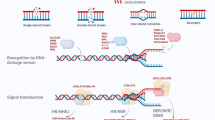
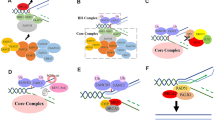
Abstract
DNA damage checkpoint is one of the surveillance systems to maintain genomic integrity. Checkpoint systems sense the DNA damage and execute cell cycle arrest through inhibiting the activity of cell cycle regulators. This pathway is essential for the maintenance of genome stability and prevention of tumor development. Recent studies have showed that the cellular responses towards DNA damage, such as cell cycle arrest, DNA repair, chromatin remodeling, and apoptosis are well coordinated. Here we describe the molecular mechanisms of checkpoint activation in response to DNA damage and the correlation between checkpoint gene mutation and genomic instability.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Mammals:
-
- ATM:
-
Ataxia-telangiectasia-mutated
- ATR:
-
AT and Rad3-related
- NBS:
-
Nimegen breakage syndrome
- ATRIP:
-
ATR-interacting protein
- MRN:
-
Mre11(Meiotic recombination protein)-Rad50(Radiation-sensitive)-Nbs1(Nijmegen breakage syndrome) complex
- Dot1L:
-
Disruptor of telomeric silencing-1 large protein
- Tip60:
-
Tat-interactive protein, 60 kDa
- BRCA1:
-
Breast cancer susceptibility gene 1
- 53BP1:
-
p53-binding protein 1
- MDC1:
-
Mediator of DNA damage checkpoint protein 1
- Gamma-H2AX:
-
Phosphorylated H2AX
- DNA-PK:
-
DNA-dependent protein kinase
- Set9:
-
su(var), e (z), trithorax domain protein 9
- Crb2:
-
cut5 repeat binding protein 2
- Esa1:
-
Essential SAS2-related acetyltransferase
- NuA4:
-
Nucleosomal acetylation of histone H4
- Ino80:
-
Inositol 1-phosphate synthase 80
- Swr1:
-
Swi2/Snf2-related
References
Abraham RT (2001) Cell cycle checkpoint signaling through the ATM and ATR kinases. Genes Dev 15:2177–2196
Ahn J, Urist M, Prives C (2003) Questioning the role of checkpoint kinase 2 in the p53 DNA damage response. J Biol Chem 278:20480–20489
Arata Y, Fujita M, Ohtani K, Kijima S, Kato JY (2000) Cdk2-dependent and -independent pathways in E2F-mediated S phase induction. J Biol Chem 275:6337–6345
Bakkenist CJ, Kastan MB (2003) DNA damage activates ATM through intermolecular autophosphorylation and dimer dissociation. Nature 421:499–506
Banin S, Moyal L, Shieh S, Taya Y, Anderson CW, Chessa L, Smorodinsky NI, Prives C, Reiss Y, Shiloh Y, Ziv Y (1998) Enhanced phosphorylation of p53 by ATM in response to DNA damage. Science 281:1674–1677
Bartek J, Lukas J (2001) Mammalian G1- and S-phase checkpoints in response to DNA damage. Curr Opin Cell Biol 13:738–747
Bartek J, Falck J, Lukas J (2001) CHK2 kinase – a busy messenger. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:877–886
Bell DW, Varley JM, Szydlo TE, Kang DH, Wahrer DC, Shannon KE, Lubratovich M, Verselis SJ, Isselbacher KJ, Fraumeni JF, Birch JM, Li FP, Garber JE, Haber DA (1999) Heterozygous germ line hChk2 mutations in Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Science 286:2528–2531
Bird AW, Yu DY, Pray-Grant MG, Qiu Q, Harmon KE, Megee PC, Grant PA, Smith MM, Christman MF (2002) Acetylation of histone H4 by Esa1 is required for DNA double-strand break repair. Nature 419:411–415
Brown EJ, Baltimore D (2000) ATR disruption leads to chromosomal fragmentation and early embryonic lethality. Genes Dev 14:397–402
