Abstract
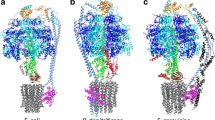
The F1F0-adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthase rotational motor synthesizes most of the ATP required for living from adenosine diphosphate, Pi, and a proton electrochemical gradient across energy-transducing membranes of bacteria, chloroplasts, and mitochondria. However, as a reversible nanomotor, it also hydrolyzes ATP during de-energized conditions in all energy-transducing systems. Thus, different subunits and mechanisms have emerged in nature to control the intrinsic rotation of the enzyme to favor the ATP synthase activity over its opposite and commonly wasteful ATPase turnover. Recent advances in the structural analysis of the bacterial and mitochondrial ATP synthases are summarized to review the distribution and mechanism of the subunits that are part of the central rotor and regulate its gyration. In eubacteria, the ε subunit works as a ratchet to favor the rotation of the central stalk in the ATP synthase direction by extending and contracting two α-helixes of its C-terminal side and also by binding ATP with low affinity in thermophilic bacteria. On the other hand, in bovine heart mitochondria, the so-called inhibitor protein (IF1) interferes with the intrinsic rotational mechanism of the central γ subunit and with the opening and closing of the catalytic β-subunits to inhibit its ATPase activity. Besides its inhibitory role, the IF1 protein also promotes the dimerization of the bovine and rat mitochondrial enzymes, albeit it is not essential for dimerization of the yeast F1F0 mitochondrial complex. High-resolution electron microscopy of the dimeric enzyme in its bovine and yeast forms shows a conical shape that is compatible with the role of the ATP synthase dimer in the formation of tubular the cristae membrane of mitochondria after further oligomerization. Dimerization of the mitochondrial ATP synthase diminishes the rotational drag of the central rotor that would decrease the coupling efficiency between rotation of the central stalk and ATP synthesis taking place at the F1 portion. In addition, F1F0 dimerization and its further oligomerization also increase the stability of the enzyme to natural or experimentally induced destabilizing conditions.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EF1, EF1F0 :
-
Escherichia coli F1 and F1F0 complexes
- EM:
-
electron microscopy
- F1F0 :
-
the whole ATP synthase complex with its catalytic (F1) and proton channel (F0) parts
- F1F0I:
-
the whole ATP synthase containing its physiological inhibitor protein (IF1)
- IF1 :
-
the intrinsic inhibitor protein of the mitochondrial ATP synthase
- MF1, MF1F0 :
-
bovine heart mitochondrial F1 and F1F0 complexes, respectively
- NMR:
-
nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
References
Penefsky, H.S., Pullman, M.E., Datta, A., Racker, E.: Partial resolution of the enzymes catalyzing oxidative phosphorylation. II. Participation of a soluble adenosine triphosphatase in oxidative phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 235, 3330–3336 (1960)
Souid, A.K., Penefsky, H.S.: Mechanism of ATP synthesis by mitochondrial ATP synthase from beef heart. J. Bioenerg. Biomembranes 26, 627–630 (1994). doi:10.1007/BF00831537
García, J.J., Gómez-Puyou, A., Maldonado, E., Tuena de Gómez-Puyou, M.: Acceleration of unisite catalysis of mitochondrial F1-adenosinetriphosphatase by ATP, ADP and pyrophosphate—hydrolysis and release of the previously bound [gamma-32P]ATP. Eur. J. Biochem. 249(2), 622–229 (1997). doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.00622.x
