Abstract
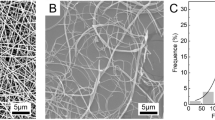
Tissue engineering requires the development of three-dimensional water-stable scaffolds. In this study, silk fibroin/chitosan (SFCS) scaffold was successfully prepared by freeze-drying method. The scaffold is water-stable, only swelling to a limited extent depending on its composition. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectra and X-Ray diffraction curves confirmed the different structure of SFCS scaffolds from both chitosan and silk fibroin. The homogeneous porous structure, together with nano-scale compatibility of the two naturally derived polymers, gives rise to the controllable mechanical properties of SFCS scaffolds. By varying the composition, both the compressive modulus and compressive strength of SFCS scaffolds can be controlled. The porosity of SFCS scaffolds is above 95% when the total concentration of silk fibroin and chitosan is below 6 wt%. The pore sizes of the SFCS scaffolds range from 100 μm to 150 μm, which can be regulated by changing the total concentration. MTT assay showed that SFCS scaffolds can promote the proliferation of HepG2 cells (human hepatoma cell line) significantly. All these results make SFCS scaffold a suitable candidate for tissue engineering.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Chan, F. Berthiaume, B.D. Nath, A.W. Tilles, M. Toner, M.L. Yarmush, Hepatic tissue engineering for adjunct and temporary liver support: Critical technologies. Liver Transpl. 10, 1331–1342 (2004). doi:10.1002/lt.20229
L.E. Freed, G. Vunjaknovakovic, R.J. Biron, D.B. Eagles, D.C. Lesnoy, S.K. Barlow et al., Biodegradable polymer scaffolds for tissue engineering. Bio-Technology 12, 689–693 (1994)
J. Mayer, E. Karamuk, T. Akaike, E. Wintermantel, Matrices for tissue engineering-scaffold structure for a bioartificial liver support system. J. Control. Release 64, 81–90 (2000). doi:10.1016/S0168-3659(99)00136-4
D.W. Hutmacher, Scaffolds in tissue engineering bone and cartilage. Biomaterials 21, 2529–2543 (2000). doi:10.1016/S0142-9612(00)00121-6
M.H. Sheridan, L.D. Shea, M.C. Peters, D.J. Mooney, Bioadsorbable polymer scaffolds for tissue engineering capable of sustained growth factor delivery. J. Control. Release 64, 91–102 (2000). doi:10.1016/S0168-3659(99)00138-8
K.M. Kulig, J.P. Vacanti, Hepatic tissue engineering. Transpl. Immunol. 12, 303–310 (2004). doi:10.1016/j.trim.2003.12.005
E. Torok, J.M. Pollock, P.X. Ma, C. Vogel, M. Dandri, J. Petersen et al., Hepatic tissue engineering on 3-dimensional biodegradable polymers within a pulsatile flow bioreactor. Dig. Surg. 18, 196–203 (2001). doi:10.1159/000050129
J.J. Ge, Y.F. Cui, Y. Yan, W.Y. Jiang, The effect of structure on pervaporation of chitosan membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 165, 75–81 (2000). doi:10.1016/S0376-7388(99)00228-8
D.K. Kim, H.S. Kim, Structure and characteristic of chitosan Bombyx mori silk fibroin blend films. Polym-Korea 29, 408–412 (2005)
X. Chen, W.J. Li, W. Zhong, C.J. Ge, H.F. Wang, T.Y. Yu, Studies on chitosan-fibroin blend membranes. 2. The pH and ion sensitivities of semi-IPN membranes. Chem. J. Chin. U 17, 968–972 (1996)
Q.A. Lv, Q.L. Feng, K. Hu, F.Z. Cui, Three-dimensional fibroin/collagen scaffolds derived from aqueous solution and the use for HepG2 culture. Polymer (Guildf) 46, 12662–12669 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2005.10.137
X.H. Wang, Y.N. Yan, F. Lin, Z. Xiong, R.D. Wu, R.J. Zhang et al., Preparation and characterization of a collagen/chitosan/heparin matrix for an implantable bioartificial liver. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 16, 1063–1080 (2005). doi:10.1163/1568562054798554
A.S. Gobin, V.E. Froude, A.B. Mathur, Structural and mechanical characteristics of silk fibroin and chitosan blend scaffolds for tissue regeneration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 74A, 465–473 (2005). doi:10.1002/jbm.a.30382
G.H. Altman, F. Diaz, C. Jakuba, T. Calabro, R.L. Horan, J.S. Chen et al., Silk-based biomaterials. Biomaterials 24, 401–416 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0142-9612(02)00353-8
Y. Gotoh, N. Minoura, T. Miyashita, Preparation and characterization of conjugates of silk fibroin and chitooligosaccharides. Colloid Polym. Sci. 280, 562–568 (2002). doi:10.1007/s00396-002-0658-3
M. Santin, A. Motta, G. Freddi, M. Cannas, In vitro evaluation of the inflammatory potential of the silk fibroin. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 46, 382–389 (1999). doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4636(19990905)46:3<382::AID-JBM11>3.0.CO;2-R
