Abstract
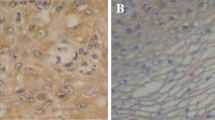
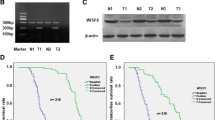
It is well documented that S100A4 is upregulated in a large amount of invasive tumors and plays a pivotal role in tumor invasion and metastasis. However, the precise role and mechanism S100A4 exerts in the invasion and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) have not been fully elucidated to date. Our data demonstrated that S100A4 was overexpressed in human ESCC tissues, especially in ESCC with poor differentiation, deep invasion and lymph node metastasis. Subsequently, the knockdown of S100A4 by RNAi in ESCC cell line (EC-1) could reduce cell invasion, metastasis and proliferation ability in vitro. Most importantly, S100A4 regulated MMP-2 positively and E-cadherin negatively in vivo and in vitro to some extent. Our results suggest that S100A4 is an important factor in the invasion, metastasis and proliferation of ESCC and may control invasion and metastasis at least in part through the regulation of MMP-2 and E-cadherin activity. S100A4 may serve as a biomarker for progression of ESCC and a potential molecular target for biotherapy of ESCC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55:74–108
Li Y, Sun DL, Duan YN, Zhang XJ, Wang N, Zhou RM, Chen ZF, Wang SJ (2010) Association of functional polymorphisms in MMPs genes with gastric cardia adenocarcinoma and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in high incidence region of North China. Mol Biol Rep 37:197–205
Mazzucchelli L (2002) Protein S100A4: too long overlooked by pathologists? Am J Pathol 160:7–13
Liotta LA, Steeg PS, Stetler-Stevenson WG (1991) Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: an imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cell 64:327–336
Garrett SC, Varney KM, Weber DJ, Bresnick AR (2006) S100A4, a mediator of metastasis. J Biol Chem 281:677–680
Ebralidze A, Tulchinsky E, Grigorian M, Afanasyeva A, Senin V, Revazova E, Lukanidin E (1989) Isolation and characterization of a gene specifically expressed in different metastatic cells and whose deduced gene product has a high degree of homology to a Ca2+-binding protein family. Genes Dev 3:1086–1093
Goto K, Endo H, Fujiyoshi T (1988) Cloning of the sequences expressed abundantly in established cell lines: identification of a cDNA clone highly homologous to S-100, a calcium binding protein. J Biochem 103:48–53
Masiakowski P, Shooter EM (1988) Nerve growth factor induces the genes for two proteins related to a family of calcium-binding proteins in PC12 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:1277–1281
Jackson-Grusby LL, Swiergiel J, Linzer DI (1987) A growth-related mRNA in cultured mouse cells encodes a placental calcium binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res 15:6677–6690
Strutz F, Okada H, Lo CW, Danoff T, Carone RL, Tomaszewski JE, Neilson EG (1995) Identification and characterization of a fibroblast marker: FSP1. J Cell Biol 130:393–405
Barraclough R, Savin J, Dube SK, Rudland PS (1987) Molecular cloning and sequence of the gene for p9Ka. A cultured myoepithelial cell protein with strong homology to S-100, a calcium-binding protein. J Mol Biol 198:13–20
Engelkamp D, Schäfer BW, Erne P, Heizmann CW (1992) S100 alpha, CAPL, and CACY: molecular cloning and expression analysis of three calcium-binding proteins from human heart. Biochemistry 31:10258–10264
Watanabe Y, Kobayashi R, Ishikawa T, Hidaka H (1992) Isolation and characterization of a calcium-binding protein derived from mRNA termed p9Ka, pEL-98, 18A2, or 42A by the newly synthesized vasorelaxant W-66 affinity chromatography. Arch Biochem Biophys 292:563–569