Bulavin DV, Higashimoto Y, Popoff IJ, Gaarde WA, Basrur V, Potapova O, Appella E, Fornace AJ Jr (2001) Initiation of a G2/M checkpoint after ultraviolet radiation requires p38 kinase. Nature 411:102–107
Burma S, Chen BP, Murphy M, Kurimasa A, Chen DJ (2001) ATM phosphorylates histone H2AX in response to DNA double-strand breaks. J Biol Chem 276:42462–42467
Canman CE, Lim DS, Cimprich KA, Taya Y, Tamai K, Sakaguchi K, Appella E, Kastan MB, Siliciano JD (1998) Activation of the ATM kinase by ionizing radiation and phosphorylation of p53. Science 281:1677–1679
Chan TA, Hermeking H, Lengauer C, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (1999) 14-3-3Sigma is required to prevent mitotic catastrophe after DNA damage. Nature 401:616–620
Cimprich KA, Shin TB, Keith CT, Schreiber SL (1996) CDNA cloning and gene mapping of a candidate human cell cycle checkpoint protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:2850–2855
Cortez D, Guntuku S, Qin J, Elledge SJ (2001) ATR and ATRIP: partners in checkpoint signaling. Science 294:1713–1716
de Klein A, Muijtjens M, van Os R, Verhoeven Y, Smit B, Carr AM, Lehmann AR, Hoeijmakers JH (2000) Targeted disruption of the cell-cycle checkpoint gene ATR leads to early embryonic lethality in mice. Curr Biol 10:479–482
DiTullio RA Jr, Mochan TA, Venere M, Bartkova J, Sehested M, Bartek J, Halazonetis TD (2002) 53BP1 functions in an ATM-dependent checkpoint pathway that is constitutively activated in human cancer. Nat Cell Biol 4:889–1002
Downs JA, Allard S, Jobin-Robitaille O, Javaheri A, Auger A, Bouchard N, Kron SJ, Jackson SP, Cote J (2004) Binding of chromatin-modifying activities to phosphorylated histone H2A at DNA damage sites. Mol Cell 16:979–990
Espejel S, Martin M, Klatt P, Martin-Caballero J, Flores JM, Blasco MA (2004) Shorter telomeres, accelerated ageing and increased lymphoma in DNA-PKcs-deficient mice. EMBO Rep 5:503–509
Falck J, Mailand N, Syljuasen RG, Bartek J, Lukas J (2001) The ATM-Chk2-Cdc25A checkpoint pathway guards against radioresistant DNA synthesis. Nature 410:842–847
Falck J, Petrini JH, Williams BR, Lukas J, Bartek J (2002) The DNA damage-dependent intra-S phase checkpoint is regulated by parallel pathways. Nat Genet 30:290–294
Falck J, Coates J, Jackson SP (2005) Conserved modes of recruitment of ATM, ATR, and DNA-PKcs to sites of DNA damage. Nature 434:605–611
Gatei M, Young D, Cerosaletti KM, Desai-Mehta A, Spring K, Kozlov S, Lavin MF, Gatti RA, Concannon P, Khanna K (2000) ATM-dependent phosphorylation of nibrin in response to radiation exposure. Nat Genet 25:115–119
Goldberg M, Stucki M, Falck J, D’Amours D, Rahman D, Pappin D, Bartek J, Jackson SP (2003) MDC1 is required for the intra-S-phase DNA damage checkpoint. Nature 421:952–956
Goodarzi AA, Jonnalagadda JC, Douglas P, Young D, Ye R, Moorhead GB, Lees-Miller SP, Khanna KK (2004) Autophosphorylation of ataxia-telangiectasia mutated is regulated by protein phosphatase 2A. EMBO J 23:4451–4461
Guo Z, Kumagai A, Wang SX, Dunphy WG (2000) Requirement for Atr in phosphorylation of Chk1 and cell cycle regulation in response to DNA replication blocks and UV-damaged DNA in Xenopus egg extracts. Genes Dev 14:2745–2756
