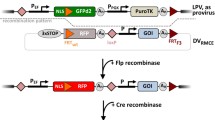
Abstract
The availability of site-specific recombinases has revolutionized the rational construction of cell lines with predictable properties. Early efforts were directed to providing pre-characterized genomic loci with a single recombinase target site that served as an address for the integration of vectors carrying a compatible tag. Efficient procedures of this type had to await recombinases like ΦC31, which recombine attP and attB target sites in a one-way reaction — at least in the cellular environment of the higher eukaryotic cell. Still these procedures lead to the co-introduction of prokaryotic vector sequences that are known to cause epigenetic silencing. This review illuminates the actual status of the more advanced recombinase-mediated cassette exchange (RMCE) techniques that have been developed for the major members of site-specific recombinases (SR), Flp, Cre and ΦC31. In RMCE the genomic address consists of a set of heterospecific recombinase target (RT-) sites permitting the exchange of the intervening sequence for the gene of interest (GOI), as part of a similar cassette. This process locks the GOI in place and it is ‘clean’ in the sense that it does not co-introduce prokaryotic vector parts nor does it leave behind a selection marker.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FRT:
-
Flp-recombinase target site
- HR:
-
homologous recombination
- RMCE:
-
recombinase-mediated cassette exchange
- RT:
-
recombinase target
- SR:
-
site-specific recombination
References
Andreas S., Schwenk F., Küter-Luks B., Faust N. and Kühn R. (2002). Enhanced efficiency through nuclear localization signal fusion on phage C31-integrase: activity comparison with Cre and FLPe recombinase in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 30: 2299–2306
Baer A., Schübeler D. and Bode J. (2000). Transcriptional properties of genomic transgene integration sites marked by electroporation or retroviral infection. Biochemistry 39: 7041–7049
Baer A. and Bode J. (2001). Coping with kinetic and thermodynamic barriers: RMCEan efficient strategy for the targeted integration of transgenes. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 12: 473–480
Baer A. 2002. Funktioneller Vergleich von S/MARs (‘scaffold/matrix attachment regions’ und Insulatoren im chromosomalen Kontext. Dissertation, University of Braunschweig; http://www.biblio.tu-bs.de/ediss/data/20021106a/20021106a.pdf.
Bautista D. and Shulman M.J. (1993). A hit-and-run system for introducing mutations into the Ig H chain locus of hybridoma cells by homologous recombination. J. Immunol. 151: 1950–1958
Belteki G., Gertsenstein M., Ow D.W. and Nagy A. (2003). Site-specific cassette exchange and germline transmission with mouse ES cells expressing phiC31 integrase. Nat. Biotechnol. 21: 321–324
Bode J., Bartsch J., Boulikas T., Iber M., Mielke C., Schübeler D., Seibler J. and Benham C. 1998. Transcription-promoting genomic sites in mammalia: their elucidation and architectural principles. Gene Ther. Mol. Biol. 1: 551–880.http://www.gtmb.org/volume1/29_Bode.htm.
Bode J., Schlake T., Iber M., Schübeler D., Seibler J., Snezhkov E. and Nikolaev L. (2000). The transgeneticist’s toolbox — novel methods for the targeted modification of eukaryotic genomes. Biol. Chem. 381: 801–813
Bode J., Goetze S., Ernst E., Huesemann Y., Baer A., Seibler J. and Mielke C. (2003). Architecture and utilization of highly-expressed genomic sites in New Comprehensive Biochemistry Vol 38. In: Makrides, S. and Bernardi, G. (eds) (volume ed.) Gene Transfer and Expression in Mammalian Cells, pp. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Bode J., Winkelmann S., Götze S., Spiker S., Tsutsui K., Bi C. and Benham C. 2005. Correlations between scaffold/matrix attachment region (S/MAR) binding activity and DNA duplex destabilization energy. J. Mol. Biol. in press.
