Abstract
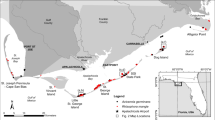
Field dispersal studies are seldom conducted at regional scales even though reliable information on mid-range dispersal distance is essential for models of colonization. The purpose of this study was to examine the potential distance of dispersal of Rhizophora mangle propagules by comparing deposition density with landscape characteristics of mangrove forests. Propagule density was estimated at various distances to mangrove sources (R. mangle) on beaches in southwestern Florida in both high-and low-energy environments, either facing open gulf waters vs. sheltered, respectively. Remote sensing and Geographic Information Systems were used to identify source forests and to determine their landscape characteristics (forest size and distance to deposition area) for the regression analyses. Our results indicated that increasing density of propagules stranded on beaches was related negatively to the distance of the deposition sites from the nearest stands of R. mangle and that deposition was greatly diminished 2 km or more from the source. Measures of fragmentation such as the area of the R. mangle forests were related to propagule deposition but only in low-energy environments. Our results suggest that geographic models involving the colonization of coastal mangrove systems should include dispersal dynamics at mid-range scales, i.e., for our purposes here, beyond the local scale of the forest and up to 5 km distant. Studies of mangrove propagule deposition at various spatial scales are key to understanding regeneration limitations in natural gaps and restoration areas. Therefore, our study of mid-range propagule dispersal has broad application to plant ecology, restoration, and modeling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ESRI. 1999. Arcview GIS 3. 2. Environmental Systems Research Institute Redlands, California, USA
F. Blasco F. Lavenu J. Baraza (1986) Remote sensing data applied to mangroves of Kenya coast Proceedings of the 20th International Symposium on Remote Sensing of the EnvironmentNairobiKenya 3: International Center for Remote Sensing of Environment Maryland, USA 1465–1480
R.A. Buchanan (1989) Bush Revegetation TAFE Sydney, Australia
H.T. Chan N. Husin (1985) ArticleTitlePropagule dispersal, establishment and survival of Rhizophora mucronata The Malaysian Forester 48 324–329
J.S. Clark B. Beckage P. Camill B. Cleveland J. HilleRisLambers J. Lichter J. McLachlan J. Mohan P. Wyckoff (1999) ArticleTitleInterpreting recruitment limitation in forests American Journal of Botany 86 1–16
P.J. Clarke (1993) ArticleTitleDispersal of grey mangrove (Avicennia marina) propagules in southeastern Australia Aquatic Botany 45 195–204 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0304-3770(93)90021-N
P.J. Clarke (2004) ArticleTitleEffects of experimental canopy gaps on mangrove recruitment: lack of habitat partitioning may explain stand dominance Journal of Ecology 92 203–213 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.0022-0477.2004.00861.x
P.J. Clarke W.G. Allaway (1993) ArticleTitleThe regeneration niche of the grey mangrove (Avicennia marina): effects of salinity, light and sediment factors on establishmentgrowth and survival in the field Oecologia 93 548–556 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00328964
P.J. Clarke P.J. Myerscough (1991) ArticleTitleBouyancy of Avicennia marina propagules in south-eastern Australia Australian Journal of Botany 39 77–83
P.J. Clarke R.A. Kerrigan (2000) ArticleTitleDo forest gaps influence the population structure and species composition of mangrove stands in northern Australia Biotropica 32 642–652
P.J. Clarke R.A. Kerrigan C.J. Westphal (2001) ArticleTitleDispersal potential and early growth in 14 tropical mangroves: do early life history traits correlate with patterns of adult distribution? Journal of Ecology 89 648–659 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.0022-0477.2001.00584.x
P.J. Clarke R.A. Kerrigan (2002) ArticleTitleThe effects of seed predators on the recruitment of mangroves Journal of Ecology 90 728–736 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2745.2002.00705.x
Davis J.H. Jr. 1940. The Ecology and Geologic Role of Mangroves in Florida Pap. Tortugas Lab. 32: 304--412. Carnegie Inst., Wash. Publ. No. 517.
