Abstract
Background
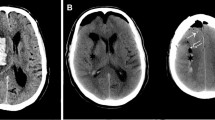
In acute liver failure (ALF), it is unclear whether the systemic inflammatory response associated with intracranial hypertension is related to brain cytokine production.
Aim
To determine the relationship of brain cytokine production with severity of intracranial hypertension in ALF patients.
Method
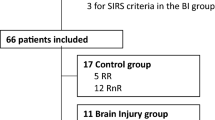
We studied 16 patients with ALF. All patients were mechanically ventilated and cerebral blood flow measured using the Kety–Schmidt technique and intracranial pressure (ICP) measured with a Camino subdural catheter. We sampled blood from an artery and a reverse jugular catheter to measure proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β) and ammonia. Additionally, in 3 patients, serial samples were obtained over a 72 h period.
Results
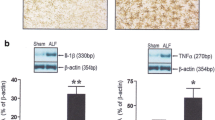
In ALF patients a good correlation between arterial pro-inflammatory cytokines and ICP (r 2 = 0.34, 0.50 and 0.52; for IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α respectively) was observed. There was a positive cerebral cytokine ‘flux’ (production), in ALF patients with uncontrolled ICP. Plasma ammonia between groups was not statistically significant. In the ALF patients studied longitudinally, brain proinflammatory cytokine production was associated with uncontrolled ICP.
Conclusion
Our results provide novel data supporting brain production of cytokines in patients with uncontrolled intracranial hypertension indicating activation of the inflammatory cascade in the brain. Also, the appearance of these cytokines in the jugular bulb catheter may indicate a compromised blood brain barrier at this late stage.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The New Royal Infirmary, Edinburgh
The New Royal Infirmary, Edinburgh
References
Abbruscato TJ, Davis TP (1999) Combination of hypoxia/aglycemia compromises in vitro blood–brain barrier integrity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 289(2):668–675
Ascher NL, Lake JR et al (1993) Liver transplantation for fulminant hepatic failure. Arch Surg 128(6):677–682
Banks WA, Kastin AJ (1997) Relative contributions of peripheral and central sources to levels of IL-1a in the cerebral cortex of mice: assessment with species-specific enzyme immunoassays. J Neuroimmunol 79:22–28
Blei AT (1991) Cerebral edema and intracranial hypertension in acute liver failure: distinct aspects of the same problem. Hepatology 13(2):376–379
Blei AT, Larsen FS (1999) Pathophysiology of cerebral edema in fulminant hepatic failure. J Hepatol 31(4):771–776
Brooks HF, Davies DC (2006) Septic encephalopathy is associated with blood–brain barrier permeability to ions and solutes but not serum proteins. J Anat 208(3):395
Butterworth RF, Giguere JF et al (1987) Ammonia: key factor in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem Pathol 6(1–2):1–12
Campisi M, Torcia E et al (1989) Monitoring of intracranial pressure. Minerva Anestesiol 55(4):205–207
Clemmesen JO, Larsen FS et al (1999) Cerebral herniation in patients with acute liver failure is correlated with arterial ammonia concentration. Hepatology 29(3):648–653
Gips CH, Wibbens-Alberts M (1968) Ammonia determination in blood using the TCA direct method. Clin Chim Acta 22(2):183–186
Grimaldi LM, Martino GV et al (1991) Elevated alpha-tumor necrosis factor levels in spinal fluid from HIV-1-infected patients with central nervous system involvement. Ann Neurol 29(1):21–25
Jakobsen M, Enevoldsen E (1989) Retrograde catheterization of the right internal jugular vein for serial measurements of cerebral venous oxygen content. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 9(5):717–720
Jalan R, Damink SW et al (1999). Moderate hypothermia for uncontrolled intracranial hypertension in acute liver failure. Lancet 354(9185):1164–1168
Jalan R, Newby DE et al (2001) Acute changes in cerebral blood flow and metabolism during portasystemic shunting. Liver Transpl 7(3):274–278
Jalan R, Davies NA et al (2002a) Hypothermia for the management of intracranial hypertension in acute liver failure. Metab Brain Dis 17(4):437–444
Jalan R, Pollok A et al (2002b) Liver derived pro-inflammatory cytokines may be important in producing intracranial hypertension in acute liver failure. J Hepatol 37(4):536–538
Jalan R, Olde Damink SW et al (2003) Moderate hypothermia prevents cerebral hyperemia and increase in intracranial pressure in patients undergoing liver transplantation for acute liver failure. Transplantation 75(12):2034–2039
Jalan R, Olde Damink SW et al. (2004a) Moderate hypothermia in patients with acute liver failure and uncontrolled intracranial hypertension. Gastroenterology 127(5):1338–1346
