Abstract
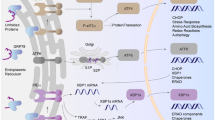
N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase (Arylsulfatase B; ARSB) is the enzyme that removes sulfate groups from the N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfate residue at the non-reducing end of chondroitin-4-sulfate (C4S) and dermatan sulfate (DS). Previous studies demonstrated reduction in cell-bound high molecular weight kininogen in normal rat kidney (NRK) epithelial cells when chondroitin-4-sulfate content was reduced following overexpression of ARSB activity, and chondroitinase ABC produced similar decline in cell-bound kininogen. Reduction in the cell-bound kininogen was associated with increase in secreted bradykinin. In this report, we extend the in vitro findings to in vivo models, and present findings in Dahl salt-sensitive (SS) rats exposed to high (SSH) and low salt (SSL) diets. In the renal tissue of the SSH rats, ARSB activity was significantly less than in the SSL rats, and chondroitin-4-sulfate and total sulfated glycosaminoglycan content were significantly greater. Disaccharide analysis confirmed marked increase in C4S disaccharides in the renal tissue of the SSH rats. In contrast, unsulfated, hyaluronan-derived disaccharides were increased in the rats on the low salt diet. In the SSH rats, with lower ARSB activity and higher C4S levels, cell-bound, high-molecular weight kininogen was greater and urinary bradykinin was lower. ARSB activity in renal tissue and NRK cells declined when exogenous chloride concentration was increased in vitro. The impact of high chloride exposure in vivo on ARSB, chondroitin-4-sulfation, and C4S-kininogen binding provides a mechanism that links dietary salt intake with bradykinin secretion and may be a factor in blood pressure regulation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Sousa, J.F., Nader, H.B., Dietrich, C.P.: Sequential degradation of chondroitin sulfate in mollusks. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 20150–20155 (1990)
Glaser, J.H., Conrad, H.E.: Chondroitin SO4 catabolism in chick embryo chondrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 254, 2316–2325 (1978)
Ingmar, B., Wasteson, B.: Sequential degradation of a chondroitin sulfate trisaccharide by lysosomal enzymes from embryonic-chick epiphysial cartilage. Biochem. J. 179, 7–13 (1979)
Bhattacharyya, S., Kotlo, K., Danziger, R.S., Tobacman, J.K.: Arylsulfatase B regulates interaction of chondroitin-4-sulfate and kininogen in renal epithelial cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1802(5), 472–477 (2010)
Gozzo, A.J., Nunes, V.A., Carmona, A.K., Nader, H.B., von Dietrich, C.P., Silveira, V.L.F., Shimamoto, K., Ura, N., Sampaio, M.U., Sampaio, C.A.M., Araujo, M.S.: Glycosaminoglycans affect the action of human plasma kallikrein on kininogen hydrolysis and inflammation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2, 1861–1865 (2002)
Renné, T., Schuh, K., Müller-Esterl, W.: Local bradykinin formation is controlled by glycosaminoglycans. J. Immunol. 175, 3377–3385 (2005)
Bhattacharyya, S., Tobacman, J.K.: Steroid sulfatase, arylsulfatases A and B, galactose 6-sulfatase, and iduronate sulfatase in mammary cells and effects of sulfated and non-sulfated estrogens on sulfatase activity. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 103, 20–34 (2007)
Ferrero, G.B., Pagliardini, S., Veljkovic, A., Porta, F., Bena, C., Tardivo, I., Restagno, G., Silengo, M.C., Bignamini, D.: In vivo specific reduction of arylsulfatase B enzymatic activity in children with Cystic Fibrosis. Mol. Genet. Metab. 94, 39 (2008)
Sharma G, Burke J, Bhattacharyya S, Sharma N, Katyal S, Park RL, Tobacman J: Reduced arylsulfatase B activity in leukocytes from cystic fibrosis patients. Pediatr. Pulmonol. (2012). doi:10.1002/ppul.22567
