Abstract
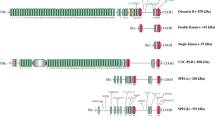
Myospryn (CMYA5, cardiomyopathy-associated 5) is a muscle-specific member of the TRIM superfamily, discovered a few years ago. Properties and functions of the little-studied protein remain largely enigmatic, but identified interactions have suggested that myospryn is involved in two seemingly distinct processes, protein kinase A signalling and vesicular trafficking. Recent findings have implicated myospryn in Duchenne muscular dystrophy and cardiac disease, making it an exciting new player in the field of muscle biology and pathology.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beene DL, Scott JD (2007) A-kinase anchoring proteins take shape. Curr Opin Cell Biol 19:192–198. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2007.02.011
Benson MA, Newey SE, Martin-Rendon E, Hawkes R, Blake DJ (2001) Dysbindin, a novel coiled-coil-containing protein that interacts with the dystrobrevins in muscle and brain. J Biol Chem 276:24232–24241. doi:10.1074/jbc.M010418200
Benson MA, Tinsley CL, Blake DJ (2004) Myospryn is a novel binding partner for dysbindin in muscle. J Biol Chem 279:10450–10458. doi:10.1074/jbc.M312664200
Database HGNC HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC), EMBL Outstation—Hinxton, European Bioinformatics Institute. http://www.genenames.org. Accessed 16 Dec 2008
Dell’Angelica EC (2004) The building BLOC(k)s of lysosomes and related organelles. Curr Opin Cell Biol 16:458–464. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2004.05.001
Durham JT, Brand OM, Arnold M, Reynolds JG, Muthukumar L, Weiler H, Richardson JA, Naya FJ (2006) Myospryn is a direct transcriptional target for MEF2A that encodes a striated muscle, alpha-actinin-interacting, costamere-localized protein. J Biol Chem 281:6841–6849. doi:10.1074/jbc.M510499200
Hackman P, Vihola A, Haravuori H, Marchand S, Sarparanta J, de Seze J, Labeit S, Witt C, Peltonen L, Richard I, Udd B (2002) Tibial muscular dystrophy is a titinopathy caused by mutations in TTN, the gene encoding the giant skeletal-muscle protein titin. Am J Hum Genet 71:492–500. doi:10.1086/342380
Kemp TJ, Sadusky TJ, Simon M, Brown R, Eastwood M, Sassoon DA, Coulton GR (2001) Identification of a novel stretch-responsive skeletal muscle gene (Smpx). Genomics 72:260–271. doi:10.1006/geno.2000.6461 erratum appears in Genomics 2001 Jun 1;74(2):251
Kouloumenta A, Mavroidis M, Capetanaki Y (2007) Proper perinuclear localization of the TRIM-like protein myospryn requires its binding partner desmin. J Biol Chem 282:35211–35221. doi:10.1074/jbc.M704733200
Li W, Zhang Q, Oiso N, Novak EK, Gautam R, O’Brien EP, Tinsley CL, Blake DJ, Spritz RA, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Amato D, Roe BA, Starcevic M, Dell’Angelica EC, Elliott RW, Mishra V, Kingsmore SF, Paylor RE, Swank RT (2003) Hermansky–Pudlak syndrome type 7 (HPS-7) results from mutant dysbindin, a member of the biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles complex 1 (BLOC-1). Nat Genet 35:84–89. doi:10.1038/ng1229
McKoy G, Kemp T, Velineni R, Coulton GR (2002) Identification of a novel stretch-sensitive SPRY domain-coding gene in skeletal muscle [abstract]. In: Abstracts: 31st Annual Meeting of the European Society for Muscle Research, 14–17 September 2002, Lunteren, The Netherlands. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 23:44
Nakagami H, Kikuchi Y, Katsuya T, Morishita R, Akasaka H, Saitoh S, Rakugi H, Kaneda Y, Shimamoto K, Ogihara T (2007) Gene polymorphism of myospryn (cardiomyopathy-associated 5) is associated with left ventricular wall thickness in patients with hypertension. Hypertens Res 30:1239–1246. doi:10.1291/hypres.30.1239
Nazarian R, Starcevic M, Spencer MJ, Dell’Angelica EC (2006) Reinvestigation of the dysbindin subunit of BLOC-1 (biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles complex-1) as a dystrobrevin-binding protein. Biochem J 395:587–598. doi:10.1042/BJ20051965
Reynolds JG, McCalmon SA, Tomczyk T, Naya FJ (2007) Identification and mapping of protein kinase A binding sites in the costameric protein myospryn. Biochem Biophys Acta 1773:891–902. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2007.04.004
Reynolds JG, McCalmon SA, Donaghey JA, Naya FJ (2008) Deregulated protein kinase A signaling and myospryn expression in muscular dystrophy. J Biol Chem 283:8070–8074. doi:10.1074/jbc.C700221200
Setty SR, Tenza D, Truschel ST, Chou E, Sviderskaya EV, Theos AC, Lamoreux ML, Di Pietro SM, Starcevic M, Bennett DC, Dell’Angelica EC, Raposo G, Marks MS (2007) BLOC-1 is required for cargo-specific sorting from vacuolar early endosomes toward lysosome-related organelles. Mol Biol Cell 18:768–780. doi:10.1091/mbc.E06-12-1066
Talbot K, Cho DS, Ong WY, Benson MA, Han LY, Kazi HA, Kamins J, Hahn CG, Blake DJ, Arnold SE (2006) Dysbindin-1 is a synaptic and microtubular protein that binds brain snapin. Hum Mol Genet 15:3041–3054. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddl246
Tkatchenko AV, Pietu G, Cros N, Gannoun-Zaki L, Auffray C, Leger JJ, Dechesne CA (2001) Identification of altered gene expression in skeletal muscles from Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients. Neuromuscul Disord 11:269–277. doi:10.1016/S0960-8966(00)00198-X
Walker MG (2001) Pharmaceutical target identification by gene expression analysis. Mini Rev Med Chem 1:197–205. doi:10.2174/1389557013407034
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarparanta, J. Biology of myospryn: what’s known?. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 29, 177–180 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-008-9165-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-008-9165-6