Abstract
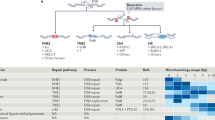
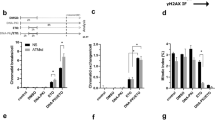
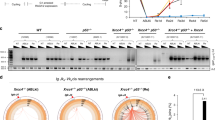
Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) and homologous recombination repair (HRR) are the main mechanisms involved in the processing of DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) in humans. We showed previously that the oncogenic tyrosine kinase BCR/ABL stimulated DSBs repair by HRR. To evaluate the role of BCR/ABL in DSBs repair by NHEJ we examined the ability of leukemic BCR/ABL-expressing cell line BV173 to repair DNA damage induced by two DNA topoisomerase II inhibitors: etoposide and sobuzoxane. DNA lesions induced by sobuzoxane are repaired by a NHEJ pathway which is dependent on the catalytic subunit of protein kinase dependent on DNA (DNA-PKCS; D-NHEJ), whereas damage evoked by etoposide are repaired by two distinct NHEJ pathways, dependent on or independent of DNA-PKCS (backup NHEJ, B-NHEJ). Cells incubated with STI571, a highly specific inhibitor of BCR/ABL, displayed resistance to these agents associated with an accelerated kinetics of DSBs repair, as measured by the neutral comet assay and pulsed field gel electrophoresis. However, in a functional NHEJ assay, cells preincubated with STI571 repaired DSBs induced by a restriction enzyme with a lower efficacy than without the preincubation and addition of wortmannin, a specific inhibitor of DNA-PKCS, did not change efficacy of the NHEJ reaction. We suggest that BCR/ABL switch on B-NHEJ which is more error-prone then D-NHEJ and in such manner contribute to the increase of the genomic instability of leukemic cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Majsterek I, Blasiak J, Mlynarski W, Hoser G, Skorski T (2002) Does the bcr/abl-mediated increase in the efficacy of DNA repair play a role in the drug resistance of cancer cells? Cell Biol Int 26:363–370
Majsterek I, Slupianek A, Blasiak J (2003) TEL-fusion oncogenic tyrosine kinases determine leukemic cells response to idarubicin. Anticancer Drugs 14:625–631
Majsterek I, Slupianek A, Hoser G, Skorski T, Blasiak J (2004) ABL-fusion oncoproteins activate multi-pathway of DNA repair: role in drug resistance? Biochimie 86:53–65
Slupianek A, Hoser G, Majsterek I, Bronisz A, Malecki M, Blasiak J, Fishel R, Skorski T (2002) Fusion tyrosine kinases induce drug resistance by stimulation of homology-dependent recombination repair, prolongation of G(2)/M phase, and protection from apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 22:4189–4201
Ahnesorg P, Smith P, Jackson SP (2006) XLF interacts with the XRCC4-DNA ligase IV complex to promote DNA nonhomologous end-joining. Cell 27:301–313
Chen L, Trujillo K, Sung P, Tomkinson AE (2000) Interactions of the DNA ligase IV-XRCC4 complex with DNA ends and the DNA-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem 275:26196–26205
Hsu HL, Yannone SM, Chen DJ (2002) Defining interactions between DNA-PK and ligase IV/XRCC4. DNA Repair 1:225–235
Ding Q, Reddy YV, Wang W, Woods T, Douglas P, Ramsden DA, Lees-Miller SP, Meek K (2003) Autophosphorylation of the catalytic subunit of the DNA-dependent protein kinase is required for efficient end processing during DNA double-strand break repair. Mol Cell Biol 23:5836–5848
Adachi N, Iiizumi S, So S, Koyama H (2004) Genetic evidence for involvement of two distinct nonhomologous end-joining pathways in repair of topoisomerase II-mediated DNA damage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 318:856–861
Wang H, Perrault AR, Takeda Y, Qin W, Wang H, Iliakis G (2003) Biochemical evidence for Ku-independent backup pathways of NHEJ. Nucleic Acids Res 31:5377–5388
Deutsch E, Dugray A, Karim BA, Marangoni E, Maggiorella L, Vaganay S, Kacher R, Rasy SD, Eschwege F, Vainchenker W, Turhan AG, Bourhis J (2001) BCR-ABL down-regulates the DNA repair protein DNA-PKcs. Blood 97:2084–2090
Gambacorti-Passerini C, Coutre P, Mologni L, Fanelli M, Bertazzoli C, Marchesi E, Di Nicola M, Biondi A, Corneo GM, Belotti D, Pogliani E, Lydon NB (1997) Inhibition of the ABL kinase activity blocks the proliferation of BCR/ABL+ leukemic cells and induces apoptosis. Blood Cells Mol Dis 23:380–394
Gupta M, Abdel-Megeed M, Hoki Y, Kohlhagen G, Paull K, Pommier Y (1995) Eukaryotic DNA topoisomerases mediated DNA cleavage induced by a new inhibitor: NSC 665517. Mol Pharmacol 48:658–665
Adachi N, Iiizumi S, Koyama H (2005) Evidence for a role of vertebrate Rad52 in the repair of topoisomerase II-mediated DNA damage. DNA Cell Biol 24:388–393
Caldecott K, Banks G, Jeggo P (1990) DNA double-strand break repair pathways and cellular tolerance to inhibitors of topoisomerase II. Cancer Res 50:5778–5783
Czechowska A, Poplawski T, Drzewoski J, Blasiak J (2005) Imatinib (STI571) induces DNA damage in BCR/ABL-expressing leukemic cells but not in normal lymphocytes. Chem Biol Interact 152:139–150
Pastwa E, Poplawski T, Czechowska A, Malinowski M, Blasiak J (2005) Non-homologous DNA end joining repair in normal and leukemic cells depends on the substrate ends. Z Naturforsch 60:493–500
Wang H, Rosidi B, Perrault R, Wang M, Zhang L, Windhofer F, Iliakis G (2005) DNA ligase III as a candidate component of backup pathways of nonhomologous end joining. Cancer Res 65:4020–4030
Perrault R, Wang H, Wang M, Rosidi B, Iliakis G (2004) Backup pathways of NHEJ are suppressed by DNA-PK. J Cell Biochem 92:781–794
Adachi N, Ishino T, Ishii Y, Takeda S, Koyama H (2001) DNA ligase IV-deficient cells are more resistant to ionizing radiation in the absence of Ku70: implications for DNA double-strand break repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:12109–12113
Adachi N, Suzuki H, Iiizumi S, Koyama H (2003) Hypersensitivity of nonhomologous DNA end-joining mutants to VP-16 and ICRF-193: implications for the repair of topoisomerase II-mediated DNA damage. J Biol Chem 278:35897–35902
Nowicki MO, Falinski R, Koptyra M, Slupianek A, Stoklosa T, Gloc E, Nieborowska-Skorska M, Blasiak J, Skorski T (2004) BCR/ABL oncogenic kinase promotes unfaithful repair of the reactive oxygen species-dependent DNA double-strand break. Blood 104:3746–3753
Sallmyr A, Tomkinson AE, Rassool FV (2008) Up-regulation of WRN and DNA ligase IIIalpha in chronic myeloid leukemia: consequences for the repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Blood 112:1413–1423
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants 505/363 (JB) and 505/394 (TP) from the University of Lodz.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poplawski, T., Blasiak, J. BCR/ABL downregulates DNA-PKCS-dependent and upregulates backup non-homologous end joining in leukemic cells. Mol Biol Rep 37, 2309–2315 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9730-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9730-0