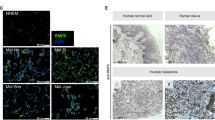
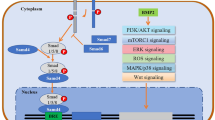
Abstract
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are members of the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) superfamily serving multiple functions in many cell and tissue types including proliferation, apoptosis, differentiation, chemotaxis, angiogenesis, and matrix production during embryogenic development as well as in adult life. Despite the tremendous progress in delineating functional derangements of BMP pathways in carcinogenesis during the last decade, the biological significance of BMPs in human melanoma has received very little attention. It is now clear that biological responses to BMPs are cell type-specific and divergent effects, i.e., both oncogenic and tumor suppressor activities, have been described. Thus, knowledge generated in one system may not translate directly to another. In this review, we summarize the current understanding of BMP signaling in various human cancers and discuss original data pertaining to cutaneous melanoma obtained in our laboratory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balemans W, Van Hul W: Extracellular regulation of BMP signaling in vertebrates: A cocktail of modulators. Dev Biol 250: 231–250, 2002
Miyazono K, Kusanagi K, Inoue H: Divergence and convergence of TGF-beta/BMP signaling. J Cell Physiol 187: 265–276, 2001
von Bubnoff A, Cho KW: Intracellular BMP signaling regulation in vertebrates: Pathway or network? Dev Biol 239: 1–14, 2001
Nohe A, Hassel S, Ehrlich M, Neubauer F, Sebald W, Henis YI, Knaus P: The mode of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) receptor oligomerization determines different BMP-2 signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 277: 5330–5338, 2002
Hassel S, Schmitt S, Hartung A, Roth M, Nohe A, Petersen N, Ehrlich M, Henis YI, Sebald W, Knaus P: Initiation of Smad-dependent and Smad-independent signaling via distinct BMP-receptor complexes. J Bone Joint Surg Am 85-A Suppl 3: 44–51, 2003
Laurikkala J, Kassai Y, Pakkasjarvi L, Thesleff I, Itoh N: Identification of a secreted BMP antagonist, ectodin, integrating BMP, FGF, and SHH signals from the tooth enamel knot. Dev Biol 264: 91–105, 2003
Canalis E, Economides AN, Gazzerro E: Bone morphogenetic proteins, their antagonists, and the skeleton. Endocr Rev 24: 218–235, 2003
Zwijsen A, Verschueren K, Huylebroeck D: New intracellular components of bone morphogenetic protein/Smad signaling cascades. FEBS Lett 546: 133–139, 2003
Onichtchouk D, Chen YG, Dosch R, Gawantka V, Delius H, Massague J, Niehrs C: Silencing of TGF-beta signalling by the pseudoreceptor BAMBI. Nature 401: 480–485, 1999
Whitman M: Smads and early developmental signaling by the TGF-beta superfamily. Genes Dev 12: 2445–2462, 1998
Botchkarev VA, Botchkareva NV, Sharov AA, Funa K, Huber O, Gilchrest BA: Modulation of BMP signaling by noggin is required for induction of the secondary (nontylotrich) hair follicles. J Invest Dermatol 118: 3–10, 2002
Zhang H, Bradley A: Mice deficient for BMP2 are nonviable and have defects in amnion/chorion and cardiac development. Development 122: 2977–2986, 1996
Winnier G, Blessing M, Labosky PA, Hogan BL: Bone morphogenetic protein-4 is required for mesoderm formation and patterning in the mouse. Genes Dev 9: 2105–2116, 1995
Blessing M, Schirmacher P, Kaiser S: Overexpression of bone morphogenetic protein-6 (BMP-6) in the epidermis of transgenic mice: Inhibition or stimulation of proliferation depending on the pattern of transgene expression and formation of psoriatic lesions. J Cell Biol 135: 227–239, 1996
