Abstract
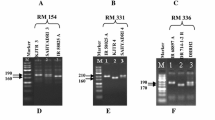
With the objective of identifying SSR markers that can distinguish parental lines of rice hybrids, we characterized 10 each of cytoplasmic male sterile (CMS) and restorer (R) lines along with 10 popular Indian rice varieties using a set of 48 hyperpolymorphic SSRs distributed uniformly across the rice genome. All the SSR markers were polymorphic, amplifying a total of 163 alleles, with an average of 3.36 ± 1.3 allelic variants per locus. Twenty-seven SSR markers showed amplification of an allele, which was very specific and unique to a particular parental line and not amplified in any other rice genotype tested. Through multiplex PCR, SSR marker combinations that were unique to a particular parental line or hybrid were also identified. With a set of 10 SSR markers, all the public bred Indian rice hybrids along with their parental lines could be clearly distinguished. To utilize these SSR markers effectively for detection of impurities in parental lines, a two dimensional bulked DNA sampling strategy involving a 20 × 20 grow-out matrix has been designed and used for detection of contaminants in a seed-lot of the popular CMS line IR58025A. We have also designed a multiplex PCR strategy involving single tube analysis using 2–3 markers for hybrid seed purity assessments and demonstrate its superiority over single marker analysis in accurate detection of impurities in hybrids. Implications of parental and hybrid specific SSR markers and strategies to utilize the informative SSR markers for detection of contaminants in a cost effective manner are discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bredemeijer GMM, Cook RJ, Ganal MW, Peeters R, Issac P, Noordijk Y, Rendell S, Jackson J, Roder MS, Wendehake K, Dijcks M, Amelaine M, Wickaert V, Bertrand L, Vosman B (2002) Construction and testing of microsatellite database containing more than 500 tomato varieties. Theor Appl Genet 105:1019–1026
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) A plant DNA minipreparation. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1:19–21
Karkousis A, Barr AR, Chalmers KJ, Ablett GA, Holton TA, Henry RJ, Lim P, Langridge P (2003) Potential of SSR markers for plant breeding and variety identification in Australian Barley germplasm. Aust J Agric Res 54:1197–1210
Mao CX, Virmani SS, Kumar I (1996) Technological innovations to lower the costs of hybrid rice seed production. In: Virmani SS et al (eds) Advances in hybrid rice technology. Proceedings of Third International Symposium on Hybrid Rice, Directorate of Rice Research, Hyderabad, India
McCouch SR, Teytelman L, Xu Y, Lobos KB, Clare K, Walton M, Fu B, Maghirang R, Li Z, Xing Y, Zhang Q, Kono Z, Yano M, Fjellstrom R, Declerck G, Schneider D, Cartinhour S, D.Ware D, Stein L (2002) Development and Mapping of 2240 New SSR Markers for Rice (Oryza sativa L.). DNA Res 9:199–207
Mishra B, Viraktamath BC, Ilyas Ahmed M, Ramesha MS, Vijayakumar CHM (2003) Hybrid rice research and development in India. In: Virmani SS, Mao CX, Hardy B (eds) Hybrid rice for food security, poverty alleviation, and environmental protection. Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Hybrid Rice, 14–17 May 2002, Hanoi, Vietnam. Los Baños (Philippines), International Rice Research Institute, pp 265–283
Nandakumar N, Singh AK, Sharma RK, Mohapatra T, Prabhu KV, Zaman FU (2004) Molecular fingerprinting of hybrids and assessment of genetic purity of hybrid seeds in rice using microsatellite markers. Euphytica 136:257–264
Nas TM, Toledo RS, Li Z, Virmani SS (2002) Two-dimensional DNA sampling: a new strategy for assessing hybridity using molecular markers. Paper presented at the 4th International Symposium on Hybrid Rice, International Rice Research Institute, Hanoi, 14–17 May 2002
Rangaswamy M, Jayamani P (1996) Hybrid rice research in Tamil Nadu. In: Rangaswamy M (ed) Hybrid rice technology. School of Genetics, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore, India
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd ed. Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, pp 5.40–5.46
Smith JSC, Register III JC (1998) Genetic purity and testing technologies for seed quality: a company perspective. Seed Sci Res 8:285–293
Temnykh S, Park WD, Ayres N, Cartinhour S, Hauck N, Lipvich L, Cho YG, Ishi T, McCouch SR (2000) Mapping and genome organization of microsatellite sequences in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 100:697–712
Temnykh S, DeClerck G, Lukashova A, Lipovich L, Cartinhour S, McCouch SR (2001) Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza sativa L.): frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential. Genome Res 11:1441–1452
UPOV-BMT (2002) BMT/36/10 Progress Report of the 36th Session of the Technical Committee, the technical working parties and working group on biochemical and molecular techniques and DNA-profiling in particular, Geneva
Virmani SS, Ish Kumar (2004) Development and use of Hybrid rice technology to increase rice productivity in the tropics. Intl Rice Res Newsl 29:10–20
Wang J, Zhong GY, Chin ECL, J.C. Register III JC, Riley RD, Niebur WS, Smith JSC (2002) Identification of parents of F1 hybrids through SSR profiling of maternal and hybrid tissue. Euphytica 124:29–34
Yashitola J, Thirumurugan T, Sundaram RM, Naseerullah MK, Ramesha MS, Sarma NP, Sonti RV (2002) Assessment of purity of rice hybrids using microsatellite and STS markers. Crop Science 42:1369–1373
Yashitola J, Sundaram RM, Biradar SK, Thirumurugan T, Vishnupriya MR, Rajeshwari R, Viraktamath BC, Sarma NP, Sonti RV (2004) A sequence specific PCR marker for distinguishing rice lines on the basis of wild abortive cytoplasm from their cognate maintainer lines. Crop Sci 44:920–924
Yuan LP (1977) The execution and theory of developing hybrid rice. Zhonggue Nongye Kexue (Chin Agric Sci) 1:27–31
Zhang LS, Clerc VL, Li S, Zhang D (2005) Establishment of an effective set of simple sequence repeat markers for sunflower variety identification and diversity assessment. Euphytica 83:66–72
Zheng K, Huang N, Bennett J, Khush GS (1995) PCR-based marker assisted selection in rice breeding. IRRI Discussion Paper Series No. 12. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, The Philippines
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sundaram, R.M., Naveenkumar, B., Biradar, S.K. et al. Identification of informative SSR markers capable of distinguishing hybrid rice parental lines and their utilization in seed purity assessment. Euphytica 163, 215–224 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9630-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9630-0