Prabhu, S.V., Bhattacharyya, S., Guzman-Hartman, G., Macias, V., Kajdacsy-Balla, A., Tobacman, J.K.: Extra-lysosomal localization of arylsulfatase B in human colonic epithelium. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 59(3), 328–335 (2011)
Bhattacharyya, S., Tobacman, J.K.: Arylsulfatase B regulates colonic epithelial cell migration by effects on MMP9 expression and RhoA activation. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 26(6), 535–545 (2009)
Achur, R.N., Valiyaveettil, M., Gowda, D.C.: The low sulfated chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans of human placenta have sulfate group-clustered domains that can efficiently bind Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 11705–11713 (2003)
Rogerson, S.J., Brown, G.: Chondroitin sulfate A as an adherence receptor for Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. Parasitol. Today 13, 70–75 (1997)
Bhattacharyya, S., Solakyildirim, K., Zhang, Z., Linhardt, R.J., Tobacman, J.K.: Cell-bound IL-8 increases in bronchial epithelial cells following Arylsulfatase B silencing. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 42(1), 51–61 (2010)
Wòjczyk, B.: Lysosomal arylsulfatases A and B from horse blood leukocytes: purification and physico-chemical properties. Biol. Cell. 57, 147–152 (1986)
Bhattacharyya, S., Kotlo, K., Shukla, S., Danziger, R.S., Tobacman, J.K.: Distinct effects of N-acetyl-galactosamine-4-sulfatase and galactose-6-sulfatase expression on chondroitin sulfates. J. Biol. Chem. 283(15), 9523–9530 (2008)
Bhattacharyya, S., Look, D., Tobacman, J.K.: Increased arylsulfatase B activity in cystic fibrosis cells following correction of CFTR. Clin. Chim. Acta 380(1–2), 122–127 (2007)
Yang, B., Chang, Y., Weyers, A.M., Sterner, E., Linhardt, R.J.: Disaccharide analysis of glycosaminoglycan mixtures by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatog. A 1225, 91–98 (2012)
Yang, B., Weyers, A., Baik, J.Y., Sterner, E., Sharfstein, S., Mousa, S.A., Zhang, F., Dordick, J.S., Linhardt, R.J.: Ultra-performance ion-pairing liquid chromatography with on-line electrospray ion trap mass spectrometry for heparin disaccharide analysis. Anal. Biochem. 314, 59–66 (2011)
Zhang, F., Sun, P., Muñoz, E., Chi, L., Sakai, S., Toida, T., Zhang, H., Mousa, S., Linhardt, R.J.: Microscale isolation and analysis of heparin from plasma using an anion-exchange spin column. Anal. Biochem. 353, 284–286 (2006)
Hernáiz, M.J., Linhardt, R.J.: Degradation of chondroitin sulfate and dermatan sulfate with chondroitin lyases. Methods Mol. Biol. 171, 363–371 (2001)
Solakyildirim, K., Zhang, Z., Linhardt, R.J.: Ultraperformance liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization ion trap mass spectrometry for chondroitinal disaccharide analysis. Anal. Biochem. 397(1), 24–28 (2010)
Yang, B., Bhattacharyya, S., Linhardt, R., Tobacman, J.: Exposure to common food additive carrageenan leads to reduced sulfatase activity and increase in sulfated glycosaminoglycans in human epithelial cells. Biochimie 94(6), 1309–1316 (2012)
Bhattacharyya, S., Solakyildirim, K., Zhang, Z., Linhardt, R.J., Tobacman, J.K.: Chloroquine reduces arylsulphatase B activity and increases chondroitin-4-sulphate: implications for mechanisms of action and resistance. Malar. J. 8(1), 303 (2009)
Rao, G.J., Christe, M.: Inhibition of rabbit liver arylsulfatase B by phosphate esters. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 788, 58–61 (1994)
Bilusic, M., Bataillard, A., Tschannen, M.R., Gao, L., Barreto, N.E., Vincent, M., Wang, T., Jacob, H.J., Sassard, J., Kwitek, A.E.: Mapping the genetic determinants of hypertension, metabolic diseases, and related phenotypes in the Lyon hypertensive rat. Hypertension 44, 695–701 (2004)