Hassa PO, Hottiger MO (2005) An epigenetic code for DNA damage repair pathways? Biochem Cell Biol 83:270–285
Hickman ES, Moroni MC, Helin K (2002) The role of p53 and pRB in apoptosis and cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 12:60–66
Hirao A, Kong YY, Matsuoka S, Wakeham A, Ruland J, Yoshida H, Liu D, Elledge SJ, Mak TW (2000) DNA damage-induced activation of p53 by the checkpoint kinase Chk2. Science 287:1824–1827
Hollstein M, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B, Harris CC (1991) p53 mutations in human cancers. Science 253:49–53
Huyen Y, Zgheib O, Ditullio RA Jr, Gorgoulis VG, Zacharatos P, Petty TJ, Sheston EA, Mellert HS, Stavridi ES, Halazonetis TD (2004) Methylated lysine 79 of histone H3 targets 53BP1 to DNA double-strand breaks. Nature 432:406–411
Jack MT, Woo RA, Hirao A, Cheung A, Mak TW, Lee PW (2002) Chk2 is dispensable for p53-mediated G1 arrest but is required for a latent p53-mediated apoptotic response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:9825–9829
Jallepalli PV, Lengauer C, Vogelstein B, Bunz F (2003) The Chk2 tumor suppressor is not required for p53 responses in human cancer cells. J Biol Chem 278:20475–20479
Jazayeri A, Falck J, Lukas C, Bartek J, Smith GC, Lukas J, Jackson SP (2006) ATM-and cell cycle-dependent regulation of ATR in response to DNA double-strand breaks. Nat Cell Biol 8:37–45
Karmakar P, Piotrowski J, Brosh RM Jr, Sommers JA, Miller SP, Cheng WH, Snowden CM, Ramsden DA, Bohr VA (2002) Werner protein is a target of DNA-dependent protein kinase in vivo and in vitro, and its catalytic activities are regulated by phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 277:18291–18302
Khanna KK, Keating KE, Kozlov S, Scott S, Gatei M, Hobson K, Taya Y, Gabrielli B, Chan D, Lees-Miller SP, Lavin MF (1998) ATM associates with and phosphorylates p53: mapping the region of interaction. Nat Genet 20:398–400
Khosravi R, Maya R, Gottlieb T, Oren M, Shiloh Y, Shkedy D (1999) Rapid ATM-dependent phosphorylation of MDM2 precedes p53 accumulation in response to DNA damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:14973–14979
Kim ST, Xu B, Kastan MB (2002) Involvement of the cohesin protein, Smc1, in Atm-dependent and independent responses to DNA damage. Genes Dev 15:560–570
Kobor MS, Venkatasubrahmanyam S, Meneghini MD, Gin JW, Jennings JL, Link AJ, Madhani HD, Rine J (2004) A protein complex containing the conserved Swi2/Snf2-related ATPase Swr1p deposits histone variant H2A.Z into euchromatin. PLoS Biol 2:E131
Kramer A, Mailand N, Lukas C, Syljuasen RG, Wilkinson CJ, Nigg EA, Bartek J, Lukas J (2004) Centrosome-associated Chk1 prevents premature activation of cyclin B-Cdk1 kinase. Nat Cell Biol 6:884–891
Lee SH, Kim CH (2002) DNA-dependent protein kinase complex: a multifunctional protein in DNA repair and damage checkpoint. Mol Cells 13:159–166
Lee JH, Paul TT (2004) Direct activation of the ATM protein kinase by the Mre11/Rad50/Nbs1 complex. Science 304:93–96
Lim DS, Kim ST, Xu B, Maser RS, Lin J, Petrini JH, Kastan MB (2000) ATM phosphorylates p95/nbs1 in an S-phase checkpoint pathway. Nature 404:613–617