W.P De Lange P.J. de Lange (1994) ArticleTitleAn appraisal of factors controlling the latitudinal distribution of mangrove (Avicennia marina var resinifera) in New Zealand. Journal of Coastal Research 10 539–548
D.F. Doak L.S. Mills (1994) ArticleTitleA useful role for theory in conservation Ecology 75 615–626
R.S. Dodd Z.A. Rafii A. Bousquet-Melou (2000) ArticleTitleEvolutionary divergence in the Pan-Atlantic mangrove Avicennia germinans New Phytologist 145 115–125 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1469-8137.2000.00551.x
R.S. Dodd Z.A. Rafii (2002) ArticleTitleEvolutionary genetics of mangroves: continental drift to recent climate change Trees 16 80–86 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00468-001-0142-6
J. Drexler (2001) ArticleTitleMaximum longevities of Rhizophora apiculataR. mucronata propagules Pacific Science 55 17–22
N.C. Duke (1992) Mangrove floristics and biogeography. A.I. Robertson D.M. Alongi (Eds) Tropical Mangrove Ecosystems Washington D.C., USA 63–100
N.C. Duke (2001) ArticleTitleGap creation and regenerative processes driving diversity and structure of mangrove ecosystems Wetlands Ecology and Management 9 257–269 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1011121109886
C.C. Ebbesmeyer Jr. Ingraham W.J. (1992) ArticleTitleShoe spill in the North Pacific Eos 73 361–368
W.K. Fehring (1985) History and development of the Port of Tampa. S.F. Treat J.L. Simon III Lewis R.R. Jr. Whitman R.L. (Eds) Proceedings of the Tampa Bay Area Scientific Information Symposium (May 1982) Burgess Publishing Company Minneapolis, MinnesotaUSA 512–524
J. Gao (1999) ArticleTitleA comparative study on spatial and spectral resolutions of satellite data in mapping mangrove forests International Journal of Remote Sensing 20 2823–2833 Occurrence Handle10.1080/014311699211813
E.P. Green C. Clark P. Mumby A. Edwards A. Ellis (1998) ArticleTitleRemote sensing techniques for mangrove mapping International Journal of Remote Sensing 19 935–956 Occurrence Handle10.1080/014311698215801
W.H. Gu R. Heikkilä I. Hanski (2002) ArticleTitleEstimating the consequences of habitat fragmentation on extinction risk in dynamic landscapes Landscape Ecology 17 699–710 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1022993317717
H.B. Guppy (1906) Observations of a Naturalist in the Pacific New Guinea Between 1896 and 1899: Vol II Plant Dispersal. MacMillan and Co. Ltd. London, UK
E.J. Gustafson R.H. Gardner (1996) ArticleTitleThe effect of landscape heterogeneity on the probability of patch colonization Ecology 77 94–107
J.L. Harper (1977) Population Biology of Plants Academic Press London, UK
S.I. Higgins R. Nathan M.L. Cain (2003) ArticleTitleAre long-distance dispersal events in plants usually caused by nonstandard means of dispersal? Ecology 84 1945–1956
J.R. Jensen H. Lin X. Yang E. Ramsey B. Davis C.W. Thoemke (1991) ArticleTitleThe measurement of mangrove characteristics in southwest Florida using SPOT multispectral data Geocarto International 2 13–21
R.R. Lewis (1977) Impacts of dredging in the Tampa Bay estuary, 1876–1976 E.L. Pruitt (Eds) Proceedings of the Second Annual Conference of the Coastal Society: Time-stressed Environments: Assessment and Future Action Coastal Society Arlington, Virginia, USA 31–55
R.R. Lewis (1986) Marine wetland loss in Tampa Bay and management/restoration recommendations E.D. Estevez J. Miller J. Morris R. Hamman (Eds) Proceedings of the Conference: Managing Cumulative Effects in Florida Wetlands, October 1985, SarasotaFlorida New College Environmental Studies Program Publication No. 37 Omnipress, Madison, Wisconsin, USA 159–174
R.R. Lewis (1990) Creation and restoration of coastal plain wetland in Florida. J.A. Kusler M.E. Kentula (Eds) Wetland Creation and Restoration: The Status of the Science U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Washington, D.C., USA 73–101
B.G. Long T.D. Skewes (1996) ArticleTitleA technique for mapping mangroves with Landsat TM Satellite Data and Geographic Information Systems EstuarineCoastal and Shelf Science 43 373–381 Occurrence Handle10.1006/ecss.1996.0076
R.H. MacArthur E.O. Wilson (1967) The Theory of Island Biogeography Princeton University Press Princeton, NJ, USA
F.J. Manson N.R. Loneragan S.R. Phinn (2003) ArticleTitleSpatial and temporal variation in distribution of mangroves in Moreton Bay, subtropical Australia: a comparison of pattern metrics and change detection analyses based on aerial photographs EstuarineCoastal and Shelf Science 57 657–670
F.J. Manson N.R. Loneragan I.M. McLeod R.A. Kenyon (2001) ArticleTitleAssessing techniques for estimating the extent of mangroves: topographical maps, aerial photographs and Landsat TM imagery Marine and Freshwater Research 52 787–792 Occurrence Handle10.1071/MF00052