Botchkarev VA, Botchkareva NV, Roth W, Nakamura M, Chen LH, Herzog W, Lindner G, McMahon JA, Peters C, Lauster R, McMahon AP, Paus R: Noggin is a mesenchymally derived stimulator of hair-follicle induction. Nat Cell Biol 1: 158–164, 1999
Mabie PC, Mehler MF, Kessler JA: Multiple roles of bone morphogenetic protein signaling in the regulation of cortical cell number and phenotype. J Neurosci 19: 7077–7088, 1999
McMahon JA, Takada S, Zimmerman LB, Fan CM, Harland RM, McMahon AP: Noggin-mediated antagonism of BMP signaling is required for growth and patterning of the neural tube and somite. Genes Dev 12: 1438–1452, 1998
Graff JM: Embryonic patterning: to BMP or not to BMP, that is the question. Cell 89: 171–174, 1997
Merino R, Rodriguez-Leon J, Macias D, Ganan Y, Economides AN, Hurle JM: The BMP antagonist Gremlin regulates outgrowth, chondrogenesis and programmed cell death in the developing limb. Development 126: 5515–5522, 1999
De Bosscher K, Hill CS, Nicolas FJ: Molecular and functional consequences of Smad4 C-terminal missense mutations in colorectal tumour cells. Biochem J 379: 209–216, 2004
Zhou XP, Woodford-Richens K, Lehtonen R, Kurose K, Aldred M, Hampel H, Launonen V, Virta S, Pilarski R, Salovaara R, Bodmer WF, Conrad BA, Dunlop M, Hodgson SV, Iwama T, Jarvinen H, Kellokumpu I, Kim JC, Leggett B, Markie D, Mecklin JP, Neale K, Phillips R, Piris J, Rozen P, Houlston RS, Aaltonen LA, Tomlinson IP, Eng C: Germline mutations in BMPR1A/ALK3 cause a subset of cases of juvenile polyposis syndrome and of Cowden and Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndromes. Am J Hum Genet 69: 704–711, 2001
Hsu MY, Elder DE, Herlyn M: The Wistar melanoma (WM) cell lines. In: Masters JRW, Palsson B (eds) Human Cell Culture. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Nowell, MA, 1999, pp 259–274
Seftor EA, Seftor REB, Hendrix MJC: Selection of invasive and metastatic subpopulation from a heterogeneous human melanoma cell line. BioTechniques 9: 324–331, 1990
Hendrix MJC, Seftor EA, Seftor EB, Fidler IJ: A simple quantitative assay for studying the invasive potential of high and low human metastatic variants. Cancer Lett 38: 137–147, 1987
Jin Y, Tipoe GL, Liong EC, Lau TY, Fung PC, Leung KM: Overexpression of BMP-2/4, -5 and BMPR-IA associated with malignancy of oral epithelium. Oral Oncol 37: 225–233, 2001
Thomas BG, Hamdy FC: Bone morphogenetic protein-6: potential mediator of osteoblastic metastases in prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 3: 283–285, 2000
De Pinieux G, Flam T, Zerbib M, Taupin P, Bellahcene A, Waltregny D, Vieillefond A, Poupon MF: Bone sialoprotein, bone morphogenetic protein 6 and thymidine phosphorylase expression in localized human prostatic adenocarcinoma as predictors of clinical outcome: A clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of 43 cases. J Urol 166: 1924–1930, 2001
Masuda H, Fukabori Y, Nakano K, Takezawa Y, T CS, Yamanaka H: Increased expression of bone morphogenetic protein-7 in bone metastatic prostate cancer. Prostate 54: 268–274, 2003
Schwalbe M, Sanger J, Eggers R, Naumann A, Schmidt A, Hoffken K, Clement JH: Differential expression and regulation of bone morphogenetic protein 7 in breast cancer. Int J Oncol 23: 89–95, 2003
Higinbotham KG, Karavanova ID, Diwan BA, Perantoni AO: Deficient expression of mRNA for the putative inductive factor bone morphogenetic protein–7 in chemically initiated rat nephroblastomas. Mol Carcinog 23: 53–61, 1998