García, J.J., Capaldi, R.A.: Unisite catalysis without rotation of the gamma-epsilon domain in Escherichia coli F1-ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 273(26), 15940–15945 (1998). doi:10.1074/jbc.273.26.15940
García, J.J.: The F0F1-ATP synthase: binding energy, coupling and rotational catalysis. In: Pandalai, S.G. (ed.) Recent Research Developments in Bioenergetics, p. 41. Transworld Research Network, Trivandrum (2000)
Boyer, P.D.: The ATP synthase a splendid molecular machine. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 66, 717–749 (1997). doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.66.1.717
Capaldi, R.A., Schulenberg, B., Murray, J., Aggeler, R.: Cross-linking and electron microscopy studies of the structure and functioning of the Escherichia coli ATP synthase. J. Exp. Biol. 203, 29–33 (2000)
Iino, R., Rondelez, Y., Yoshida, M., Noji, H.: Chemomechanical coupling in single-molecule F-type ATP synthase. J. Bioenerg. Biomembranes 37, 451–454 (2005). doi:10.1007/s10863-005-9489-5
Feniouk, B.A., Yoshida, M.: Regulatory mechanisms of proton-translocating F(O)F (1)-ATP synthase. Results Probl. Cell Differ. 45, 279–308 (2008). doi:10.1007/400_2007_043
Noji, H., Yasuda, R., Yoshida, M., Kinosita, K., Jr.: Direct observation of the rotation of F1-ATPase. Nature 386, (6622), 299–302 (1997). doi:10.1038/386299a0
Kato-Yamada, Y., Noji, H., Yasuda, R., Kinosita, K., Jr., Yoshida, M.: Direct observation of the rotation of epsilon subunit in F1-ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 273(31), 19375–19377 (1998). doi:10.1074/jbc.273.31.19375
Omote, H., Iwamoto-Kihara, A., Ueda, T., Yanagida, Y., Wada, M., Futai, M.: Mechanical rotation of the c subunit oligomer in ATP synthase (F0F1): direct observation. Science 286(5445), 1722–1724 (1999). doi:10.1126/science.286.5445.1722
Tsunoda, S.P., Aggeler, R., Yoshida, M., Capaldi, R.A.: Rotation of the c subunit oligomer in fully functional F1Fo ATP synthase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98(3), 898–902 (2001). doi:10.1073/pnas.031564198
Wilkens, S., Capaldi, R.: Electron microscopic evidence of two stalks linking the F1 and F0 parts of the Escherichia coli ATP synthase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1365(1–2), 93–97 (1998). doi:10.1016/S0005-2728(98)00048-6
Karrasch, S., Walker, J.E.: Novel features in the structure of bovine ATP synthase. J. Mol. Biol. 290(2), 379–384 (1999). doi:10.1006/jmbi.1999.2897
Wilkens, S., Borchardt, D., Weber, J., Senior, A.: Structural characterization of the interaction of the \(\updelta\) and \(\upalpha\) subunits of the Escherichia coli F1F0-ATP synthase by NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry 44(35), 11786–11794 (2005)
Dickson, V.K., Silvester, J.A., Fearnley, I.M., Leslie, A.G., Walker, J.E.: On the structure of the stator of the mitochondrial ATP synthase. EMBO J. 25(12), 2911–2918 (2006). doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601177
Rodgers, A.J., Wilce, M.C.: Structure of the gamma-epsilon complex of ATP synthase. Nat. Struct. Biol. 7(11), 1051–1054 (2000). doi:10.1038/80975
Abrahams, J.P., Leslie, A.G., Lutter, R., Walker, J.E.: Structure at 2.8 A resolution of F1-ATPase from bovine heart mitochondria. Nature 370(6491), 621–628 (1994)
Gibbons, C., Montgomery, M.G., Leslie, A.G.W., Walker, J.E.: The structure of the central stalk in bovine F(1)-ATPase at 2.4 A resolution. Nat. Struct. Biol. 7(11), 1055–1061 (2000). doi:10.1038/80981
Gledhill, J.R., Montgomery, M.G., Leslie, A.G., Walker, J.E.: How the regulatory protein, IF(1), inhibits F(1)-ATPase from bovine mitochondria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 104(40), 15671–15676 (2007). doi:10.1073/pnas.0707326104