Bouhassira E., Westerman K. and Leboulch P. (1997). Transcriptional behavior of LCR enhancer elements integrated at the same chromosomal locus by recombinase-mediated cassette exchange. Blood 90: 3332–3344
Branda C.S. and Dymecki S.M. (2004). Talking about a revolution: the impact of site-specific recombinases on genetic analyses in mice. Develop. Cell 6: 7–28
Buchholz F., Ringrose L., Angrand P., Rossi F. and Stewart A. (1996). Different thermostabilities of FLP and Cre recombinases: implications for applied site specific recombination. Nucl. Acids Res. 24: 4256–4262
Buchholz F., Angrand P.-O. and Stewart A.F. (1998). Improved properties of Flp recombinase evolved by cycling mutagenesis. Nat. Biotechnol. 16: 657–662
Cesari F., Rennekampff V., Vintersten K., Vuong L.G., Seibler J., Bode J., Wiebel F.F. and Nordheim A. (2004). Elk-1 knock-out mice engineered by Flp recombinase-mediated cassette exchange. Genesis 38: 87–92
Cobellis G., Nicolaus G., Iovino M., Romito A., Marra E., Barbarisi M., Sardiello M., Di Giorgio F.P., Iovino N., Zollo M., Ballabio A. and Cortese R. (2005). Tagging genes with cassette-exchange sites. Nucl. Acids Res. 33(4): e44, doi:10.1093/nar/gni045
Coroadinha A.S., Schucht R., Gama-Norton L., Wirth D., Hauser H. and Carrondo M.J.T. 2005. The use of recombinase cassette exchange in retroviral vector producer cell lines: predictability and efficiency in transgene replacement. J. Biotechnol., Submitted.
Fukushige S. and Sauer B. (1992). Genomic targeting with a positive-selection lox integration vector allows highly reproducible gene expression in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 89: 7905–7909
Garrick D., Fiering S., Martin D.I.K. and Whitelaw E. (1998). Repeat-induced gene silencing in mammals. Nat. Genet. 18: 56–59
Goetze S., Huesemann Y., Baer A. and Bode J. (2003). Functional characterization of transgene integration patterns by Halo-FISH: electroporation versus retroviral infection. Biochemistry 42: 7035–7043
Goetze S., Baer A., Winkelmann S., Nehlsen K., Seibler J., Maass K. and Bode J. (2005). Mol. Cell. Biol. 25: 2260–2272
Grabenhorst E., Schlenke P., Pohl S., Nimtz M. and Conradt H.S. (1999). Genetic engineering of recombinant glycoproteins and the glycosylation pathway in mammalian host cells. Glycoconjugate J. 16: 81–97
Groth A.C., Olivares E.C., Thyagarajan B. and Calos M.P. (2000). A phage integrase directs efficient site-specific integration in human cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 5995–6000
Kolot M., Silberstein N. and Yagil E. (1999). Site specific recombination in mammalian cells expressing the Int recombinase of bacteriophage HK022. Mol. Biol. Rep. 26: 207–213
Kouzine K., Liu L., Sanford S., Chung H.J. and Levens D. (2004). The dynamic response of upstream DNA to transcription-generated torsional stress. Nature Struct. Mol. Biol. 11: 1092–1100
Lauth M., Spreafico F., Dethleffsen K. and Meyer M. (2002). Stable and efficient cassette exchange under non-selectable conditions by combined use of two site-specific recombinases. Nucl. Acids Res. 30: e115
Mlynarova L., Libantova J., Vrba L. and Nap J.P. (2002). The promiscuity of heterospecific lox sites increases dramatically in the presence of palindromic DNA. Gene 296: 129–137
Nakano M., Odaka K., Takahashi Y., Ishimura M., Saito I. and Kanegae Y. (2005). Production of viral vectors using recombinase-mediated cassette exchange. Nucl. Acids Res. 33: e76
Ng P. and Baker M.D. (1998). High efficiency site-specific modification of the chromosomal immunoglobulin locus by gene targeting. J. Immunol. Meth. 214: 81–96
O’Gorman S., Fox D.T. and Wahl G.M. (1991). Recombinase-mediated gene activation and site-specific integration in mammalian cells. Science 251: 1351–1355
Peitz M., Pfannkuche K., Rajewsky K. and Edenhofer F. (2002). Ability of the hydrophobic FGF and basic TAT peptides to promote cellular uptake of recombinant Cre recombinase: a tool for efficient genetic engineering of mammalian genomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99: 4489–4494
Roebroek A.J.M., Reekmans S., Lauwers A., Feyaerts N., Smeijers L. and Hartmann D. 2006. Mutant Lrp1 knock-in mice generated by RMCE reveal differential importance of the NPXY motifs in the intracellular domain of LRP1 for normal fetal development. Mol. Cell Biol. 26: 605–616
Riu E., Grimm D., Huang Z., Mark A. and Kay M.A. (2005). Increased maintenance and persistence of transgenes by excision of expression cassettes from plasmid sequences in vivo Hum. Gene. Ther. 16: 558–570
Schlake T. and Bode J. (1994). Use of mutated FLP recognition target (FRT) sites for the exchange of expression cassettes at defined chromosomal loci. Biochemistry 33: 12746–12751
Schmidt E.E., Taylor D.S., Prigge J.R., Arnett S. and Capecchi M.R. (2000). Illegitimate Cre-dependent chromosome rearrangements in transgenic mouse spermatids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 13702–13707
Schnütgen F., Doerflinger N., Calléja C., Wendling O., Chambon P. and Ghyselinck N.B. (2003). A directional strategy for monitoring Cre-mediated recombination at the cellular level in the mouse. Nat. Biotechnol. 21: 562–565
Schucht R., Coroadinha A.S., Zanta-Boussif M.A., Carrondo M., Hauser H. and Wirth D. 2005. A new generation of retroviral producer cells: predictable and stable virus production by Flp mediated site-specific integration of retroviral vectors. Mol. Thera., Submitted.