C.Z. Zhou, F. Confalonieri, M. Jacquet, R. Perasso, Z.G. Li, J. Janin, Silk fibroin: structural implications of a remarkable amino acid sequence. Proteins-Structure Funct. Genet. 44, 119–122 (2001). doi:10.1002/prot.1078
R. Rujiravanit, S. Kruaykitanon, A.M. Jamieson, S. Tokura, Preparation of crosslinked chitosan/silk fibroin blend films for drug delivery system. Macromol. Biosci. 3, 604–611 (2003). doi:10.1002/mabi.200300027
C.H. Du, B.K. Zhu, J.Y. Chen, Y.Y. Xu, Metal ion permeation properties of silk fibroin/chitosan blend membranes. Polym. Int. 55, 377–382 (2006). doi:10.1002/pi.1995
H. Kweon, M.K. Yoo, I.K. Park, T.H. Kim, H.C. Lee, H.S. Lee et al., A novel degradable polycaprolactone networks for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 24, 801–808 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0142-9612(02)00370-8
M.N.V.R. Kumar, A review of chitin and chitosan applications. React. Funct. Polym. 46, 1–27 (2000). doi:10.1016/S1381-5148(00)00038-9
A. Di Martino, M. Sittinger, M.V. Risbud, Chitosan: a versatile biopolymer for orthopaedic tissue-engineering. Biomaterials 26, 5983–5990 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.03.016
A. Subramanian, D. Vu, G.F. Larsen, H.Y. Lin, Preparation and evaluation of the electrospun chitosan/PEO fibers for potential applications in cartilage tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 16, 861–873 (2005). doi:10.1163/1568562054255682
B. Krajewska, Application of chitin- and chitosan-based materials for enzyme immobilizations: a review. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 35, 126–139 (2004). doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2003.12.013
J.K.F. Suh, H.W.T. Matthew, Application of chitosan-based polysaccharide biomaterials in cartilage tissue engineering: a review. Biomaterials 21, 2589–2598 (2000). doi:10.1016/S0142-9612(00)00126-5
S.V. Madihally, H.W.T. Matthew, Porous chitosan scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 20, 1133–1142 (1999). doi:10.1016/S0142-9612(99)00011-3
P.J. VandeVord, H.W.T. Matthew, S.P. DeSilva, L. Mayton, B. Wu, P.H. Wooley, Evaluation of the biocompatibility of a chitosan scaffold in mice. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 59, 585–590 (2002). doi:10.1002/jbm.1270
Q. Lv, S.J. Zhang, K. Hu, Q.L. Feng, C.B. Cao, F.Z. Cui, Cytocompatibility and blood compatibility of multifunctional fibroin/collagen/heparin scaffolds. Biomaterials 28, 2306–2313 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.01.031
S. Woodward, R.J. Thomson, Micropropagation of the silk tassel bush, Garrya elliptica Dougl. Plant Cell Tissue Organ. Cult. 44, 31–35 (1996). doi:10.1007/BF00045910
T. Mosmann, Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 65, 55–63 (1983). doi:10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4
T. Yui, K. Imada, K. Okuyama, Y. Obata, K. Suzuki, K. Ogawa, Molecular and crystal-structure of the anhydrous form of Chitosan. Macromolecules 27, 7601–7605 (1994). doi:10.1021/ma00104a014
A.K. Tetsuo Asakura, R. Tabeta, H. Saito, Conformational characterization of Bombyx mori silk fibroin in the solid state by high-frequency carbon-13 cross polarization-magic angle spinning NMR, x-ray diffraction, and infrared spectroscopy. Macromolecules 18, 1841–1845 (1985)
S. Sampaio, P. Taddei, P. Monti, J. Buchert, G. Freddi, Enzymatic grafting of chitosan onto Bombyx mori silk fibroin: kinetic and IR vibrational studies. J. Biotechnol. 116, 21–33 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2004.10.003
S.J. Park, K.Y. Lee, W.S. Ha, S.Y. Park, Structural changes and their effect on mechanical properties of silk fibroin/chitosan blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 74, 2571–2575 (1999). doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4628(19991209)74:11<2571::AID-APP2>3.0.CO;2-A
T. Nakamura, A. Teramoto, A. Hachimori, K. Abe, Preparation of silk fibroin-chitosan membranes and the effects on macrophage. Sen-I Gakkaishi 55, 369–375 (1999)
H. Kweon, H.C. Ha, I.C. Um, Y.H. Park, Physical properties of silk fibroin/chitosan blend films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 80, 928–934 (2001)
G.D. Kang, K.H. Lee, C.S. Ki, J.H. Nahm, Y.H. Park, Silk fibroin/chitosan conjugate crosslinked by tyrosinase. Macromol. Res. 12, 534–539 (2004)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2005CB623905) and the Foundation of Analysis and Testing in Tsinghua University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
She, Z., Jin, C., Huang, Z. et al. Silk fibroin/chitosan scaffold: preparation, characterization, and culture with HepG2 cell. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 19, 3545–3553 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-008-3526-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-008-3526-y