Abstract
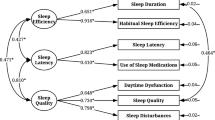
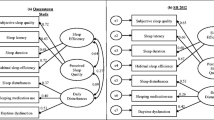
The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) is an effective instrument for measuring the quality of sleep in older adults. In this study, we used Rasch analysis to validate the items of the revised PSQI (SC_PSQI) that contribute to a single construct. A total of 3,742 workers agreed to participate in this study. Both the appropriateness of the scoring rubrics and the unidimensionality of the SC_PSQI scale were investigated. All nine items fit the model’s expectations rather well. These results indicate that the SC_PSQI with a 0 to 2 scoring scale can be used as a unidimensionality to assess sleep quality.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrich, D. (1978). A rating scale formulation for ordered response categories. Psychometrika, 43, 561–573.
Beck-Little, R., & Weinrich, S. P. (1998). Assessment and management of sleep disorders in the elderly. Journal of Gerontological Nursing, 24(4), 21–29.
Bond, T. G., & Fox, C. M. (2001). Applying the Rasch model: Fundamental measurement in the human sciences. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum, p. 179.
Buysse, D. J., Reynolds, C. F. III, Monk, T. H., Berman, S. R., & Kupfer, D. J. (1989). The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 28, 193–213.
Doi, Y., Minowa, M., Uchiyama, M., Okawa, M., Kim, K., Shibui, K., & Kamei, Y. (2000). Psychometric assessment of subjective sleep quality using the Japanese version of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI-J) in psychiatric disordered and control subjects. Psychiatry Research, 97(2–3), 165–172.
Embretson, S. E., & Reise, S. P. (2000). Item response theory for psychologists. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Escobar-Cordoba, F., & Eslava-Schmalbach, J. (2005). Colombian validation of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index. Revista de neurologia, 40, 150–155.
Hsueh, I.-P., Wang, W.-C., Sheu, C.-F., & Hsieh, C.-L. (2004). Rasch analysis of combining two indices to assess comprehensive ADL function in stroke patients. Stroke, 35(3), 721–726.
Linacre, J. M. (1998). Detecting multidimensionality: Which residual data-type works best? Journal of Outcome Measurement, 2, 266–283.
Linacre, J. M. (1999a). Investigating rating scale category utility. Journal of Outcome Measurement, 3(2), 103–122.
Linacre, J. M. (1999b). Category disordering vs. step (threshold) disordering. Rasch Measurement Transactions, 13(1), 675. retrieved from http://www.rasch.org/rmt/rmt131a.htm.
Linacre, J. M. (2000). Comparing “partial credit” and “rating scale” models. Rasch Measurement Transactions, 14(3), 768.
Linacre, J. M. (2008). WINSTEPS [computer program]. Chicago, IL: http://www.winsteps.com.
Rasch, G. (1960). Probabilistic models for some intelligent and attainment tests. Copenhagen, Denmark: Institute of Educational Research.
Rost J., & Langeheine R. (Eds.). (1997). Applications of latent trait and latent class models in the social sciences. Muenster, Germany: Waxmann.
Shaw, F., Wright, B., & Linacre, J. M. (1992). Disordered steps? Rasch Measurement Transactions, 6(2), 225.
Smith, R. M. (1999). Rasch measurement models: Interpreting WINSTEPS/BIGSTEPS and FACETS output. Chicago, IL: MESA press.
Smith, E. V. Jr., Wakeky, M. B., de Kruif, R. E. L., & Swartz, C. W. (2003). Optimizing rating scales for self-efficacy (and other). Research.Educational and Psychological Measurement, 63(3), 369–391.
Sodring, K. M., Bautz-Holter, E., Ljunggren, A. E., & Wyller, T. B. (1995). Description and validation of a test of motor function and activities in stroke patients: The Sodring motor evaluation of stroke patients. Scandinavian Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine, 27, 211–217.
Su, S.-B., & Chien, T.-W. (2007/7). Using rasch analysis to validate the TSQI to assess sleep disorders in Taiwan’s hi-tech workers. Pacific Rim Objective Measurement Symposium (PROMS 2007), Taiwan.
Tsai, P. S., Wang, S. Y., Wang, M. Y., Su, C. T., Yang, T. T., Huang, C. J., & Fang, S. C. (2005). Psychometric evaluation of the Chinese version of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (CPSQI) in primary insomnia and control subjects. Quality of Life Research, 14, 1943–1952.
Velozo, C. A., & Peterson, E. W. (2001). Developing meaningful fear of falling measures for community dwelling elderly. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation, 80, 662–673.
Violani, C., Devoto, A., Lucidi, F., Lombardo, C., & Russo, P. M. (2004). Validity of a short insomnia questionnaire: the SDQ. Brain Research Bulletin, 63(5), 415–421.
von Davier, M. (2001). WINMIRA user manual. Kiel, Germany: IPN.
Waugh, R. F., & Addison, P. A. (1998). A Rasch measurement model analysis of the revised approaches to studying inventory. The British Journal of Educational Psychology, 68, 95–112.
Wright, B. D. (1998). Model selection: Rating scale or partial credit? Rasch Measurement Transactions, 12, 641–642.
Wright, B. D. (1999). Model selection: Rating scale or partial credit? Rasch Measurement Transactions, 12, 641–642.
Wright, B. D., & Masters, G.N. (1982). Rating scale analysis. Chicago, Ill: MESAPress.
Wright, B. D., Mead, R. J., & Ludlow, L. H. (1980). KIDMAP: Person-by-item interaction mapping. Research Memorandum No. 29. MESA Psychometric Laboratory, Department of Education, University of Chicago.
Wright, B. D, & Mok, M. (2000). Rasch models overview. Journal of Applied Measurement, 1, 83–106.
Zhu, W., Updyke, W. F., & Lewandowski, C. (1997). Post-hoc Rasch analysis of optimal categorization of an ordered-response scale. Journal of Outcome Measurement, 1, 286–304.
Zou, K. H., Tuncali, K., & Silverman, S. G. (2003). Correlation and simple linear regression. Radiology, 227, 617–622.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Grant DOH93-HP-1404 from the Bureau of Health Promotion, Department of Health, Taiwan. Mr. Chien and Dr. Su provided concept/ideas/research design, writing, data analysis, facilities/equipment and fund procurement. Dr. Hsu provided institutional liaisons and project management. Professor Guo and Professor Tai provided consultation (including English revision and review of manuscript before submission).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper had been presented at Pacific Rim Objective Measurement Symposium (PROMS 2007) in Taiwan, July of 2007 (Su and Chien).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chien, TW., Hsu, SY., Tai, C. et al. Using Rasch Analysis to Validate the Revised PSQI to Assess Sleep Disorders in Taiwan’s Hi-tech Workers. Community Ment Health J 44, 417–425 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10597-008-9144-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10597-008-9144-9