Lin WC, Lin FT, Nevins JR (2001) Selective induction of E2F1 in response to DNA damage, mediated by ATM-dependent phosphorylation. Genes Dev 15:1833–1844
Lou Z, Minter-Dykhouse K, Wu X, Chen J (2003) MDC1 is coupled to activated CHK2 in mammalian DNA damage response pathway. Nature 421:957–961
Lusser A, Kadonaga JT (2003) Chromatin remodeling by ATP-dependent molecular machines. Bioessays 25:1192–1200
Mailand N, Falck J, Lukas C, Syljuasen RG, Welcker M, Bartek J, Lukas J (2000) Rapid destruction of human Cdc25A in response to DNA damage. Science 288:1425–1429
Marmorstein R (2001) Protein modules that manipulate histone tails for chromatin regulation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:422–432
Maya R, Balass M, Kim ST, Shkedy D, Leal JF, Shifman O, Moas M, Buschmann T, Ronai Z, Shiloh Y, Kastan MB, Katzir E, Oren M (2001) ATM-dependent phosphorylation of Mdm2 on serine 395: role in p53 activation by DNA damage. Genes Dev 15:1067–1077
McGowan CH (2002) Checking in on Cds1 (Chk2): a checkpoint kinase and tumor suppressor. Bioessays 24:502–511
McKinnon PJ (2004) ATM and ataxia telangiectasia. EMBO Rep 5:772–776
Michael D, Oren M (2002) The p53 and Mdm2 families in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 12:53–59
Mizuguchi G, Shen X, Landry J, Wu WH, Sen S, Wu C (2004) ATP-driven exchange of histone H2AZ variant catalyzed by SWR1 chromatin remodeling complex. Science 303:343–348
Morrison AJ, Highland J, Krogan NJ, Arbel-Eden A, Greenblatt JF, Haber JE, Shen X (2004) INO80 and gamma-H2AX interaction links ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling to DNA damage repair. Cell 119:767–775
O’Driscoll M, Ruiz-Perez VL, Woods CG, Jeggo PA, Goodship JA (2003) A splicing mutation affecting expression of ataxia-telangiectasia and Rad3-related protein (ATR) results in Seckel syndrome. Nat Genet 33:497–501
Paull TT, Rogakou EP, Yamazaki V, Kirchgessner CU, Gellert M, Bonner WM (2000) A critical role for histone H2AX in recruitment of repair factors to nuclear foci after DNA damage. Curr Biol 10:886–895
Sanders SL, Portoso M, Mata J, Bahler J, Allshire RC, Kouzarides T (2004) Methylation of histone H4 lysine 20 controls recruitment of Crb2 to sites of DNA damage. Cell 119:603–614
Shechter D, Costanzo V, Gautier J (2004) ATR and ATM regulate the timing of DNA replication origin firing. Nat Cell Biol 6:648–655
Shen X, Mizuguchi G, Hamiche A, Wu C (2000)A chromatin remodeling complex involved in transcription and DNA processing. Nature 406:541–544
Shiloh Y (1997) Ataxia-telangiectasia and the Nijmegen breakage syndrome: related disorders but genes apart. Annu Rev Genet 31:635–662
Shiloh Y (2003) ATM and related protein kinases: safeguarding genome integrity. Nat Rev Cancer 3:155–168
Shroff R, Arbel-Eden A, Pilch D, Ira G, Bonnre WM, Petrini JH, Haber JE, Lichten M (2004) Distribution and dynamics of chromatin modification induced by a defined DNA double-strand break. Curr Biol 14:1703–1711
Sorensen CS, Syljuasen RG, Falck J, Schroeder T, Ronnstrand L, Khanna KK, Zhou BB, Bartek J, Lukas J (2003) Chk1 regulates the S phase checkpoint by coupling the physiological turnover and ionizing radiation-induced accelerated proteolysis of Cdc25A. Cancer Cell 3:247–258