Cabezón, E., Montgomery, M.G., Leslie, A.G., Walker, J.E.: The structure of bovine F1-ATPase in complex with its regulatory protein IF1. Nat. Struct. Biol. 10(9), 744–750 (2003). doi:10.1038/nsb966
Stock, D., Leslie, A.G.W., Walker, J.E.: Molecular architecture of the rotary motor in ATP synthase. Science 286(5445), 1700–1705 (1999). doi:10.1126/science.286.5445.1700
Tsunoda, S., Rodgers, A.J.W., Aggeler, R., Wilce, M.C.J., Yoshida, M., Capaldi, R.A.: Large conformational changes of the epsilon subunit in the bacterial F1F0 ATP synthase provide a ratchet action to regulate this rotary motor enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98(12), 6560–6564 (2001). doi:10.1073/pnas.111128098
Hausrath, A.C., Capaldi, R.A., Matthews, B.W.: The conformation of the epsilon- and gamma-subunits within the Escherichia coli F(1) ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 276(50), 47227–47232 (2001). doi:10.1074/jbc.M107536200
Iino, R., Murakami, T., Iizuka, S., Kato-Yamada, Y., Suzuki, T., Yoshida, M.: Real-time monitoring of conformational dynamics of the epsilon subunit in F1-ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 280(48), 40130–40134 (2005). doi:10.1074/jbc.M506160200
Yagi, H., Kajiwara, N., Tanaka, H., Tsukihara, T., Kato-Yamada, Y., Yoshida, M., Akutsu, H.: Structures of the thermophilic F1-ATPase epsilon subunit suggesting ATP-regulated arm motion of its C-terminal domain in F1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 104(27), 11233–11238 (2007). doi:10.1073/pnas.0701045104
Kato-Yamada, Y.: Isolated epsilon subunit of Bacillus subtilis F1-ATPase binds ATP. FEBS Lett. 579(30), 6875–6878 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2005.11.036
Yoshida, M., Kato-Yamada, Y.: Role of the epsilon subunit of thermophilic F1-ATPase as a sensor for ATP. J. Biol. Chem. 282(52), 37618–37623 (2007). doi:10.1074/jbc.M707509200
Zharova, T.V., Vinogradov, A.D.: Proton-translocating ATP-synthase of Paracoccus denitrificans: ATP-hydrolytic activity. Biochemistry (Mosc.) 68(10), 1101–1108 (2003). doi:10.1023/A:1026306611821
Stocker, A., Keis, S., Vonck, J., Cook, G.M., Dimroth, P.: The structural basis for unidirectional rotation of thermoalkaliphilic F1-ATPase. Structure 15(8), 904–914 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.str.2007.06.009
Suzuki, T., Ozaki, Y., Sone, N., Feniouk, B.A., Yoshida, M.: The product of uncI gene in F1F0-ATP synthase operon plays a chaperone-like role to assist c ring assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 104(52), 20776–20781 (2007). doi:10.1073/pnas.0708075105
Brosché, M., Kalbina, I., Arnfelt, M., Benito, G., Karlsson, B.G., Strid, Å.: Occurrence, overexpression and partial purification of the protein (majastridin) corresponding to the URF6 gene of the Rhodobacter blasticus atp operon. Eur. J. Biochem. 255(1), 87–92 (1998). doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2550087.x
Arnold, I., Pfeiffer, K., Neupert, W., Stuart, R.A., Schagger, H.: Yeast mitochondrial F1F0-ATP synthase exists as a dimer: identification of three dimer-specific subunits. EMBO J. 17(24), 7170–7178 (1998). doi:10.1093/emboj/17.24.7170
Paumard, P., Vaillier, J., Coulary, B., Schaeffer, J., Soubannier, V., Mueller, D.M., Brèthes, D., di Rago, J.P., Velours, J.: The ATP synthase is involved in generating mitochondrial cristae morphology. EMBO J. 21(3), 221–230 (2002). doi:10.1093/emboj/21.3.221
Collinson, I.R., Van Raaij, M.J., Runswick, M.J., Fearnley, I.M., Skehel, J.M., Orriss, G.L., Miroux, B., Walker, J.E.: ATP synthase from bovine heart mitochondria. In vitro assembly of a stalk complex in the presence of F1-ATPase and in its absence. J. Mol. Biol. 242(4), 408–421 (1994)