Duong, C., Charron, S., Xiao, C., Hamet, P., Menard, A., Roy, J., Deng, A.Y.: Distinct quantitative trait loci for kidney, cardiac, and aortic mass dissociated from and associated with blood pressure in Dahl congenic rats. Mamm. Genome 17(12), 1147–1161 (2006)
Garrett, M.R., Joe, B., Dene, H., Rapp, J.P.: Identification of blood pressure quantitative trait loci that differentiate two hypertensive strains. J. Hypertens. 20(12), 2399–2406 (2002)
Garrett, M.R., Dene, H., Walder, R., Zhang, Q.Y., Cicila, G.T., Assadnia, S., Deng, A.Y., Rapp, J.P.: Genome scan and congenic strains for blood pressure QTL using Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Genome Res. 8(7), 711–723 (1998)
Schork, N.J., Krieger, J.E., Trolliet, M.R., Franchini, K.G., Koike, G., Krieger, E.M., Lander, E.S., Dzau, V.J., Jacob, H.J.: A biometrical genome search in rats reveals the multigenic basis of blood pressure variation. Genome Res. 5, 164–172 (1995)
Ye, Z.Y., Li, D.P., Byun, H.S., Li, L., Pan, H.L.: NKCC1 upregulation disrupts chloride homeostasis in the hypothalamus and increases neuronal activity-sympathetic drive in hypertension. J. Neurosci. 32(25), 8560–8568 (2012)
Trepiccione, F., Zacchia, M., Capasso, G.: The role of the kidney in salt-sensitive hypertension. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 16(1), 68–72 (2012)
Etscheid, M., Beer, N., Fink, E., Seitz, R., Johannes, D.: The hyaluronan-binding serine protease from human plasma cleaves HMW and LMW kininogen and releases bradykinin. Biol. Chem. 383(10), 1633–1643 (2002)
Batlle, D., Redon, J., Gutterman, C., LaPointe, M., Saleh, A., Sharma, A., Rombola, G., Ye, M., Alsheikha, W., Gomez, L., Sobrero, M.: Acid–base status and intracellular pH regulation in lymphocytes from rats with genetic hypertension. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 5(5Suppl 1), S12–S22 (1994)
Cuthbert, A.W.: New horizons in the treatment of cystic fibrosis: Br. J. Pharmacol. 163(1), 173–183 (2011)
Sharma, M., Benharounga, M., Hu, W., Lukacs, G.L.: Conformation and temperature-sensitive stability defects of the ∆F508 cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in post-endoplasmic reticulum compartments. J. Biol. Chem. 276(12), 8942–8950 (2001)
Cosma, M.P., Pepe, S., Annunziata, I., Newbold, R.F., Grompe, M., Parenti, G., Ballabio, A.: The multiple sulfatase deficiency gene encodes an essential and limiting factor for the activity of sulfatases. Cell 113(4), 445–456 (2003)
Roeser, D., Preusser-Kunze, A., Schmidt, B., Gasow, K., Wittmann, J.G., Dierks, T., von Figura, K., Rudolph, M.G.: A general binding mechanism for all human sulfatases by the formylglycine-generating enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103(1), 81–86 (2006)
Bhattacharyya, S., Tobacman, J.K.: Hypoxia reduces arylsulfatase B activity and silencing arylsulfatase B replicates and mediates the effects of hypoxia. PLoS One 7(3), e33250 (2012)
Roeser, D., Schmidt, B., Preusser-Kunze, A., Rudolph, M.G.: Probing the oxygen-binding site of the human formylglycine generating enzyme using halide ions. Acta Crystallog. D Biol. Crystallogr. 63(Pt 5), 621–627 (2007)
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Robert Chanthimabha for his help with determinations of creatinine and electrolytes. Research was supported by VA Merit Awards to R.S. Danziger, M.D. and J.K. Tobacman, M.D. and NIDDK R21HL096031 to Dr. Danziger.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Kumar Kotlo and Sumit Bhattacharyya are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kotlo, K., Bhattacharyya, S., Yang, B. et al. Impact of salt exposure on N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase (arylsulfatase B) activity, glycosaminoglycans, kininogen, and bradykinin. Glycoconj J 30, 667–676 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-013-9468-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-013-9468-8