Raida M, Sarbia M, Clement JH, Adam S, Gabbert HE, Hoffken K: Expression, regulation and clinical significance of bone morphogenetic protein 6 in esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 83: 38–44, 1999
Blessing M, Nanney LB, King LE, Hogan BL: Chemical skin carcinogenesis is prevented in mice by the induced expression of a TGF-beta related transgene. Teratog Carcinog Mutagen 15: 11–21, 1995
Wach S, Schirmacher P, Protschka M, Blessing M: Overexpression of bone morphogenetic protein-6 (BMP-6) in murine epidermis suppresses skin tumor formation by induction of apoptosis and downregulation of fos/jun family members. Oncogene 20: 7761–7769, 2001
Kleeff J, Maruyama H, Ishiwata T, Sawhney H, Friess H, Buchler MW, Korc M: Bone morphogenetic protein 2 exerts diverse effects on cell growth in vitro and is expressed in human pancreatic cancer in vivo. Gastroenterology 116: 1202–1216, 1999
Yamada N, Kato M, ten Dijke P, Yamashita H, Sampath TK, Heldin CH, Miyazono K, Funa K: Bone morphogenetic protein type IB receptor is progressively expressed in malignant glioma tumours. Br J Cancer 73: 624–629, 1996
Kim IY, Lee DH, Ahn HJ, Tokunaga H, Song W, Devereaux LM, Jin D, Sampath TK, Morton RA: Expression of bone morphogenetic protein receptors type-IA, -IB and -II correlates with tumor grade in human prostate cancer tissues. Cancer Res 60: 2840–2844, 2000
Kim IY, Lee DH, Lee DK, Kim BC, Kim HT, Leach FS, Linehan WM, Morton RA, Kim SJ: Decreased expression of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) receptor type II correlates with insensitivity to BMP-6 in human renal cell carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 9: 6046–6051, 2003
Zavadil J, Brezinova J, Svoboda P, Zemanova Z, Michalova K: Smad5, a tumor suppressor candidate at 5q31.1, is hemizygously lost and not mutated in the retained allele in human leukemia cell line HL60. Leukemia 11: 1187–1192, 1997
Cheng KH, Ponte JF, Thiagalingam S: Elucidation of epigenetic inactivation of SMAD8 in cancer using targeted expressed gene display. Cancer Res 64: 1639–1646, 2004
Maliekal TT, Antony ML, Nair A, Paulmurugan R, Karunagaran D: Loss of expression, and mutations of Smad 2 and Smad 4 in human cervical cancer. Oncogene 22: 4889–4897, 2003
Xie W, Rimm DL, Lin Y, Shih WJ, Reiss M: Loss of Smad signaling in human colorectal cancer is associated with advanced disease and poor prognosis. Cancer J 9: 302–312, 2003
Tannapfel A, Anhalt K, Hausermann P, Sommerer F, Benicke M, Uhlmann D, Witzigmann H, Hauss J, Wittekind C: Identification of novel proteins associated with hepatocellular carcinomas using protein microarrays. J Pathol 201: 238–249, 2003
Liu FS, Chen JT, Hsieh YT, Ho ES, Hung MJ, Lu CH, Chiou LC: Loss of Smad4 protein expression occurs infrequently in endometrial carcinomas. Int J Gynecol Pathol 22: 347–352, 2003
Hahn SA, Schutte M, Hoque AT, Moskaluk CA, da Costa LT, Rozenblum E, Weinstein CL, Fischer A, Yeo CJ, Hruban RH, Kern SE: DPC4, a candidate tumor suppressor gene at human chromosome 18q21.1. Science 271: 350–353, 1996
Natsugoe S, Xiangming C, Matsumoto M, Okumura H, Nakashima S, Sakita H, Ishigami S, Baba M, Takao S, Aikou T: Smad4 and transforming growth factor beta1 expression in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Clin Cancer Res 8: 1838–1842, 2002
Cerutti JM, Ebina KN, Matsuo SE, Martins L, Maciel RM, Kimura ET: Expression of Smad4 and Smad7 in human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines. J Endocrinol Invest 26: 516–521, 2003
Boulay JL, Mild G, Lowy A, Reuter J, Lagrange M, Terracciano L, Laffer U, Herrmann R, Rochlitz C: SMAD7 is a prognostic marker in patients with colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 104: 446–449, 2003