Collinson, I.R., Skehel, J.M., Fearnley, I.M., Runswick, M.J., Walker, J.E.: The F1F0-ATPase complex from bovine heart mitochondria: the molar ratio of the subunits in the stalk region linking the F1 and F0 domains. Biochemistry 35(38), 12640–12646 (1996). doi:10.1021/bi960969t
Xu, T., Zanotti, F., Gaballo, A., Raho, G., Papa, S.: F1 and F0 connections in the bovine mitochondrial ATP synthase: the role of the of alpha subunit N-terminus, oligomycin-sensitivity conferring protein (OCSP) and subunit d. Eur. J. Biochem. 267(14), 4445–4455 (2000). doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01492.x
Pullman, M.E., Monroy, G.C.: A naturally occurring inhibitor of mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. J. Biol. Chem. 238, 3762–3769 (1963)
Dreyfus, G., Gómez-Puyou, A., Tuena de Gómez-Puyou, M.: Electrochemical gradient induced displacement of the natural ATPase inhibitor protein from mitochondrial ATPase as directed by antibodies against the inhibitor protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 100(1), 400–406 (1981). doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(81)80110-6
Sánchez-Bustamante, V.J., Darszon, A., Gómez-Puyou, A.: On the function of the natural ATPase inhibitor protein in intact mitochondria. Eur. J. Biochem. 126(3), 611–616 (1982). doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06824.x
Schwerzmann, K., Pedersen, P.L.: Proton adenosine triphosphatase complex of rat liver mitochondria: effect of energy state on its interaction with the adenosine triphosphatase inhibitory peptide. Biochemistry 20(22), 6305–6311 (1981). doi:10.1021/bi00525a004
Power, J., Cross, R.L., Harris, D.A.: Interaction of F1-ATPase, from ox heart mitochondria with its naturally occurring inhibitor protein. Studies using radio-iodinated inhibitor protein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 724(1), 128–141 (1983). doi:10.1016/0005-2728(83)90034-8
Minauro-Sanmiguel, F., Bravo, C., García, J.J.: Cross-linking of the endogenous inhibitor protein (IF1) with rotor (gamma, epsilon) and stator (alpha) subunits of the mitochondrial ATP synthase. J. Bioenerg. Biomembranes 34(6), 433–443 (2002). doi:10.1023/A:1022514008462
Papa, S., Zanotti, F., Cocco, T., Perrucci, C., Candita, C., Minuto, M.: Identification of functional domains and critical residues in the adenosine triphosphatase inhibitor protein of mitochondrial F0F1 ATP synthase. Eur. J. Biochem. 240(2), 461–467 (1996). doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.0461h.x
Harris, D.A.: Functional regions of the H(+)-ATPase inhibitory protein from ox heart mitochondria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 13208–16 (1997). doi:10.1016/S0005-2728(97)00003-0
van Raaij, M.J., Orriss, G.L., Montgomery, M.G., Runswick, M.J., Fearnley, I.M., Skehel, J.M., Walker, J.E.: The ATPase inhibitor protein from bovine heart mitochondria: the minimal inhibitory sequence. Biochemistry 35(49), 15618–15625 (1996). doi:10.1021/bi960628f
Jackson, P.J., Harris, D.A.: The mitochondrial ATP synthase inhibitor protein binds near the C-terminus of the F1 beta-subunit. FEBS Lett. 229(1), 224–228 (1988). doi:10.1016/0014-5793(88)80832-9
Cabezón, E., Arechaga, I., Jonathan, P., Butler, G., Walker, J.E.: Dimerization of bovine F1-ATPase by binding the inhibitor protein, IF1. J. Biol. Chem. 275(37), 28353–28355 (2000). doi:10.1074/jbc.C000427200
Schägger, H., Pfeiffer, K.: Supercomplexes in the respiratory chains of yeast and mammalian mitochondria. EMBO J. 19(8), 1777–1783 (2000). doi:10.1093/emboj/19.8.1777
