Abstract
Introduction
In the present study, we examined the effect of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-32γ, the most biologically active isoform, and its related molecules in fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS).
Materials and Methods
FLS were isolated from synovial tissues of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. The secretion and expression of IL-6 and IL-8 were examined by ELISA and real-time PCR, and the activation of signaling molecules was evaluated by Western blot, electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA), real-time PCR, and siRNA transfection.
Results
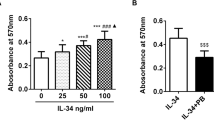
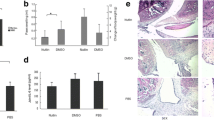
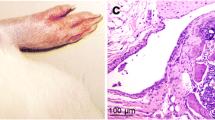
By IL-32γ stimulation in RA FLS, the expressions of IL-6 and IL-8 were increased significantly, and the phosphorylated Erk1/2 and AP-1 were expressed prominently in Western blot and EMSA. In the Erk1/2 inhibited cells, IL-32γ stimulation did not increase the mRNA expression of IL-6 and IL-8.
Conclusion
Our results suggest that IL-32γ stimulation can induce the production of IL-6 and IL-8 from RA FLS via Erk1/2 activation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Edwards JC. The nature and origins of synovium: experimental approaches to the study of synoviocyte differentiation. J Anat. 1994;184:493–501.
Noss EH, Brenner MB. The role and therapeutic implications of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in inflammation and cartilage erosion in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev. 2008;223:252–70.
Kim KW, Cho ML, Kim HR, Ju JH, Park MK, Oh HJ, et al. Up-regulation of stromal cell-derived factor 1 (CXCL12) production in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts through interactions with T lymphocytes: role of interleukin-17 and CD40L-CD40 interaction. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:1076–86.
Nanki T, Nagasaka K, Hayashida K, Saita Y, Miyasaka N. Chemokines regulate IL-6 and IL-8 production by fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 2001;167:5381–5.
Kim SH, Han SY, Azam T, Yoon DY, Dinarello CA. Interleukin-32: a cytokine and inducer of TNFalpha. Immunity. 2005;22:131–42.
Netea MG, Azam T, Ferwerda G, Girardin SE, Walsh M, Park JS, et al. IL-32 synergizes with nucleotide oligomerization domain (NOD) 1 and NOD2 ligands for IL-1beta and IL-6 production through a caspase 1-dependent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:16309–14.
Goda C, Kanaji T, Kanaji S, Tanaka G, Arima K, Ohno S, et al. Involvement of IL-32 in activation-induced cell death in T cells. Int Immunol. 2006;18:233–40.
Choi JD, Bae SY, Hong JW, Azam T, Dinarello CA, Her E, et al. Identification of the most active interleukin-32 isoform. Immunology. 2009;126:535–42.
Joosten LA, Netea MG, Kim SH, Yoon DY, Oppers-Walgreen B, Radstake TR, et al. IL-32, a proinflammatory cytokine in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:3298–303.
Kim YG, Lee CK, Oh JS, Kim SH, Kim KA, Yoo B. Effect of interleukin-32γ on differentiation of osteoclasts from CD14+ monocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2010 (in press).
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31:315–24.
Takayanagi H, Oda H, Yamamoto S, Kawaguchi H, Tanaka S, Nishikawa T, et al. A new mechanism of bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis: synovial fibroblasts induce osteoclastogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;240:279–86.
Johnson MR, Wang K, Smith JB, Heslin MJ, Diasio RB. Quantitation of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase expression by real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. Anal Biochem. 2000;278:175–84.
Schreiber E, Matthias P, Muller MM, Schaffner W. Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with ‘mini-extracts’, prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989;17:6419.
Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–54.
Shoda H, Fujio K, Yamaguchi Y, Okamoto A, Sawada T, Kochi Y, et al. Interactions between IL-32 and tumor necrosis factor alpha contribute to the exacerbation of immune-inflammatory diseases. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8:R166.
Shioya M, Nishida A, Yagi Y, Ogawa A, Tsujikawa T, Kim-Mitsuyama S, et al. Epithelial overexpression of interleukin-32alpha in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 2007;149:480–6.
Nishida A, Andoh A, Shioya M, Kim-Mitsuyama S, Takayanagi A, Fujiyama Y. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling mediates interleukin-32alpha induction in human pancreatic periacinar myofibroblasts. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008;294:G831–8.
Mun SH, Kim JW, Nah SS, Ko NY, Lee JH, Kim JD, et al. Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced interleukin-32 is positively regulated via the Syk/protein kinase Cdelta/JNK pathway in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60:678–85.
Novick D, Rubinstein M, Azam T, Rabinkov A, Dinarello CA, Kim SH. Proteinase 3 is an IL-32 binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:3316–21.
Firestein GS, Manning AM. Signal transduction and transcription factors in rheumatic disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42:609–21.
Neff L, Zeisel M, Sibilia J, Scholler-Guinard M, Klein JP, Wachsmann D. NF-kappaB and the MAP kinases/AP-1 pathways are both involved in interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 expression in fibroblast-like synoviocytes stimulated by protein I/II, a modulin from oral streptococci. Cell Microbiol. 2001;3:703–12.
Mabilleau G, Sabokbar A. Interleukin-32 promotes osteoclast differentiation but not osteoclast activation. PLoS ONE. 2009;4:e4173.
Garcia-Vicuna R, Gomez-Gaviro MV, Dominguez-Luis MJ, Pec MK, Gonzalez-Alvaro I, Alvaro-Gracia JM, et al. CC and CXC chemokine receptors mediate migration, proliferation, and matrix metalloproteinase production by fibroblast-like synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:3866–77.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant from Asan Institute for Life Science (2008-330) and Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF, 2009-0071413).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, YG., Lee, CK., Kim, SH. et al. Interleukin-32γ Enhances the Production of IL-6 and IL-8 in Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes Via Erk1/2 Activation. J Clin Immunol 30, 260–267 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-009-9360-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-009-9360-2