Franceschi RT, Wang D, Krebsbach PH, Rutherfold RB: Gene therapy for bone formation: in vitro and in vivo osteogenic activity of an adenovirus expressing BMP7. J Cell Biochem 78: 476–486, 2000
Andrews PW, Damjanov I, Berends J, Kumpf S, Zappavigna V, Mavilio F, Sampath K: Inhibition of proliferation and induction of differentiation of pluripotent human embryonal carcinoma cells by osteogenic protein-1 (or bone morphogenetic protein-7). Lab Invest 71: 243–251, 1994
Maliakal JC, Asahina I, Hauschka PV, Sampath TK: Osteogenic protein-1 (BMP-7) inhibits cell proliferation and stimulates the expression of markers characteristic of osteoblast phenotype in rat osteosarcoma (17/2.8) cells. Growth Factors 11: 227–234, 1994
Franzen A, Heldin NE: BMP-7-induced cell cycle arrest of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells via p21(CIP1) and p27(KIP1). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 285: 773–781, 2001
Hardwick JC, Van Den Brink GR, Bleuming SA, Ballester I, Van Den Brande JM, Keller JJ, Offerhaus GJ, Van Deventer SJ, Peppelenbosch MP: Bone morphogenetic protein 2 is expressed by, and acts upon, mature epithelial cells in the colon. Gastroenterology 126: 111–121, 2004
Reinholz MM, Iturria SJ, Ingle JN, Roche PC: Differential gene expression of TGF-beta family members and osteopontin in breast tumor tissue: Analysis by real-time quantitative PCR. Breast Cancer Res Treat 74: 255–269, 2002
Soda H, Raymond E, Sharma S, Lawrence R, Cerna C, Gomez L, Timony GA, Von Hoff DD, Izbicka E: Antiproliferative effects of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 on human tumor colony-forming units. Anticancer Drugs 9: 327–331, 1998
Wen XZ, Miyake S, Akiyama Y, Yuasa Y: BMP-2 modulates the proliferation and differentiation of normal and cancerous gastric cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 316: 100–106, 2004
Brubaker KD, Corey E, Brown LG, Vessella RL: Bone morphogenetic protein signaling in prostate cancer cell lines. J Cell Biochem 91: 151–160, 2004
Ghosh-Choudhury N, Ghosh-Choudhury G, Celeste A, Ghosh PM, Moyer M, Abboud SL, Kreisberg J: Bone morphogenetic protein-2 induces cyclin kinase inhibitor p21 and hypophosphorylation of retinoblastoma protein in estradiol-treated MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1497: 186–196, 2000
Ghosh-Choudhury N, Woodruff K, Qi W, Celeste A, Abboud SL, Ghosh Choudhury G: Bone morphogenetic protein-2 blocks MDA MB 231 human breast cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting cyclin-dependent kinase-mediated retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 272: 705–711, 2000
Dumont N, Arteaga CL: A kinase-inactive type II TGF-beta receptor impairs BMP signaling in human breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 301: 108–112, 2003
Langenfeld EM, Calvano SE, Abou-Nukta F, Lowry SF, Amenta P, Langenfeld J: The mature bone morphogenetic protein-2 is aberrantly expressed in non-small cell lung carcinomas and stimulates tumor growth of A549 cells. Carcinogenesis 24: 1445–1454, 2003
Katoh M, Terada M: Overexpression of bone morphogenic protein (BMP)-4 mRNA in gastric cancer cell lines of poorly differentiated type. J Gastroenterol 31: 137–139, 1996
Buckley S, Shi W, Driscoll B, Ferrario A, Anderson K, Warburton D: BMP4 signaling induces senescence and modulates the oncogenic phenotype of A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 286: L81–86, 2004
Langenfeld EM, Langenfeld J: Bone morphogenetic protein-2 stimulates angiogenesis in developing tumors. Mol Cancer Res 2: 141–149, 2004
