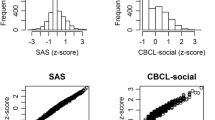
The objective of this study was to refine the Children’s Social Behavior Questionnaire (CSBQ), to reduce its length, and to verify its psychometric properties. The CSBQ is a questionnaire for parents or caregivers of children with PDD. The items describe a broad range of features that are typical of PDD, particularly in its milder forms. Based on conceptual judgment and factor analyses, the number of items was reduced from 96 to 49. Six subscales were constructed to allow a differentiated description of PDD problems. Estimates for internal, test–retest, and inter-rater reliability, and for convergent and divergent validity were good. Different clinical and control groups showed the hypothesized patterns in nature and degree of their problems.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach T. M., (1991). Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist/4–18 and 1991 profileUniversity of Vermont, Department of PsychiatryBurlington, VT
Althaus, M. (2000). Visual attention and autonomic adaptivity to attention-demanding tasks in children with autistic-type behavioural problems. PhD. thesis. University of Groningen
American Psychiatric Association (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4). American Psychiatric AssociationWashington, DC
Bakker S. C., van der Meulen E. M., Buitelaar J. K., Sandkuijl L. A., Pauls D. L., Monsuur A. J., van ‘t Slot R., Minderaa R. B., Gunning W. B., Pearson P. L., Sinke R. J., (2003). A whole genome scan in 164 Dutch sib pairs with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Suggestive evidence for linkage on chromosomes 7p and 15qAmerican Journal of Human genetics 72:1251–1260
Barkley R. A., (1997). Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: A handbook for diagnosis and treatment (2). Guilford PressNew York
Beglinger L. J., Tristram H. Smith., (2001). A review of subtyping in autism and proposed dimensional classification modelJournal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 31:411–422
Berument S. K., Rutter M., Lord C., Pickles A., Bailey A., (1999). Autism screening questionnaire: diagnostic validityBritish Journal of Psychiatry 175:444–451
Bildt A. de., Sytema S., Kraijer D., Ketelaars C., Volkmar F., Minderaa R., (2003). Measuring pervasive developmental disorders in children and adolescents with mental retardation Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 33:595–605
Bishop D. V., Norbury C. F., (2002). Exploring the borderlands of autistic disorder and specific language impairment: A study using standardized diagnostic instrumentsJournal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 43:917–929
Bryson S. E., (1997). Epidemiology of autism: Overview and issues outstanding. In: Cohen D. J., Volkmar F. R., (Eds) Handbook of autism and developmental disordersJohn Wiley & SonsNew York, 41–46
Buitelaar J. K., Van der Gaag R., Klin A., Volkmar F., (1999). Exploring the boundaries of pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified: Analyses of data from the DSM-IV Autistic Disorder Field TrialJournal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 29:33–43
Cattell R. B. (1966). The meaning and strategic use of factor analysis In: Cattell R. B. (eds). Handbook of multivariate experimental psychology Rand McNally, Chicago, pp. 174–243
Chakrabarti S., Fombonne E., (2001). Pervasive developmental disorders in preschool childrenJournal of the American Medical Association 285: 3093–3099
Cohen J., (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences Lawrence Erlbaum, Hillsdale
Constantino J. N., Przybeck T., Friesen D., Todd R.O., (2000). Reciprocal social behavior in children with and without pervasive developmental disorders. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics 21:2–11
Hartman C. A. (2000). Changing concepts of child psychopathology. Dissertation, Amsterdam, The Netherlands: TT Publications.
Hartman C. A., Hox J., Auerbach J., Erol N., Fonseca A. C., Mellenbergh G. J., Nøvik T. S., Oosterlaan J., Roussos A. C., Shalev R. S., Zilber N., Sergeant J. A. (1999). Syndrome dimensions of the Child Behavior Checklist and the Teacher Report Form: A critical empirical evaluationJournal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 40: 1095–1116
Hartman C. A., Hox J., Mellenbergh G. J., Boyle M., Offord D., Racine Y., McNamee J., Gadow K., Sprafkin J., Kelly K. L., Nolan E., Tannock R., Schachar R., Schut H., Postma I., Drost R., Sergeant J. A. (2001). DSM-IV internal construct validity: When a taxonomy meets dataJournal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 42: 817–836
Jensen V. K., Larrieu J. A., Mack K. K. (1997). Differential diagnosis between attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and pervasive developmental disorder-not otherwise specifiedClinical Pediatrics 36: 555–561
Kaiser H. F., (1960). The application of electronic computers to factor analysis Educational and Psychological Measurement 20: 141–151
Kraijer D. W., (1997). Autism and autistic-like conditions in mental retardation Swets & Zeitlinger, Lisse
Kraijer D. W., de Bildt A., (2005). The PDD-MRS: An instrument for identification of autism spectrum disorders in persons with mental retardation. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 35: 499–513
Krug D. A., Arick J. R., Almond P. J., (1980). Autism screening instrument for educational planning ASIEP, Portland, OR