Jalan R, Olde Damink SW et al (2004b) Pathogenesis of intracranial hypertension in acute liver failure: inflammation, ammonia and cerebral blood flow. J Hepatol 41(4):613–620
Jiang W, Qu H, Desjardins P, Chatauret N, Bélanger M, Butterworth RF (2005) Benificial effects of mild hypothermia on the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in rats with acute liver failure. AASLD, Moscone Centre, San Francisco
Jones E (1990) Fulminant hepatic failure. In: Zakim D, Boyer TD (eds) A textbook of liver diseases. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 460–492
Kety SS, Schmidt CF (1947) The nitrous oxide method for the quantitive determination of cerebral blood flow in man: theory, procedure and normal values. J Clin Invest 27:476–483
Kim KS, Wass CA et al (1992) Modulation of blood–brain barrier permeability by tumor necrosis factor and antibody to tumor necrosis factor in the rat. Lymphokine Cytokine Res 11(6):293–298
Larsen FS, Adel Hansen B et al. (1996) Dissociated cerebral vasoparalysis in acute liver failure. A hypothesis of gradual cerebral hyperaemia. J Hepatol 25(2):145–151
Licinio J, Wong ML (1997) Pathways and mechanisms for cytokine signaling of the central nervous system. J Clin Invest 100(12):2941–2947
Makin AJ, Wendon J et al. (1995) A 7-year experience of severe acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity (1987–1993). Gastroenterology 109(6):1907–1916
Mark KS, Miller DW (1999) Increased permeability of primary cultured brain microvessel endothelial cell monolayers following TNF-a exposure. Life Sci 64(21):1941–1953
O’Grady JG, Alexander GJ et al (1989) Early indicators of prognosis in fulminant hepatic failure. Gastroenterology 97(2):439–445
Philips BJ, Armstrong IR et al (1998) Cerebral blood flow and metabolism in patients with chronic liver disease undergoing orthotopic liver transplantation. Hepatology 27(2):369–376
Quagliarello VJ, Wispelwey B et al (1991) Recombinant human interleukin-1 induces meningitis and blood–brain barrier injury in the rat. Characterization and comparison with tumor necrosis factor. J Clin Invest 87(4):1360–1366
Ringe B, Lubbe N et al (1993) Total hepatectomy and liver transplantation as two-stage procedure. Ann Surg 218(1):3–9
Rolando NE, DeGroote T, Wendon D, Williams JR (1996). IL-6 and coma after paracetamol hepatotoxicity. Proceedings of the IX ISA: Recent advances in hepatic encephalopathy and metabolism, p 51
Rolando N, Wade J et al (2000) The systemic inflammatory response syndrome in acute liver failure. Hepatology 32(4 Pt 1):734–739
Rousseau V, Denizot B et al (1999) Early detection of liposome brain localization in rat experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Exp Brain Res 125(3):255–264
Rozga J, Podesta L et al (1993) Control of cerebral oedema by total hepatectomy and extracorporeal liver support in fulminant hepatic failure. Lancet 342(8876):898–899
Shawcross DL, Davies NA et al (2004) Systemic inflammatory response exacerbates the neuropsychological effects of induced hyperammonemia in cirrhosis. J Hepatol 40(2):247–254
Sternberg EM (1997). Neural-immune interactions in health and disease. J Clin Invest 100(11):2641–2647
Takada Y, Ishiguro S et al (2001) Increased intracranial pressure in a porcine model of fulminant hepatic failure using amatoxin and endotoxin. J Hepatol 34(6):825–831
Traber P, DalCanto M et al (1989) Effect of body temperature on brain edema and encephalopathy in the rat after hepatic devascularization. Gastroenterology 96(3):885–891
Trey C, Davidson CS (1970) The management of fulminant hepatic failure. Prog Liver Dis 3:282–98
Vaquero J, Polson J et al (2003) Infection and the progression of hepatic encephalopathy in acute liver failure. Gastroenterology 125(3):755–764
Wade J, Rolando N et al (2003) Timing and aetiology of bacterial infections in a liver intensive care unit. J Hosp Infect 53(2):144–146
Wright JL, Merchant RE (1992) Histopathological effects of intracerebral injections of human recombinant tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the rat. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 85(1):93–100
Acknowledgement
We are grateful to Dr A LeeFootnote 1 and Prof P C HayesFootnote 2 for their help with this study.
Disclosures
None of the authors of this manuscript have any competing interests to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wright, G., Shawcross, D., Olde Damink, S.W.M. et al. Brain cytokine flux in acute liver failure and its relationship with intracranial hypertension. Metab Brain Dis 22, 375–388 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-007-9071-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-007-9071-4