Tomasetig, L., Di Pancrazio, F., Harris, D.A., Mavelli, I., Lippe, G.: Dimerization of F0F1ATP synthase from bovine heart is independent from the binding of the inhibitor protein IF1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1556(2–3), 133–141 (2002). doi:10.1016/S0005-2728(02)00344-4
Dienhart, M., Pfeiffer, K., Schagger, H., Stuart, R.A.: Formation of the yeast F1F0-ATP synthase dimeric complex does not require the ATPase inhibitor protein, Inh1. J. Biol. Chem. 277(42), 39289–39295 (2002). doi:10.1074/jbc.M205720200
Cabezón, E., Butler, P.J., Runswick, M.J., Carbajo, R.J., Walker, J.E.: Homologous and heterologous inhibitory effects of ATPase inhibitor proteins on F-ATPases. J. Biol. Chem. 277(44), 41334–41341 (2002). doi:10.1074/jbc.M207169200
Minauro-Sanmiguel, F., Wilkens, S., García, J.J.: Structure of dimeric mitochondrial ATP synthase: novel F0 bridging features and the structural basis of mitochondrial cristae biogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 102(35), 12356–12358 (2005). doi:10.1073/pnas.0503893102
García, J.J., Morales-Ríos, E., Cortés-Hernandez, P., Rodríguez-Zavala, J.S.: The inhibitor protein (IF1) promotes dimerization of the mitochondrial F1F0-ATP synthase. Biochemistry 45(42), 12695–12703 (2006). doi:10.1021/bi060339j
Fornells, L.A., Guimaraes-Motta, H., Nehme, J.S., Martins, O.B., Silva, J.L.: Pressure effects on the interaction between natural inhibitor protein and mitochondrial F1-ATPase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 349(2), 304–312 (1998). doi:10.1006/abbi.1997.0454
Campanella, M., Casswell, E., Chong, S., Farah, Z., Wieckowski, M.R., Abramov, A.Y., Tinker, A., Duchen, M.R.: Regulation of mitochondrial structure and function by the F1F0-ATPase inhibitor protein, IF1. Cell Metab. 8(1), 13–25 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2008.06.001
Fillingame, R.H., Jiang, W., Dmitriev, O.Y., Jones, P.C.: Structural interpretations of F(0) rotary function in the Escherichia coli F(1)F(0) ATP synthase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1458(2–3), 387–403 (2000). doi:10.1016/S0005-2728(00)00089-X
Vik, S.B., Patterson, A.R., Antonio, B.J.: Insertion scanning mutagenesis of subunit a of the F1F0 ATP synthase near His245 and implications on gating of the proton channel. J. Biol. Chem. 273(26), 16229–16234 (1998). doi:10.1074/jbc.273.26.16229
Devenish, R.J., Prescott, M., Roucou, X., Nagley, P.: Insights into ATP synthase assembly and function through the molecular genetic manipulation of subunits of the yeast mitochondrial enzyme complex. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 458(2–3), 428–442 (2000)
Dupuis, A., Lunardi, J., Issartel, J.P., Vignais, P.V.: Interactions between the oligomycin sensitivity conferring protein (OSCP) and beef heart mitochondrial F1-ATPase. 2. Identification of the interacting F1 subunits by cross-linking. Biochemistry 24(3), 734–739 (1985)
Joshi, S., Burrows, R.: ATP synthase complex from bovine heart mitochondria. Subunit arrangement as revealed by nearest neighbor analysis and susceptibility to trypsin. J. Biol. Chem. 265(24), 14518–14525 (1990)
Belogrudov, G.I., Tomich, J.M., Hatefi, Y.: Membrane topography and near-neighbor relationships of the mitochondrial ATP synthase subunits e, f, and g. J. Biol. Chem. 271(34), 20340–20345 (1996). doi:10.1074/jbc.271.34.20340
Velours, J., Paumard, P., Soubannier, V., Spannagel, C., Vaillier, J., Arselin, G., Graves, P.V.: Organisation of the yeast ATP synthase F(0): a study based on cysteine mutants, thiol modification and cross-linking reagents. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1458(2–3), 443–456 (2000). doi:10.1016/S0005-2728(00)00093-1
