YC, Wu MH, Huang HB, Jeng YL, Wu CC, Yu CP, Yu JC, You SL, Chu TY, Chen CJ, Sun CA (2004) The MTHFR C677T polymorphism, estrogen exposure and breast cancer risk: a nested case-control study in Taiwan. Anticancer Res 24:3863–3868
Le Marchand L, Haiman CA, Wilkens LR, Kolonel LN, Henderson BE (2004) MTHFR polymorphisms, diet, HRT, and breast cancer risk: the multiethnic cohort study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 13:2071–2077
Qi J, Miao XP, Tan W, Yu CY, Liang G, Lü WF, Lin DX (2004) Association between genetic polymorphisms in methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase and risk of breast cancer. Chin J Oncol 26:287–289
Kalemi TG, Lambropoulos AF, Gueorguiev M, Chrisafi S, Papazisis KT, Kotsis A (2005) The association of p53 mutations and p53 codon 72, Her 2 codon 655 and MTHFR C677T polymorphisms with breast cancer in Northern Greece. Cancer Lett 222:57–65. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2004.11.025
Deligezer U, Akisik EE, Dalay N (2005) Homozygosity at the C677T of the MTHFR gene is associated with increased breast cancer risk in the Turkish population. In Vivo 19:889–893
Justenhoven C, Hamann U, Pierl CB, Rabstein S, Pesch B, Harth V, Baisch C, Vollmert C, Illig T, Bruning T, Ko Y, Brauch H (2005) One-carbon metabolism and breast cancer risk: no association of MTHFR, MTR, and TYMS polymorphisms in the GENICA study from Germany. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14:3015–3018. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-05-0592
Chou YC, Wu MH, Yu JC, Lee MS, Yang T, Shih HL, Wu TY, Sun CA (2006) Genetic polymorphisms of the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene, plasma folate levels, and breast cancer susceptibility: a case-control study in Taiwan. Carcinogenesis 27:2295–2300. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgl108
Xu X, Gammon MD, Zhang H, Wetmur JG, Rao M, Teitelbaum SL, Britton JA, Neugut AI, Santella RM, Chen J (2007) Polymorphisms of one-carbon-metabolizing genes and risk of breast cancer in a population-based study. Carcinogenesis 28:1504–1509. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgm061
Hekim N, Ergen A, Yaylim I, Yilmaz H, Zeybek U, Ozturk O, Isbir T (2007) No association between methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T polymorphism and breast cancer. Cell Biochem Funct 25:115–117. doi:10.1027/cbf.1274
Macis D, Maisonneuve P, Johansson H, Bonanni B, Botteri E, Iodice S, Santillo B, Penco S, Gucciardo G, D’Aiuto G, Rosselli Del Turco M, Amadori M, Costa A, Decensi A (2007) Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) and breast cancer risk: a nested-case-control study and a pooled meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 106:263–271. doi:10.1007/s10549-006-9491-6
Yu CP, Wu MH, Chou YC, Yang T, You SL, Chen CJ, Sun CA (2007) Breast cancer risk associated with multigenotypic polymorphisms in folate-metabolizing genes: a nested case-control study in Taiwan. Anticancer Res 27:1727–1732
Kan XX, Zou TN, Wu XY, Wang X (2007) Association between mTHFR genotype polymorphism and breast cancer susceptibility in human population from Yunnan. Cancer Res Prev Treat 34:716–718
Stevens VL, McCullough ML, Pavluck AL, Talbot JT, Feigelson HS, Thun MJ, Calle EE (2007) Association of polymorphisms in one-carbon metabolism genes and postmenopausal breast cancer incidence. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 16:1140–1147. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-06-1037
Reljic A, Simundic AM, Topic E, Nikolac N, Justinic D, Stefanovic M (2007) The methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) C677T polymorphism and cancer risk: the Croatian case-control study. Clin Biochem 40:981–985. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-06-1037
Inoue M, Robien K, Wang R, Van Den Berg DJ, Koh WP, Yu MC (2008) Green tea intake, MTHFR/TYMS genotype and breast cancer risk: the Singapore Chinese Health Study. Carcinogenesis 29:1967–1972. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgn177
Kotsopoulos J, Zhang WW, Zhang S, McCready D, Trudeau M, Zhang P, Sun P, Narod SA (2008) Polymorphisms in folate metabolizing enzymes and transport proteins and the risk of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 112:585–593. doi:10.1007/s10549-008-9895-6
Suzuki T, Matsuo K, Hirose K, Hiraki A, Kawase T, Watanabe M, Yamashita T, Iwata H, Tajima K (2008) One-carbon metabolism-related gene polymorphisms and risk of breast cancer. Carcinogenesis 2:356–362. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgm295
Cheng CW, Yu JC, Huang CS, Shieh JC, Fu YP, Wang HW, Wu PE, Shen CY (2008) Polymorphism of cytosolic serine hydroxymethyltransferase, estrogen and breast cancer risk among Chinese women in Taiwan. Breast Cancer Res Treat 111:145–155. doi:10.1007/s10549-007-9754-x
Langsenlehner T, Renner W, Yazdani-Biuki B, Langsenlehner U (2008) Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) and breast cancer risk: a nested-case-control study and a pooled meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 107:459–460. doi:10.1007/s10549-007-9564-1
