Abstract
Objective and methods
The association of 17 candidate single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in IL10 and other immune response genes (CRP, TLR4, IL6, IL1B, IL8, TNF, RNASEL) and genes related to obesity (PPARG, TCF7L2, ADIPOQ, LEP) with colorectal cancer was investigated. Haplotype tagging SNPs were chosen for IL10, CRP, and TLR4. Incident colorectal cancer cases (n = 208) and matched controls (n = 381) were identified between baseline in 1989 and 2003 among participants in the CLUE II cohort. Odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were estimated using conditional logistic regression.
Results
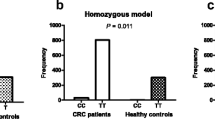
Compared with the AA genotype at the candidate IL10-1082 locus (rs1800896), carrying one (OR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.53–1.18) or two (OR, 0.58; 95% CI, 0.35–0.95) G alleles, a known higher producer of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10, was associated with lower risk of colorectal cancer (p trend = 0.03). Statistically significant associations with colorectal cancer were observed for three tagSNPs in IL10 (rs1800890, rs3024496, rs3024498) and one common haplotype, but these associations were due to high linkage disequilibrium with IL10-1082. Two CRP haplotypes (global p = 0.04) and TLR4 tagSNPs (rs7873784, rs11536891), but not TLR4 haplotypes, were associated with colorectal cancer.
Conclusions
Our study suggests that polymorphisms in IL10, and also possibly in CRP and other genes related to immune response or obesity may be associated with colorectal cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giovannucci E (2003) Diet, body weight, and colorectal cancer: a summary of the epidemiologic evidence. J Womens Health (Larchmt) 12:173–182
Gunter MJ, Leitzmann MF (2006) Obesity and colorectal cancer: epidemiology, mechanisms and candidate genes. J Nutr Biochem 17:145–156
Tsilidis KK, Branchini C, Guallar E, Helzlsouer KJ, Erlinger TP, Platz EA (2008) C-reactive protein and colorectal cancer risk: a systematic review of prospective studies. Int J Cancer 123:1133–1140
Wei EK, Ma J, Pollak MN et al (2005) A prospective study of C-peptide, insulin-like growth factor-I, insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1, and the risk of colorectal cancer in women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14:850–855
Erlinger TP, Platz EA, Rifai N, Helzlsouer KJ (2004) C-reactive protein and the risk of incident colorectal cancer. Jama 291:585–590
Saydah SH, Platz EA, Rifai N, Pollak MN, Brancati FL, Helzlsouer KJ (2003) Association of markers of insulin and glucose control with subsequent colorectal cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 12:412–418
Gunter MJ, Canzian F, Landi S, Chanock SJ, Sinha R, Rothman N (2006) Inflammation-related gene polymorphisms and colorectal adenoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 15:1126–1131
Landi S, Moreno V, Gioia-Patricola L et al (2003) Association of common polymorphisms in inflammatory genes interleukin (IL)6, IL8, tumor necrosis factor alpha, NFKB1, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma with colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 63:3560–3566
Macarthur M, Sharp L, Hold GL, Little J, El-Omar EM (2005) The role of cytokine gene polymorphisms in colorectal cancer and their interaction with aspirin use in the northeast of Scotland. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14:1613–1618
Slattery ML, Wolff RK, Herrick J, Caan BJ, Potter JD (2007) Leptin and leptin receptor genotypes and colon cancer: gene–gene and gene-lifestyle interactions. Int J Cancer 122:1611–1617
Slattery ML, Wolff RK, Herrick JS, Caan BJ, Potter JD (2007) IL6 genotypes and colon and rectal cancer. Cancer Causes Control 18:1095–1105
Theodoropoulos G, Papaconstantinou I, Felekouras E et al (2006) Relation between common polymorphisms in genes related to inflammatory response and colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 12:5037–5043
Folsom AR, Pankow JS, Peacock JM, Bielinski SJ, Heiss G, Boerwinkle E (2008) Variation in TCF7L2 and increased risk of colon cancer: the atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study. Diabetes Care 31:905–909
Moore KW, de Waal Malefyt R, Coffman RL, O’Garra A (2001) Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor. Annu Rev Immunol 19:683–765
Tsan MF (2006) Toll-like receptors, inflammation and cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 16:32–37
Silverman RH (2003) Implications for RNase L in prostate cancer biology. Biochemistry 42:1805–1812
Kershaw EE, Flier JS (2004) Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:2548–2556
Hardwick JC, Van Den Brink GR, Offerhaus GJ, Van Deventer SJ, Peppelenbosch MP (2001) Leptin is a growth factor for colonic epithelial cells. Gastroenterology 121:79–90
Moller DE, Berger JP (2003) Role of PPARs in the regulation of obesity-related insulin sensitivity and inflammation. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 27:S17–S21