Lord C., Rutter M., LeCouteur A., (1994). Autism diagnostic interview-revised: A revised version of a diagnostic interview for caregivers of individuals with possible Pervasive Developmental DisordersJournal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 24: 659–685
Luteijn E. F., Jackson A. E., Volkmar F. R., Minderaa R. B., (1998). The development of the Children’s Social Behavior Questionnaire: Preliminary dataJournal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 28: 559–565
Luteijn E. F., Luteijn F., Jackson A. E., Volkmar F. R., Minderaa R. B., (2000a). The Children’s Social Behavior Questionnaire for milder variants of PDD problems: Evaluation of the psychometric characteristicsJournal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 30: 317–330
Luteijn E. F., Serra M., Jackson A. E., Steenhuis M. P., Althaus M., Volkmar F. R., Minderaa R. B., (2000b). How unspecified are disorders of children with a Pervasive Developmental Disorder Not otherwise Specified? A study of social problems in children with PDDNOS and or ADHDEuropean Child and Adolescent psychiatry 9: 168–179
Mahoney W. J., Szatmari P., MacLean J. E., Bryson S. E., Bartolucci G., Walter S. D., Jones M. B., Zwaigenbaum L., (1998). Reliability and accuracy of differentiating pervasive developmental disorder subtypesJournal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 37: 278–285
Mayes L. C., Volkmar F. R., Hooks M., Cicchetti D., (1993). Differentiating pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified from autism and language disordersJournal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 23: 79–90
Nunnally J. C., Bernstein I. H., (1994). Psychometric theory 3 McGraw-Hill, New York
Perry R., (1998). Misdiagnosed ADD/ADHD; rediagnosed PDDJournal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 37: 113–114
Prior M., Leekam S., Ong B., Eisenmajer R., Wing L., Gould J., Dowe D., (1998). Are there subgroups within the autistic spectrum? A cluster analysis of a group of children with autistic spectrum disordersJournal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 39: 893–902
Rutter M., Bailey A., Lord C., (2003). Social Communication Questionnaire. Los Angeles: Western Psychological Services
Rutter M., Caspi A., Moffit T. E., (2003). Using sex differences in psychopathology to study causal mechanisms: Unifying issues and research strategies Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 44: 1092–1115
Shaffer D., Fisher P. Lucas C. P., Dulcan M. K., Schwab-Stone M. E., (2000). NIMH Diagnostic Interview Schedule of Children Version-IV (NIMH DISC IV): Description, differences from previous versions, and reliability of some common diagnoses Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 39: 28–38
Smalley S. L., (1997). Genetic influences in childhood-onset psychiatric disorders: Autism and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorderAmerican Journal of Human Genetics 60: 1276–1282
Sparrow, S. S., Balla, D., & Cicchetti, D.V. (1984). Vineland adaptive behavior scales (survey ed.). Circle Pines, MN: American Guidance Service
Steffenburg S., Gillberg C., (1986) Autism and autistic-like conditions in Swedish rural and urban areas: A population studyThe British Journal of Psychiatry 149: 81–87
Stevens J. P. (2002). Applied multivariate statistics for the social sciences 4 Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Mahwah, NJ
Towbin K. E., (1997). Pervasive developmental disorders not otherwise specified In: Cohen D. J., Volkmar F. R., (eds). Handbook of autism and pervasive developmental disorders. John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp. 123–147
Verhulst, F. C., van der Ende, J., & Koot, J. M. (1996). Handleiding voor de CBCL/4–18. Rotterdam: Afdeling kinder- en jeugdpsychiatrie, Sophia kinderziekenhuis/Academisch Ziekenhuis Rotterdam/Erasmus Universiteit Rotterdam
Volkmar F. R., Klin A., Cohen, (1997). Diagnosis and classification of autism and related conditions: Consensus and issues In: Cohen D. J., Volkmar F. R., (eds). Handbook of autism and developmental disorders. John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp. 5–40
Walker D. R., Thompson A., Zwaigenbaum L., Goldberg J., Bryson S. E., Mahoney W. J., Strawbridge C. P., Szatmari P., (2004). Specifying pdd-nos: A comparison of pdd-nos, asperger syndrome, and autismJournal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 43: 172–180
Waterhouse L., Morris R., Allen D., Dunn M., Fein D., Feinstein C., Rapin I., Wing L., (1996). Diagnosis and classification in autismJournal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 26: 59–86
World Health Organisation (1994). The ICD-10 classification of mental and behavioural disorders. Clinical descriptions and guidelines WHO, Geneva
Wing L., (1981). Language, social, and cognitive impairments in autism and severe mental retardationJournal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 11: 31–44
Wing L., Gould J., (1979). Severe impairments of social interaction and associated abnormalities in children: Epidemiology and classificationJournal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 9: 11–29
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hartman, C.A., Luteijn, E., Serra, M. et al. Refinement of the Children’s Social Behavior Questionnaire (CSBQ): An Instrument that Describes the Diverse Problems Seen in Milder Forms of PDD. J Autism Dev Disord 36, 325–342 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-005-0072-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-005-0072-z