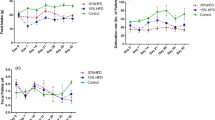
This study deals with the enteropathy recently identified in diabetes-prone BB rats (BBdp). Diabetes-resistant BB rats (BBc) and BBdp rats were fed from days 32–39 onward either a protective diabetes-retardant hydrolyzed casein diet (HC) or a plant-based diabetogenic (NTP) diet. The NTP diet decreased body weight and plasma insulin in BBc and BBdp rats. The BBdp rats displayed low intestinal invertase and increased intestinal peroxidase activity. In the BBdp rats fed the HC diet, the mucin content 30–35 cm below the pylorus was higher and the gut permeability lower than in the other three rat groups. There was a significant inverse correlation between gut permeability and the insulinogenic index in the BBdp rats fed the HC or NTP diet. Thus, in BBdp rats, the HC diet somehow prevents the increase in gut permeability and the decrease in the insulinogenic index otherwise found in some of these diabetes-prone animals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Graham S, Scott F, Malaisse W, Mowat AM: Enteropathy and diet are unrelated risk factors in the pathogenesis of Type 1 diabetes in BB rats. Mucos Immunol Update 10:A2473, 2002 (abstr)
Courtois P, Meuris S, Sener A, Malaisse WJ, Scott FW: Invertase, maltase, lactase, and peroxidase activities in duodenum of BB rats. Endocrine 19:293–299, 2002
Hardin JA, Donegan L, Woodman RC, Trevenen C, Gall DG: Mucosal inflammation in a genetic model of spontaneous type 1 diabetes mellitus. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 80:1064–1070, 2002
Courtois P, Sener A, Scott FW, Malaisse WJ: Peroxidase activity in the intestinal tract of Wistar-Furth, BBc and BBdp rats. Diabetes/ Metab Res Rev 20:305–314, 2004
Courtois P, Sener A, Scott FW, Malaisse WJ: Disaccharidase activity in the intestinal tract of Wistar-Furth, BBc and BBdp rats. Br J Nutr 91:201–209, 2004
Malaisse WJ, Valverde I, Redonda A, Acitores A, Villanueva-Peñacarrillo ML, Meuris S, Courtois P, Sener A, Scott FW: Glucagon-like peptide 1 content of the intestinal tract in BB rats. Diabetes 51 (Suppl 2):A580, 2002 (abstr)
Meddings JB, Jarand J, Urbanski SJ, Hardin J, Gall DG: Increased gastrointestinal permeability is an early lesion in the spontaneously diabetic BB rat. Am J Physiol 276:G951–G957, 1999
MacFarlane AJ, Burghardt KM, Kelly J, Simell T, Simell O, Altosaar I, Scott FW: A type-1 diabetes-related protein from wheat (Tritium aestivum). cDNA clone of a wheat storage globulin, Glb1, linked to islet damage. J Biol Chem 278:54–63, 2002
Cohen PS, Laux DC: Bacterial adhesion to and penetration of intestinal mucus in vitro. Methods Enzymol 253:309–314, 1995
Napolitano LM, Koruda MS, Meyer AA, Baker CC: The impact of femur fracture with associated soft tissue injury on immune function and intestinal permeability. Shock 5:202–207, 1996
Miller RS, Hoskins LC: Mucin degradation in human colon ecosystems. Gastroenterology 81:759–765, 1981
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall R: Protein measurement by the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 195:265–276, 1951
Lowry OH, Passonneau JV: A Flexible System of Enzymatic Analysis. New York, Academic Press, 1972
Leclercq-Meyer V, Marchand J, Woussen-Colle MC, Giroix MH, Malaisse WJ: Multiple effects of leucine on glucagon, insulin and somatostatin secretion from the perfused rat pancreas. Endocrinology 116:1168–1174, 1985
Snedecor GW: Statistical Methods. Ames, Iowa State University Press, 1956
Olivares E, Ladrière L, Laghmich A, Sener A, Malaisse WJ, Scott FW: Effects of a protective hydrolyzed casein diet upon the metabolic and secretory responses of pancreatic islets to IL-1ß, cytokine production by mesenteric lymph node cells, mitogenic and biosynthetic activities in Peyer’s patch cells, and mitogenic activity in pancreatic lymph node cells from control and diabetes-prone BB rats. Mol Gen Metab 68:379–390, 1999
Scott FW, Olivares E, Sener A, Malaisse WJ: Dietary effects on insulin and nutrient metabolism in mesenteric lymph node cells, splenocytes, and pancreatic islets of BB rats. Metabolism 49:1111–1117, 2000
Malaisse WJ, Olivares E, Laghmich A, Ladrière L, Sener A, Scott FW: Feeding a protective hydrolysed casein diet to young diabetes-prone BB rats affects oxidation of L-[U-14C]glutamine in islets and Peyer’s patches, reduces abnormally high mitotic activity in mesenteric lymph nodes, enhances islet insulin and tends to normalize NO production. Int J Exp Diabetes Res 1:121–130, 2000
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Courtois, P., Nsimba, G., Jijakli, H. et al. Gut Permeability and Intestinal Mucins, Invertase, and Peroxidase in Control and Diabetes-Prone BB Rats Fed Either a Protective or a Diabetogenic Diet. Dig Dis Sci 50, 266–275 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-1594-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-1594-0