Cauchi S, El Achhab Y, Choquet H et al (2007) TCF7L2 is reproducibly associated with type 2 diabetes in various ethnic groups: a global meta-analysis. J Mol Med 85:777–782
Schaid DJ, Rowland CM, Tines DE, Jacobson RM, Poland GA (2002) Score tests for association between traits and haplotypes when linkage phase is ambiguous. Am J Hum Genet 70:425–434
Lake SL, Lyon H, Tantisira K et al (2003) Estimation and tests of haplotype-environment interaction when linkage phase is ambiguous. Hum Hered 55:56–65
Wacholder S, Chanock S, Garcia-Closas M, El Ghormli L, Rothman N (2004) Assessing the probability that a positive report is false: an approach for molecular epidemiology studies. J Natl Cancer Inst 96:434–442
Crawley E, Kay R, Sillibourne J, Patel P, Hutchinson I, Woo P (1999) Polymorphic haplotypes of the interleukin-10 5′ flanking region determine variable interleukin-10 transcription and are associated with particular phenotypes of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 42:1101–1108
Kilpinen S, Huhtala H, Hurme M (2002) The combination of the interleukin-1alpha (IL-1alpha-889) genotype and the interleukin-10 (IL-10 ATA) haplotype is associated with increased interleukin-10 (IL-10) plasma levels in healthy individuals. Eur Cytokine Netw 13:66–71
Kuhn R, Lohler J, Rennick D, Rajewsky K, Muller W (1993) Interleukin-10-deficient mice develop chronic enterocolitis. Cell 75:263–274
Sturlan S, Oberhuber G, Beinhauer BG et al (2001) Interleukin-10-deficient mice and inflammatory bowel disease associated cancer development. Carcinogenesis 22:665–671
Franke A, Balschun T, Karlsen TH et al (2008) Sequence variants in IL10, ARPC2 and multiple other loci contribute to ulcerative colitis susceptibility. Nat Genet 40:1319–1323
Diez JJ, Iglesias P (2003) The role of the novel adipocyte-derived hormone adiponectin in human disease. Eur J Endocrinol 148:293–300
Maeda N, Shimomura I, Kishida K et al (2002) Diet-induced insulin resistance in mice lacking adiponectin/ACRP30. Nat Med 8:731–737
Otake S, Takeda H, Suzuki Y et al (2005) Association of visceral fat accumulation and plasma adiponectin with colorectal adenoma: evidence for participation of insulin resistance. Clin Cancer Res 11:3642–3646
Wei EK, Giovannucci E, Fuchs CS, Willett WC, Mantzoros CS (2005) Low plasma adiponectin levels and risk of colorectal cancer in men: a prospective study. J Natl Cancer Inst 97:1688–1694
Brakenhielm E, Veitonmaki N, Cao R et al (2004) Adiponectin-induced antiangiogenesis and antitumor activity involve caspase-mediated endothelial cell apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:2476–2481
Menzaghi C, Ercolino T, Salvemini L et al (2004) Multigenic control of serum adiponectin levels: evidence for a role of the APM1 gene and a locus on 14q13. Physiol Genomics 19:170–174
Mousavinasab F, Tahtinen T, Jokelainen J et al (2006) Common polymorphisms (single-nucleotide polymorphisms SNP + 45 and SNP + 276) of the adiponectin gene regulate serum adiponectin concentrations and blood pressure in young Finnish men. Mol Genet Metab 87:147–151
Kaklamani VG, Wisinski KB, Sadim M et al (2008) Variants of the adiponectin (ADIPOQ) and adiponectin receptor 1 (ADIPOR1) genes and colorectal cancer risk. Jama 300:1523–1531
Gabay C, Kushner I (1999) Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J Med 340:448–454
Bassuk SS, Rifai N, Ridker PM (2004) High-sensitivity C-reactive protein: clinical importance. Curr Probl Cardiol 29:439–493
Nielsen HJ, Christensen IJ, Sorensen S, Moesgaard F, Brunner N (2000) Preoperative plasma plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 and serum C-reactive protein levels in patients with colorectal cancer. The RANX05 colorectal cancer study group. Ann Surg Oncol 7:617–623
Lange LA, Carlson CS, Hindorff LA et al (2006) Association of polymorphisms in the CRP gene with circulating C-reactive protein levels and cardiovascular events. Jama 296:2703–2711
Miller DT, Zee RY, Suk Danik J et al (2005) Association of common CRP gene variants with CRP levels and cardiovascular events. Ann Hum Genet 69:623–638
Suk HJ, Ridker PM, Cook NR, Zee RY (2005) Relation of polymorphism within the C-reactive protein gene and plasma CRP levels. Atherosclerosis 178:139–145
Gallicchio L, Chang H, Christo DK et al (2008) Single nucleotide polymorphisms in inflammation-related genes and mortality in a community-based cohort in Washington County, Maryland. Am J Epidemiol 167:807–813
Siemes C, Visser LE, Coebergh JW et al (2006) C-reactive protein levels, variation in the C-reactive protein gene, and cancer risk: the Rotterdam study. J Clin Oncol 24:5216–5222
Landi S, Gemignani F, Bottari F et al (2006) Polymorphisms within inflammatory genes and colorectal cancer. J Negat Results Biomed 5:15
Elbein SC, Chu WS, Das SK et al (2007) Transcription factor 7-like 2 polymorphisms and type 2 diabetes, glucose homeostasis traits and gene expression in US participants of European and African descent. Diabetologia 50:1621–1630