Ericson U, Sonestedt E, Ivarsson MI, Gullberg B, Carlson J, Olsson H, Wirfält E (2009) Folate intake, methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase polymorphisms, and breast cancer risk in women from the Malmö Diet and Cancer cohort. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 18:1101–1110. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-08-0401
Gao CM, Tang JH, Cao HX, Ding JH, Wu JZ, Wang J, Liu YT, Li SP, Su P, Matsuo K, Takezaki T, Tajima K (2009) MTHFR polymorphisms, dietary folate intake and breast cancer risk in Chinese women. J Hum Genet 54:414–418. doi:10.1038/jhg.2009.57
Ma E, Iwasaki M, Kobayashi M, Kasuga Y, Yokoyama S, Onuma H, Nishimura H, Kusama R, Tsugane S (2009) Dietary intake of folate, vitamin B2, vitamin B6, vitamin B12, genetic polymorphism of related enzymes, and risk of breast cancer: a case-control study in Japan. Nutr Cancer 61:447–456. doi:10.1080/01635580802610123
Platek ME, Shields PG, Marian C, McCann SE, Bonner MR, Nie J, Ambrosone CB, Millen AE, Ochs-Balcom HM, Quick SK, Trevisan M, Russell M, Nochajski TH, Edge SB, Freudenheim JL (2009) Alcohol consumption and genetic variation in methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase and 5-methyltetrahydrofolate-homocysteine methyltransferase in relation to breast cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 18:2453–2459. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-09-0159
Henríquez-Hernández LA, Murias-Rosales A, Hernández González A, Cabrera De León A, Díaz-Chico BN, Mori De Santiago M, Fernández Pérez L (2009) Gene polymorphisms in TYMS, MTHFR, p53 and MDR1 as risk factors for breast cancer: a case-control study. Oncol Rep 22:1425–1433. doi:10.3892/or_00000584
Cam R, Eroglu A, Egin Y, Akar N (2009) Dihydrofolate reductase (DHRF) 19-bp intron-1 deletion and methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) C677T polymorphisms in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 115:431–432. doi:10.1007/s10549-008-0054-x
Maruti SS, Ulrich CM, Jupe ER, White E (2009) MTHFR C677T and postmenopausal breast cancer risk by intakes of one-carbon metabolism nutrients: a nested case-control study. Breast Cancer Res 11:R91. doi:10.1186/bcr2462
Ma E, Iwasaki M, Junko I, Hamada GS, Nishimoto IN, Carvalho SM, Motola J Jr, Laginha FM, Tsugane S (2009) Dietary intake of folate, vitamin B6, and vitamin B12, genetic polymorphism of related enzymes, and risk of breast cancer: a case-control study in Brazilian women. BMC Cancer 9:122. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-9-122
Li WD, Chen SQ (2009) Association of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T polymorphism and breast cancer risk. J Prac Med 25:2031–2033
Yuan H, Xu XY, Wang ZL (2009) The relation between polymorphisms of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T and the risk of breast cancer. J MuDanJiang Med Univ 30:2–4
Jin ZZ, Lu Q, Ge DH, Zong M, Zhu QH (2009) Effect of the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene C677Tpolymorphism on C-erbB-2 methylation status and its association with cancer. Mol Med Rep 2:283–289. doi:10.3892/mmr_00000097
Bentley AR, Raiszadeh F, Stover PJ, Hunter DJ, Hankinson SE, Cassano PA (2010) No association between cSHMT genotypes and the risk of breast cancer in the Nurses’ Health Study. Eur J Clin Nutr 64:108–110. doi:10.1038/ejcn.2009.104
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55:74–108. doi:10.3322/canjclin.55.2.74
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ (2009) Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin 59:225–249. doi:10.3322/caac.20006
Sergentanis TN, Economopoulos KP (2009) Association of two CASP8 polymorphisms with breast cancer risk: a meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. doi:10.1007/s10549-009-0471-5
Wang Z, Fu Y, Tang C, Lu S, Chu WM (2009) SULT1A1 R213H polymorphism and breast cancer risk: a meta-analysis based on 8,454 cases and 11,800 controls. Breast Cancer Res Treat. doi:10.1007/s10549-009-0648-y
Qiu LX, Yuan H, Yu KD, Mao C, Chen B, Zhan P, Xue K, Zhang J, Hu XC (2009) Glutathione S-transferase M1 polymorphism and breast cancer susceptibility: a meta-analysis involving 46,281 subjects. Breast Cancer Res Treat. doi:10.1007/s10549-009-0636-2
Yu KD, Chen AX, Yang C, Qiu LX, Fan L, Xu WH, Shao ZM (2009) Current evidence on the relationship between polymorphisms in the COX-2 gene and breast cancer risk: a meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. doi:10.1007/s10549-009-0688-3
Yuan W, Xu L, Feng Y, Yang Y, Chen W, Wang J, Pang D, Li D (2010) The hOGG1 Ser326Cys polymorphism and breast cancer risk: a meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. doi:10.1007/s10549-009-0722-5
Acknowledgment
This work was not supported by any funds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
X. Qi and X. Ma contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, X., Ma, X., Yang, X. et al. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase polymorphisms and breast cancer risk: a meta-analysis from 41 studies with 16,480 cases and 22,388 controls. Breast Cancer Res Treat 123, 499–506 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-010-0773-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-010-0773-7