K.A. McGuinness (1997) ArticleTitleDispersal, establishment and survival of Ceriops tagal propagules in a north Australian mangrove forest Oecologia 109 80–87 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004420050061
B.A. Middleton (1999) Wetland Restoration, Flood Pulsing and Disturbance Dynamics John Wiley and Sons New York, NY, USA
B.A. Middleton (2000) ArticleTitleHydrochory, seed banks, and regeneration dynamics along the landscape boundaries of a forested wetland Plant Ecology 146 169–184 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1009871404477
B.A. Middleton (2003) ArticleTitleSoil seed banks and the potential restoration of forested wetlands after farming Journal of Applied Ecology 40 1025–1034 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1365-2664.2003.00866.x
T.E. Minchinton (2001) ArticleTitleCanopy and substratum heterogeneity influence recruitment of the mangrove Avicennia marina Journal of Ecology 89 888–902 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.0022-0477.2001.00599.x
D.R Murray (Eds) (1986) Seed Dispersal Academic Press OrlandoFloridaUSA
R. Nathan (2001) Dispersal biogeography. S.A. Levin (Eds) Encyclopedia of Biodiversity Academic Press San Diego, California, USA 127–152
R.F. Noss L.D. Harris (1986) ArticleTitleNodes, networks and MUMs: preserving diversity at all scales Environmental Management 10 299–309
W.E. Odum C.C. McIvor (1990) Mangroves. R.L. Myers J.J. Ewel (Eds) Ecosystems of Florida University of Central Florida Press Orlando, Florida, USA 517–548
J. Pither P.D. Taylor (1998) ArticleTitleAn experimental assessment of landscape connectivity Oikos 83 166–174
D. Rabinowitz (1978) ArticleTitleEarly growth of mangrove seedlings in Panamá, and an hypothesis concerning the relationship of dispersal and zonation Journal of Biogeography 5 113–133
H.N. Ridley (1930) The Dispersal of Plants Throughout the World L. Reeve and Co. Ltd. Ashford, Kent, UK
Inc. SAS Institute (1997) SAS JMP Version 3 2.1. SAS Insitute Inc. Cary, North Carolina, USA
D.A. Saunders R.J. Hobbs C.R. Margules (1991) ArticleTitleBiological consequences of ecosystem fragmentation: a review Conservation Biology 5 18–32
R.R. Sokal F.J. Rohlf (1995) Biometry W.H. Freeman and Company New York, NY, USA
W.P. Sousa S.P. Quek B.J. Mitchell (2003) ArticleTitleRegeneration of Rhizophora mangle in a Caribbean mangrove forest: interacting effects of canopy disturbance and a stem-boring beetle Oecologia 137 436–445 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00442-003-1350-0 Occurrence Handle12920640
T.D. Steinke (1975) Some factors affecting the dispersal and establishment of propagules of Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh G.E. Walsh S.C. Snedaker H.J. Teas (Eds) Proceedings of the International Symposium on the Biology and Management of Mangroves, Vol 2. Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida, USA 404–414
P.D. Taylor L. Fahrig K. Henein G. Merriam (1993) ArticleTitleConnectivity is a vital element of landscape structure Oikos 68 571–573
L. Tischendorf L. Fahrig (2000) ArticleTitleHow should we measure landscape connectivity? Landscape Ecology 15 633–641 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1008177324187
P.B. Tomlinson (1986) The Botany of Mangroves Cambridge University Press London, UK
A.P. Tyagi (2003) ArticleTitleLocation and interseasonal variation in flowering, propagule setting and propagule size in mangrove species of the family Rhizophoraceae Wetlands Ecology and Management 11 167–174 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1024251221118
U.S.D.A. 2003. Integrated taxonomic information system. http://www.itis.usda.gov/index.html. U.S.D.A., Washington, D.C. (retrieved on December 17, 2003).
K.A. With T.O. Crist (1995) ArticleTitleCritical thresholds in species’ responses to landscape structure Ecology 76 2446–2459
E. Wolanski (1992) ArticleTitleHydrodynamics of mangrove swamps of their coastal water Hydrobiologia 247 141–146 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00008214
L.P. Zann (1995) Our SeaOur Future: The State of the Marine Environment Report for Australia Commonwealth Department of Environment Sport and Territories, Canberra, Australian Capital Territories, Australia
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sengupta, R., Middleton, B., Yan, C. et al. Landscape characteristics of Rhizophora mangle forests and propagule deposition in coastal environments of Florida (USA). Landscape Ecol 20, 63–72 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-004-0468-8
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-004-0468-8