Schübeler D. and Bode J. (1998). Retargeting of retroviral integration sites for the predictable expression of transgenes and the analysis of cis-acting sequences. Biochemistry 37: 11907–11914
Seibler J., Schübeler D., Fiering S., Groudine M. and Bode J. (1998). DNA cassette exchange mediated by FLP recombinase: an efficient strategy for the repeated modification of tagged loci by marker-free constructs. Biochemistry 37: 6229–6234
Seibler J., Küter-Luks B., Kern H., Streu S., Plum L., Mauer J., Kühn R., Brüning J.C. and Schwenk F. (2005). Single copy shRNA configuration for ubiquitous gene knockdown in mice. Nucl. Acids Res. 33: e67
Stark W.M., Boocock M.R. and Sherratt D.J. (1992). Catalysis by site-specific recombinases. Trends Genet. 8: 432–439
Taniguchi M., Sanbo M., Watanabe S., Naruse I., Mishina M. and Yagi T. (1998). Efficient production of Cre-mediated site-directed recombinants through the utilization of the puromycin resistance genepac: a transient gene-integration marker for ES cells. Nucl. Acids Res. 26: 679–680
Thorpe H.M. and Smith M.C.M. (1998). In vitro site-specific integration of bacteriophage DNA catalyzed by a recombinase of the resolvase/invertase family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 5505–5510
Thyagarajan B., Olivares E.C., Hollis R.P., Ginsburg D.S. and Calos M.P. (2001). Site-specific genomic integration in mammalian cells mediated by phage phiC31 integrase. Mol. Cell Biol. 21: 3926–3934
Umlauf S.W. and Cox M.M. (1988). The functional significance of DNA sequence structure in a site-specific genetic recombination reaction. EMBO J. 7: 1845–1852
Unsinger J., Lindenmaier W., May T., Hauser H. and Wirth D. (2004). Stable and strictly controlled expression of LTR-flanked autoregulated expression cassettes upon adenoviral transfer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 319: 879–887
Weidle U.H., Buckel P. and Wienberg J. (1988). Amplified expression constructs for human tissue-type plasminogen activator in Chinese hamster ovary cells: instability in the absence of selective pressure. Gene 66: 193–203
Winkler K., Wermelinger T., Paul C., Koch S., Brecht S., Zietze S., Nuck R., Thiel G., Marx U. and Sandig V. 2005. Targeting the human IgH loci for high level heterologous gene expression. In: Gòdia F. and Fussenegger M.(eds) ESACT Proceedings, Vol. 2. Animal Cell Technology Meets Genomics. SpringerNetherlands, pp.403–409.ISBN: 1-4020-2791-5
Wirth M., Bode J., Zettelmeissl G. and Hauser H. (1988). Isolation of overproducing recombinant mammalian cell lines by a fast and simple selection procedure. Gene 73: 419–426
Wirth D. and Hauser H. (2004). Flp-mediated integration of expression cassettes into FRT-tagged chromosomal loci in mammalian cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 267: 467–476
Wong E.T., Kolman J.L., Li Y.C., Mesner L.D., Hillen W., Berens C. and Wahl G.M. (2005). Reproducible doxycycline-inducible transgene expression at specific loci generated by Cre-recombinase mediated cassette exchange. Nucl. Acids Res. 33(17): e147, doi:10.1093/nar/gni145
Wurm F.M. and Jordan M. (2003). Gene transfer and gene amplification in mammalian cells in “New Comprehensive Biochemistry 38” In: Bernardi, G. (eds) A Gene Transfer and Expression in Mammalian Cells, Chapter 7. S. Makrides, Volume Ed, pp 307–335. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oumard, A., Qiao, J., Jostock, T. et al. Recommended Method for Chromosome Exploitation: RMCE-based Cassette-exchange Systems in Animal Cell Biotechnology. Cytotechnology 50, 93–108 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-006-6550-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-006-6550-0