Ide H, Yoshida T, Matsumoto N, Aoki K, Osada Y, Sugimura T, Terada M: Growth regulation of human prostate cancer cells by bone morphogenetic protein-2. Cancer Res 57: 5022–5027, 1997
Medrano EE: Repression of TGF-beta signaling by the oncogenic protein SKI in human melanomas: consequences for proliferation, survival, and metastasis. Oncogene 22: 3123–3129, 2003
Fukuchi M, Fukai Y, Masuda N, Miyazaki T, Nakajima M, Sohda M, Manda R, Tsukada K, Kato H, Kuwano H: High-level expression of the Smad ubiquitin ligase Smurf2 correlates with poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 62: 7162–7165, 2002
Saikali Z, Sinnett D: Expression of glypican 3 (GPC3) in embryonal tumors. Int J Cancer 89: 418–422, 2000
Lage H, Dietel M, Froschle G, Reymann A: Expression of the novel mitoxantrone resistance associated gene MXR7 in colorectal malignancies. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 36: 58–60, 1998
Hsu HC, Cheng W, Lai PL: Cloning and expression of a developmentally regulated transcript MXR7 in hepatocellular carcinoma: biological significance and temporospatial distribution. Cancer Res 57: 5179–5184, 1997
Zhu ZW, Friess H, Wang L, Abou-Shady M, Zimmermann A, Lander AD, Korc M, Kleeff J, Buchler MW: Enhanced glypican-3 expression differentiates the majority of hepatocellular carcinomas from benign hepatic disorders. Gut 48: 558–564, 2001
Midorikawa Y, Ishikawa S, Iwanari H, Imamura T, Sakamoto H, Miyazono K, Kodama T, Makuuchi M, Aburatani H: Glypican-3, overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma, modulates FGF2 and BMP-7 signaling. Int J Cancer 103: 455–465, 2003
Berking C, Takemoto R, Schaider H, Showe L, Satyamoorthy K, Robbins P, Herlyn M: Transforming growth factor-beta1 increases survival of human melanoma through stroma remodeling. Cancer Res 61: 8306–8316, 2001
Derynck R, Akhurst RJ, Balmain A: TGF-beta signaling in tumor suppression and cancer progression. Nat Genet 29: 117–129, 2001
Akhurst RJ: TGF-beta antagonists: Why suppress a tumor suppressor? J Clin Invest 109: 1533–1536, 2002
Wakefield LM, Roberts AB: TGF-beta signaling: Positive and negative effects on tumorigenesis. Curr Opin Genet Dev 12: 22–29, 2002
Dai J, Kitagawa Y, Zhang J, Yao Z, Mizokami A, Cheng S, Nor J, McCauley LK, Taichman RS, Keller ET: Vascular endothelial growth factor contributes to the prostate cancer-induced osteoblast differentiation mediated by bone morphogenetic protein. Cancer Res 64: 994–999, 2004
Wang SN, Lapage J, Hirschberg R: Loss of tubular bone morphogenetic protein-7 in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 12: 2392–2399, 2001
Fu SC, Wong YP, Chan BP, Pau HM, Cheuk YC, Lee KM, Chan KM: The roles of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) 12 in stimulating the proliferation and matrix production of human patellar tendon fibroblasts. Life Sci 72: 2965–2974, 2003
Hallahan AR, Pritchard JI, Chandraratna RA, Ellenbogen RG, Geyer JR, Overland RP, Strand AD, Tapscott SJ, Olson JM: BMP-2 mediates retinoid-induced apoptosis in medulloblastoma cells through a paracrine effect. Nat Med 9: 1033–1038, 2003
van der Poel HG, Hanrahan C, Zhong H, Simons JW: Rapamycin induces Smad activity in prostate cancer cell lines. Urol Res 30: 380–386, 2003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsu, MY., Rovinsky, S., Penmatcha, S. et al. Bone morphogenetic proteins in melanoma: Angel or devil?. Cancer Metastasis Rev 24, 251–263 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-005-1575-y
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-005-1575-y