Zanotti, F., Raho, G., Gaballo, A., Papa, S.: Inhibitory and anchoring domains in the ATPase inhibitor protein IF1 of bovine heart mitochondrial ATP synthase. J. Bioenerg. Biomembranes 36(5), 447–457 (2004). doi:10.1023/B:JOBB.0000047327.68173.9b
Pan, W., Ko, Y.H., Pedersen, P.L.: Delta subunit of rat liver mitochondrial ATP synthase: molecular description and novel insights into the nature of its association with the F1-moiety. Biochemistry 37(19), 6911–6923 (1998). doi:10.1021/bi9800698
Ko, Y.H., Hullihen, J., Hong, S., Pedersen, P.L.: Mitochondrial F(0)F(1) ATP synthase. Subunit regions on the F1 motor shielded by F(0), Functional significance, and evidence for an involvement of the unique F(0) subunit F(6). J. Biol. Chem. 275(42), 32931–32939 (2000). doi:10.1074/jbc.M004453200
Cabezón, E., Runswick, M.J., Leslie, A.G., Walker, J.E.: The structure of bovine IF(1), the regulatory subunit of mitochondrial F-ATPase. EMBO J. 20(24), 6990–6996 (2001). doi:10.1093/emboj/20.24.6990
Dudkina, N.V., Heinemeyer, J., Keegstra, W., Boekema, E.J., Braun, H.P.: Structure of dimeric ATP synthase from mitochondria: an angular association of monomers induces the strong curvature of the inner membrane. FEBS Lett. 579(25), 5769–5772 (2005)
Dudkina, N.V., Sunderhaus, S., Braun, H.P., Boekema, E.J.: Characterization of dimeric ATP synthase and cristae membrane ultrastructure from Saccharomyces and Polytomella mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 580(14), 3427–3432 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2006.04.097
Strauss, M., Hofhaus, G., Schröder, R.R., Kühlbrandt, W.: Dimer ribbons of ATP synthase shape the inner mitochondrial membrane. EMBO J. 27(7), 1154–1160 (2008). doi:10.1038/emboj.2008.35
Vonck, J., Schäfer, E.: Supramolecular organization of protein complexes in the mitochondrial inner membrane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta; Epub ahead of print (2008). doi:1016/j.bbamcr.2008.05.019
Thomas, D., Bron, P., Weimann, T., Dautant, A., Giraud, M.F., Paumard, P., Salin, B., Cavalier, A., Velours, J., Brèthes, D.: Supramolecular organization of the yeast F1Fo-ATP synthase. Biol. Cell; Epub ahead of print (2008). doi:10.1042/BC20080022
Fronzes, R., Weimann, T., Vaillier, J., Velours, J., Brèthes, D.: The peripheral stalk participates in the yeast ATP synthase dimerization independently of e and g subunits. Biochemistry 45(21), 6715–6723 (2006). doi:10.1021/bi0601407
Allen, R.D., Schroeder, C.C., Fok, A.K.: An investigation of mitochondrial inner membranes by rapid-freeze deep-etch techniques. J. Cell Biol. 108(6), 2233–2240 (1989). doi:10.1083/jcb.108.6.2233
Turina, P., Rebecchi, A., D’Alessandro, M., Anefors, S., Melandri, B.A.: Modulation of proton pumping efficiency in bacterial ATP synthases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1757(5–6), 320–325 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2006.04.018
Feniouk, B.A., Mulkidjanian, A.Y., Junge, W.: Proton slip in the ATP synthase of Rhodobacter capsulatus: induction, proton conduction, and nucleotide dependence. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1706(1–2), 184–194 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2004.10.010
Acknowledgements
This work and our work reviewed here were supported by the CONACyT grants No. I32903-N, J34744-N, and V43814-M.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García-Trejo, J.J., Morales-Ríos, E. Regulation of the F1F0-ATP Synthase Rotary Nanomotor in its Monomeric-Bacterial and Dimeric-Mitochondrial Forms. J Biol Phys 34, 197–212 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-008-9114-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-008-9114-z