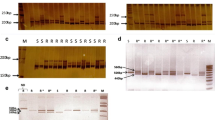
Abstract
Resistance to root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne incognita) is determined by a single major gene rkn1 in Gossypium hirsutum Acala NemX cotton. Bulked segregant analysis (BSA) combined with amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) was used to identify molecular markers linked to rkn1. DNA pools from homozygous susceptible (S) and resistant (R) bulks of an F2:3 originating from the intraspecific cross NemX × SJ-2 were screened with 128 EcoR1/Mse1 primer combinations. Putative AFLP markers were then screened with 60 F2:7 RIL plants and four AFLP markers were found linked to rkn1. The linkage of AFLP markers to rkn1 was also confirmed in a F2 population. The closest AFLP marker was converted to a cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence (CAPS) marker (designated GHACC1) by aligning the sequences from both susceptible and resistant parents. GHACC1 linkage to rkn1 was confirmed in the F2 (1R:3S), F2:7 RIL (1R:1S) and the backcross population SJ-2 × F1 (NemX × SJ-2) (1 heterozygous: 1 homozygous). The four AFLP markers, GHACC1 plus two SSR markers (CIR316 and BNL1231) linked to rkn1 from previous work were mapped to intervals of 2.6–14.2 cM from the rkn1 locus, and the genomic region around rkn1 was spanned to about 28.2 cM in the F2:7 population. The PCR-based GHACC1 and CIR316 markers were tested on 21 nematode resistant and susceptible cotton breeding lines and cultivars. GHACC1 was suitable for nematode resistance screening within G.␣hirsutum, but not G. barbadense, whereas CIR316 was useful in both species, indicating their␣potential for utilization in marker-assisted selection.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AFLP:
-
Amplified fragment length polymorphism
- CAPS:
-
Cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence
- MAS:
-
Marker-assisted selection
- RIL:
-
Recombinant inbred line
- STS:
-
Sequence tag site
References
Abawi GS, Chen J (1998) Concomitant pathogen and pest interactions. In: Barker KR, Pederson GA, Windham GL (eds), Plant and nematode interactions. Am Soc Agron, Crop Sci Am, and Soil Sci Soc, Madsion, WI pp. 135–158
Bassam BJ, Caetano-Anolles G, Gresshoff PM (1991) Fast and sensitive silver staining of DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 196:80–83
Bezawada C, Saha S, Jenkins JN, Creech RG, McCarty JC (2003) SSR marker(s) associated with root-knot nematode resistance gene(s) in cotton. J Cotton Sci 7:179–184
Bridge J, Page SLJ (1980) Estimation of root-knot nematode infestation levels on roots using a rating chart. Trop Pest Manage 26:296–298
Caranta C, Thabuis A, Palloix A (1999) Development of a CAPS marker for the Pvr4 locus: a tool for pyramiding potyvirus resistance genes in pepper. Genome 42:1111–1116
Feaster CV, Turcotte EL (1965) Fruiting height response: a consideration in varietal improvement of Pima cotton, Gossypium barbadense L. Crop Sci 5:460–464
Goodell PB, Montez GH (1994) Acala cotton tolerance to southern root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita. Proc of Beltwide Cotton Prod Res Conf, Natl Cotton Council of Am, Memphis, TN pp. 265–267
Hussey RS, Barker KR (1973) A comparison of methods of collecting inocula of Meloidogyne spp. including a new technique. Plant Dis Rep 57:1025–1028
Hyer AH, Jorgenson EC (1984) Root-knot nematode resistance in cotton breeding: techniques and results. Proc of Beltwide Cotton Prod Res Conf, Natl Cotton Council of Am, Memphis, TN pp. 377–379
Jeffers DP, Roberts PA (1993) Effect of planting date and host genotype on the root-knot nematode-Fusarium wilt disease complex of cotton. Phytopathology 83:645–654
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172--175
McPherson RG, Jenkins JN, McCarty JC, Watson C (1995) Combining ability analysis of root-knot nematode resistance in cotton. Crop Sci 35:373–375
McPherson MG, Jenkins JN, Watson CE, McCarty JC (2004) Inheritance of root-knot nematode resistance in M-315 RNR and M-78-RNR cotton. J Cotton Sci 8:154–161
Mechanda SM, Baum BR, Johnson DA, Arnason TJ (2004) Sequence assessment of comigrating AFLP bands in Echinacea – implications for comparative biological studies. Genome 47:15–25
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9828–9832
