Abstract
Objective
We used a nested case–control design within a large, multi-center cohort of women who underwent a biopsy for benign breast disease (BBD) to assess the association of broad histologic groupings and specific histologic entities with risk of breast cancer.
Methods
Cases were all women who had a biopsy for BBD and who subsequently developed breast cancer; controls were individually matched to cases and were women with a biopsy for BBD who did not develop breast cancer in the same follow-up interval as that for the cases. After exclusions, 1,239 records (615 cases and 624 controls) were available for analysis. We used conditional logistic regression to estimate odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results
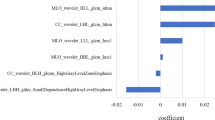
Relative to non-proliferative BBD/normal pathology, the multivariable-adjusted odds ratio for proliferative lesions without atypia was 1.45 (95% CI 1.10–1.90), and that for atypical hyperplasia was 5.27 (95% CI 2.29–12.15). The presence of multiple foci of columnar cell hyperplasia and of complex fibroadenoma without atypia was associated with a non-significantly increased risk of breast cancer, whereas sclerosing adenosis, radial scar, and papilloma showed no association with risk.
Conclusion
Our results indicate that, compared to women with normal pathology/non-proliferative disease, women with proliferative disease without atypia have a modestly increased risk of breast cancer, whereas women with atypical hyperplasia have a substantially increased risk.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rohan TE, Henson DE, Franco EL, Albores-Saavedra J (2006) Cancer precursors. In: Schottenfeld D, Fraumeni JF Jr (eds) Cancer epidemiology and prevention, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Schnitt SJ (2003) Benign breast disease and breast cancer risk: morphology and beyond. Am J Surg Pathol 27:836–841
Dupont WD, Page DL (1985) Risk factors for breast cancer in women with proliferative breast disease. N Engl J Med 312:146–151
Carter CL, Corle DK, Micozzi MS, Schatzkin A, Taylor PR (1988) A prospective study of the development of breast cancer in 16,692 women with benign breast disease. Am J Epidemiol 128:467–477
London SJ, Connolly JL, Schnitt SJ, Colditz GA (1992) A prospective study of benign breast disease and the risk of breast cancer. JAMA 267:941–944
Dupont WD, Parl FF, Hartmann WH, Brinton LA, Winfield AC, Worrell JA, Schuyler PA, Plummer WD (1993) Breast cancer risk associated with proliferative breast disease and atypical hyperplasia. Cancer 71:1258–1265
Marshall LM, Hunter DJ, Connolly JL, Schnitt SJ, Byrne C, London SJ, Colditz GA (1997) Risk of breast cancer associated with atypical hyperplasia of lobular and ductal types. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 6:297–301
Hartmann LC, Sellers TA, Frost MH, Lingle WL, Degnim AC, Ghosh K, Vierkant RA, Maloney SD, Pankratz VS, Hillman DW, Suman VJ, Johnson J, Blake C, Tlisty T, Vachon CM, Melton LJ, Visscher DW (2005) Benign breast disease and the risk of breast cancer. N Engl J Med 353:229–237
Worsham MJ, Raju U, Lu M, Kapke A, Bottrell A, Cheng J, Shah V, Savera A, Wolman SR (2008) Risk factors for breast cancer from benign breast disease in a diverse population. Breast Cancer Res Treat [Epub ahead of print]
Krieger N, Hiatt RA (1992) Risk of breast cancer after benign breast diseases: variation by histologic type, degree of atypia, age at biopsy, and length of follow-up. Am J Epidemiol 135:619–631
Dupont WD, Page DL, Parl FF, Vnencak-Jones CL, Plummer WD Jr, Rados MS, Schuyler PA (1994) Long-term risk of breast cancer in women with fibroadenoma. N Engl J Med 331:10–15
McDivitt RW, Stevens JA, Lee NC, Wingo PA, Rubin GL, Gersell D (1992) Histologic types of benign breast disease and the risk of breast cancer: the Cancer and Steroid Hormone Study Group. Cancer 69:1408–1414
Ashbeck EL, Rosenberg RD, Stauber PM, Key CR (2007) Benign breast biopsy diagnosis and subsequent risk of breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 16:467–472