Stewart GS, Wang B, Bignell CR, Taylor AM, Elledge SJ (2003) MDC1 is a mediator of the mammalian DNA damage checkpoint. Nature 421:961–966
Stiff T, O’Driscoll M, Rief N, Iwabuchi K, Lobrich M, Jeggo PA (2004) ATM and DNA-PK function redundantly to phosphorylate H2AX after exposure to ionizing radiation. Cancer Res 64:2390–2396
Sun Y, Jiang X, Chen S, Fernandes N, Price BD (2005) A role for the Tip60 histone acetyltransferase in the acetylation and activation of ATM. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:13182–13187
Takai H, Naka K, Okada Y, Watanabe M, Harada N, Saito S, Anderson CW, Appella E, Nakanishi M, Suzuki H, Nagashima K, Sawa H, Ikeda K, Motoyama N (2002) Chk2-deficient mice exhibit radioresistance and defective p53-mediated transcription. EMBO J 21:5195–5205
Tibbetts RS, Brumbaugh KM, Williams JM, Sarkaria JN, Cliby WA, Shieh SY, Taya Y, Prives C, Abraham RT (1999) A role for ATR in the DNA damage-induced phosphorylation of p53. Genes Dev 13:152–157
van Attikum H, Gasser SM (2005) The histone code at DNA breaks: a guide to repair? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:757–765
van Attikum H, Fritsch O, Hohn B, Gasser SM (2004) Recruitment of the INO80 complex by H2A phosphorylation links ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling with DNA double-strand break repair. Cell 119:777–788
Wang X, McGowan CH, Zhao M, He L, Downey JS, Fearns C, Wang Y, Huang S, Han J (2000) Involvement of the MKK6-p38gamma cascade in gamma-radiation-induced cell cycle arrest. Mol Cell Biol 20:4543–4552
Ward IM, Chen J (2001) Histone H2AX is phosphorylated in an ATR-dependent manner in response to replicational stress. J Biol Chem 276:47759–47762
Wu X, Ranganathan V, Weisman DS, Heine WF, Ciccone DN, O’Neill TB, Crick KE, Pierce KA, Lane WS, Rathbun G, Livingston DM, Weaver DT (2000) ATM phosphorylation of Nijmegen breakage syndrome protein is required in a DNA damage response. Nature 405:477–482
Yazdi PT, Wang Y, Zhao S, Patel N, Lee EY, Qin J (2002) SMC1 is a downstream effector in the ATM/NBS1 branch of the human S-phase checkpoint. Genes Dev 16:571–582
Zhao H, Piwnica-Worms H (2001) ATR-mediated checkpoint pathways regulate phosphorylation and activation of human Chk1. Mol Cell Biol 21:4129–4139
Zhao S, Weng YC, Yuan SS, Lin YT, Hsu HC, Lin SC, Gerbino E, Song MH, Zdzienicka MZ, Gatti RA, Shay JW, Ziv Y, Shiloh Y, Lee EY (2000) Functional link between ataxia-telangiectasia and Nijmegen breakage syndrome gene products. Nature 405:473–477
Zhao H, Watkins JL, Piwnica-Worms H (2002) Disruption of the checkpoint kinase 1/cell division cycle 25A pathway abrogates ionizing radiation-induced S and G2 checkpoints. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:14795–14800
Zou L, Elledge SJ (2003) Sensing DNA damage through ATRIP recognition of RPA-ssDNA complexes. Science 300:1542–1548
Zou L, Cortez D, Elledge SJ (2002) Regulation of ATR substrate selection by Rad17-dependent loading of Rad9 complexes onto chromatin. Genes Dev 16:198–208
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimada, M., Nakanishi, M. DNA Damage Checkpoints and Cancer. J Mol Hist 37, 253–260 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-006-9039-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-006-9039-4