Nguyen TB, Giband M, Brottier P, Risterucci AM, Lacape JM (2004) Wide coverage of the tetraploid cotton genome using newly developed microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 109:167–175
Oakley SR (1995) CPCSD Acala C-225: a new nematode-resistant Acala variety for California’s San Joaquin Valley. Proc of Beltwide Cotton Prod Res Conf, Natl Cotton Council of Am, Memphis, TN p. 39
Ogallo JL, Goodell PB, Eckert J, Roberts PA (1997) Evaluation of NemX, a new cultivar of cotton with high resistance to Meloidogyne incognita. J Nematol 29:531–537
Prins R, Groenewald JZ, Marais GF, Snape JW, Koebner RMD (2001) AFLP and STS tagging of Lr19, a gene conferring resistance to leaf rust in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 103:618–624
Roberts PA, Matthews WC, Veremis JC (1998) Genetic mechanisms of host–plant resistance to nematodes. In: Barker KR, Pederson GA, Windham GL (eds), Plant and nematode interactions. Am Soc Agron, Crop Sci Am, and Soil Sci Soc, Madsion, WI, pp. 209–238
Robinson AF, Cook CG, Percival AE (1999) Resistance to Rotylenchulus reniformis and Meloidogyne incognita race 3 in the major cotton cultivars planted since 1950. Crop Sci 39:850–858
Robinson AF, Bowman DT, Cook CG, Jenkins JN, Jones JE, May LO, Oakley SR, Oliver MJ, Roberts PA, Robinson M, Smith CW, Starr JL, Stewart JM (2001) Nematode resistance. In: Kirkpatrick TL, Rothrock CS (eds), Compendium of Cotton Diseases. APS Press, St. Paul, MN, pp. 68–72
Rong J, Abbey C, Bowers JE, Brubaker CL, Chang C, Chee PW, Delmonte TA, Ding X, Garza JJ, Marler BS, Park C, Pierce GJ, Rainey KM, Rastogi VK, Schulze SR, Trolinder NL, Wendel JF, Wilkins TA, Williams-Coplin␣TD, Wing RA, Wright RJ, Zhao X, Zhu L, Paterson AH (2004) A 3347-locus genetic recombination map of sequence-tagged sites reveals features of genome organization, transmission and evolution of cotton (Gossypium). Genetics 166:389–417
Sasser JN (1977) Worldwide dissemination and importance of the root-knot nematodes, Meloidogyne spp. J Nematol 9:26–29
Shepherd RL (1974) Transgressive segregation for root-knot nematode resistance in cotton. Crop Sci 14:872–875
Shepherd RL (1982) Registration of three germplasm lines of cotton. Crop Sci 22:692
Shepherd RL, McCarty JC, Jenkins JN, Parrott WL (1988) Registration of twelve nonphotoperiodic lines with root-knot nematode resistant primitive cotton germplasm. Crop Sci 28:868–869
Shepherd RL, McCarty JC, Jenkins JN, Parrott WL (1989) Notice of release of nine root-knot nematode resistant germplasm lines of upland cotton Gossypium hirsutum L. USDA Miss Agric and Forestry Exp Stn
Starr JL, Roberts PA (2004) Resistance to plant-parasitic nematodes. In: Chen ZX, Chen SY, Dickson DW (eds) Nematology advances and perspectives, vol 2. Tsinghua University Press, Beijing, pp 879–907
Turcotte EL, Harold WR, O’Bannon JH, Feaster CV (1963) Evaluation of cotton root-knot nematodes resistance of a strain of G. barbadense var. darwinii. Cotton Improve Conf Proc 15:36–44
Van Ooijen JW, Voorrips RE (2001) JoinMap® 3.0, software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen, the Netherlands
von Stackelberg M, Lindemann S, Menke M, Riesselmann S, Jacobsen HJ, (2003) Identification of AFLP and STS markers closely linked to the def locus in pea. Theor Appl Genet 106:1293–1299
Wang C, Ulloa M, Roberts PA (2006) Identification and mapping of microsatellite markers linked to a root-knot nematode resistance gene (rkn1) in Acala NemX cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Theor Appl Genet 112:770–777
Young EF, Feaster CV, Turcotte EL (1976) Registration of Pima S-3 cotton. Crop Sci 16:604
Acknowledgments
This study was funded in part by a Cooperative Research Agreement from Cotton Incorporated and a grant from the University of California Discovery Grant (BioSTAR) Program. The authors thank Steven Oakley, James Starr, California Planting Cotton Seed Distributors, and USDA Cotton Germplasm Center for providing cotton seed, Mikeal Roose for helpful advice, Mauricio Ulloa for providing SSR markers, and William Matthews, Teresa Mullens, Kathie Carter, Joe Kepiro and Xiangyang Shi for technical help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Roberts, P.A. Development of AFLP and derived CAPS markers for root-knot nematode resistance in cotton. Euphytica 152, 185–196 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-006-9197-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-006-9197-1