Sanders ME, Page DL, Simpson JF, Schuyler PA, Plummer WD, Dupont WD (2006) Interdependence of radial scar and proliferative disease with respect to invasive breast carcinoma risk in patients with benign breast biopsies. Cancer 106:1453–1461
Berg JC, Visscher DW, Vierkant RA, Pankratz VS, Maloney SD, Lewis JT, Frost MH, Ghosh K, Degnim AC, Brandt KR, Vachon CM, Reynolds CA, Hartmann LC (2008) Breast cancer risk in women with radial scars in benign breast biopsies. Breast Cancer Res Treat 108:167–174
Shaaban AM, Sloane JP, West CR, Moore FR, Jarvis C, Williams EMI, Foster CS (2002) Histopathologic types of benign breast lesions and the risk of breast cancer. Am J Surg Pathol 26:421–430
Jacobs TW, Byrne C, Colditz G, Connolly JL, Schnitt SJ (1999) Radial scars in benign breast-biopsy specimens and the risk of breast cancer. N Engl J Med 340:430–436
Jensen RA, Page DL, Dupont WD, Rogers LW (1989) Invasive breast cancer risk in women with sclerosing adenosis. Cancer 64:1977–1983
Lewis JT, Hartmann LC, Vierkant RA, Maloney SD, Pankratz S, Allers TM, Frost MH, Visscher DW (2006) An analysis of breast cancer risk in women with single, multiple, and atypical papilloma. Am J Surg Pathol 30:665–672
Boulos FI, Dupont WD, Simpson JF, Schuyler PA, Sanders ME, Freudenthal ME, Page DL (2008) Histologic associations and long-term cancer risk in columnar cell lesions of the breast: a retrospective cohort and nested case-control study. Cancer 113:2415–2421
Page DL, Anderson TJ (1987) Diagnostic histopathology of the breast. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh
Fitzgibbons PL, Henson DE, Hutter RV (1998) Benign breast changes and the risk of subsequent breast cancer: an update of the 1985 consensus statement. Cancer Committee of the College of American Pathologists. Arch Pathol Lab Med 122:1053–1055
Bodian CA (1993) Benign breast diseases, carcinoma in situ, and breast cancer risk. Epidemiol Rev 15:177–187
Schnitt SJ, Collins LC (2009) Pathology of benign breast disorders. In: Harris JR, Lippman ME, Morrow M, Osborne CK (eds) Diseases of the breast. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, New York, pp 69–85
Rohan TE, Hartwick W, Miller AB, Kandel RA (1998) Immunohistochemical detection of c-erbB-2 and p53 in benign breast disease and breast cancer risk. J Natl Cancer Inst 90:1247–1248
Collins LC, Baer HJ, Tamimi RM, Connolly JL, Colditz GA, Schnitt SJ (2007) Magnitude and laterality of breast cancer risk according to histologic type of atypical hyperplasia: results from the Nurses’ Health Study. Cancer 109:180–187
Dupont WD, Page DL (1989) Relative risk of breast cancer varies with time since diagnosis of atypical hyperplasia. Hum Pathol 20:723–725
Degnim AC, Visscher DW, Berman HK, Frost MH, Sellars TA, Vierkant RA, Maloney SD, Pankratz S, deGroen PC, Lingle WL, Ghosh K, Penheiter L, Tlsty T, Melton LJ III, Reynolds CA, Hartmann LC (2007) Stratification of breast cancer risk in women with atypia: a Mayo cohort study. J Clin Oncol 25:2671–2677
Page DL, Dupont WD, Rogers LW, Rados MS (1985) Atypical hyperplastic lesions of the female breast: a long-term follow-up study. Cancer 55:2698–2708
King TA, Scharfenberg JC, Smetherman DH, Farkas EA, Bolton JS, Fuhrman GM (2000) A better understanding of the term radial scar. Am J Surg 180:428–433
Patterson JA, Scott M, Anderson N, Kirk SJ (2004) Radial scar, complex sclerosing lesion and risk of breast cancer: analysis of 175 cases in Northern Ireland. Eur J Surg Oncol 30:1065–1068
Acknowledgments
We thank Emily Harris for her contributions to the development of this study, and we also thank Victor Kamensky for his programming and database management support. This study was supported by NIH: RO1-CA95661-01 “p53 in BBD and breast cancer risk: a multicenter cohort.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kabat, G.C., Jones, J.G., Olson, N. et al. A multi-center prospective cohort study of benign breast disease and risk of subsequent breast cancer. Cancer Causes Control 21, 821–828 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-010-9508-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-010-9508-7