Lyssenko V, Lupi R, Marchetti P et al (2007) Mechanisms by which common variants in the TCF7L2 gene increase risk of type 2 diabetes. J Clin Invest 117:2155–2163
Larsson SC, Orsini N, Wolk A (2005) Diabetes mellitus and risk of colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst 97:1679–1687
Weedon MN (2007) The importance of TCF7L2. Diabet Med 24:1062–1066
Wong NA, Pignatelli M (2002) Beta-catenin—a linchpin in colorectal carcinogenesis? Am J Pathol 160:389–401
Slattery ML, Folsom AR, Wolff R, Herrick J, Caan BJ, Potter JD (2008) Transcription factor 7-like 2 polymorphism and colon cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 17:978–982
Hazra A, Fuchs CS, Chan AT, Giovannucci EL, Hunter DJ (2008) Association of the TCF7L2 polymorphism with colorectal cancer and adenoma risk. Cancer Causes Control 19:975–980
Kiechl S, Lorenz E, Reindl M et al (2002) Toll-like receptor 4 polymorphisms and atherogenesis. N Engl J Med 347:185–192
Zheng SL, Augustsson-Balter K, Chang B et al (2004) Sequence variants of toll-like receptor 4 are associated with prostate cancer risk: results from the CAncer prostate in Sweden study. Cancer Res 64:2918–2922
Rivera-Chavez FA, Peters-Hybki DL, Barber RC, O’Keefe GE (2003) Interleukin-6 promoter haplotypes and interleukin-6 cytokine responses. Shock 20:218–223
Ferrari SL, Ahn-Luong L, Garnero P, Humphries SE, Greenspan SL (2003) Two promoter polymorphisms regulating interleukin-6 gene expression are associated with circulating levels of C-reactive protein and markers of bone resorption in postmenopausal women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:255–259
Fishman D, Faulds G, Jeffery R et al (1998) The effect of novel polymorphisms in the interleukin-6 (IL-6) gene on IL-6 transcription and plasma IL-6 levels, and an association with systemic-onset juvenile chronic arthritis. J Clin Invest 102:1369–1376
Chen H, Wilkins LM, Aziz N et al (2006) Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the human interleukin-1B gene affect transcription according to haplotype context. Hum Mol Genet 15:519–529
Hall SK, Perregaux DG, Gabel CA et al (2004) Correlation of polymorphic variation in the promoter region of the interleukin-1 beta gene with secretion of interleukin-1 beta protein. Arthritis Rheum 50:1976–1983
Kikuchi M, Hishida A, Ishikawa K et al (2007) Associations between serum C-reactive protein (CRP) levels and polymorphisms of CRP, interleukin 1B, and tumor necrosis factor genes among Japanese health checkup examinees. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 8:87–92
Hull J, Thomson A, Kwiatkowski D (2000) Association of respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis with the interleukin 8 gene region in UK families. Thorax 55:1023–1027
Abraham LJ, Kroeger KM (1999) Impact of the -308 TNF promoter polymorphism on the transcriptional regulation of the TNF gene: relevance to disease. J Leukoc Biol 66:562–566
Casey G, Neville PJ, Plummer SJ et al (2002) RNASEL Arg462Gln variant is implicated in up to 13% of prostate cancer cases. Nat Genet 32:581–583
Deeb SS, Fajas L, Nemoto M et al (1998) A Pro12Ala substitution in PPARgamma2 associated with decreased receptor activity, lower body mass index and improved insulin sensitivity. Nat Genet 20:284–287
Hager J, Clement K, Francke S et al (1998) A polymorphism in the 5′ untranslated region of the human ob gene is associated with low leptin levels. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 22:200–205
Kovacs A, Green F, Hansson LO et al (2005) A novel common single nucleotide polymorphism in the promoter region of the C-reactive protein gene associated with the plasma concentration of C-reactive protein. Atherosclerosis 178:193–198
Crawford DC, Sanders CL, Qin X et al (2006) Genetic variation is associated with C-reactive protein levels in the third national health and nutrition examination survey. Circulation 114:2458–2465
Kathiresan S, Larson MG, Vasan RS et al (2006) Contribution of clinical correlates and 13C-reactive protein gene polymorphisms to interindividual variability in serum C-reactive protein level. Circulation 113:1415–1423
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the continued efforts of the staff members at the Johns Hopkins George W. Comstock Center for Public Health Research and Prevention in the conduct of the CLUE II study.
Financial support
This research was supported by a grant from the American Institute for Cancer Research. Konstantinos Tsilidis was funded by a J. William Fulbright grant and a scholarship from the Hellenic State Scholarships Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsilidis, K.K., Helzlsouer, K.J., Smith, M.W. et al. Association of common polymorphisms in IL10, and in other genes related to inflammatory response and obesity with colorectal cancer. Cancer Causes Control 20, 1739–1751 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-009-9427-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-009-9427-7