Barraclough R (1998) Calcium-binding protein S100A4 in health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1448:190–199
Schäfer BW, Heizmann CW (1996) The S100 family of EF-hand calcium-binding proteins: functions and pathology. Trends Biochem Sci 21:134–140
Donato R (2001) S100: a multigenic family of calcium-modulated proteins of the EF-hand type with intracellular and extracellular functional roles. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 33:637–668
Chen XL, Zhang WG, Chen XY, Sun ZM, Liu SH (2006) Correlations of S100A4 protein expression to invasion and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer. Ai Zheng 25:1134–1137
Matsumoto K, Irie A, Satoh T, Ishii J, Iwabuchi K, Iwamura M, Egawa S, Baba S (2007) Expression of S100A2 and S100A4 predicts for disease progression and patient survival in bladder cancer. Urology 70:602–607
Kim JH, Kim CN, Kim SY, Lee JS, Cho D, Kim JW, Yoon SY (2009) Enhanced S100A4 protein expression is clinicopathologically significant to metastatic potential and p53 dysfunction in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep 22:41–47
Cho YG, Nam SW, Kim TY, Kim YS, Kim CJ, Park JY, Lee JH, Kim HS, Lee JW, Park CH, Song YH, Lee SH, Yoo NJ, Lee JY, Park WS (2003) Overexpression of S100A4 is closely related to the aggressiveness of gastric cancer. APMIS 111:539–545
Yoon CS, Hyung WJ, Lee JH, Chae YS, Won NH, Yeom BW, Choi JS (2008) Expression of S100A4, E-cadherin, alpha- and beta-catenin in gastric adenocarcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology 55:1916–1920
Zou M, Al-Baradie RS, Al-Hindi H, Farid NR, Shi Y (2005) S100A4 (Mts1) gene overexpression is associated with invasion and metastasis of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Br J Cancer 93:1277–1284
Moriyama-Kita M, Endo Y, Yonemura Y, Heizmann CW, Schäfer BW, Sasaki T, Yamamoto E (2004) Correlation of S100A4 expression with invasion and metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 40:496–500
Levett D, Flecknell PA, Rudland PS, Barraclough R, Neal DE, Mellon JK, Davies BR (2002) Transfection of S100A4 produces metastatic variants of an orthotopic model of bladder cancer. Am J Pathol 160:693–700
Davies BR, Davies MP, Gibbs FE, Barraclough R, Rudland PS (1993) Induction of the metastatic phenotype by transfection of a benign rat mammary epithelial cell line with the gene for p9Ka, a rat calcium-binding protein, but not with the oncogene EJ-ras-1. Oncogene 8:999–1008
Grum-Schwensen B, Klingelhofer J, Berg CH, El-Naaman C, Grigorian M, Lukanidin E, Ambartsumian N (2005) Suppression of tumor development and metastasis formation in mice lacking the S100A4(mts1) gene. Cancer Res 65:3772–3780
Mathisen B, Lindstad RI, Hansen J, El-Gewely SA, Maelandsmo GM, Hovig E, Fodstad O, Loennechen T, Winberg JO (2003) S100A4 regulates membrane induced activation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 in osteosarcoma cells. Clin Exp Metastasis 20:701–711
Oida Y, Yamazaki H, Tobita K, Mukai M, Ohtani Y, Miyazaki N, Abe Y, Imaizumi T, Makuuchi H, Ueyama Y, Nakamura M (2006) Increased S100A4 expression combined with decreased E-cadherin expression predicts a poor outcome of patients with pancreatic cancer. Oncol Rep 16:457–463
Wu CY, Wu MS, Chen YJ, Chen CJ, Chen HP, Shun CT, Chen GH, Huang SP, Lin JT (2007) Clinicopathological significance of MMP-2 and TIMP-2 genotypes in gastric cancer. Eur J Cancer 43:799–808
Takeichi M (1995) Morphogenetic roles of classic cadherins. Curr Opin Cell Biol 7:619–627
Li S, Xi Y, Zhang H, Wang Y, Wang X, Liu H, Chen K (2010) A pivotal role for Pim-1 kinase in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma involving cell apoptosis induced by reducing Akt phosphorylation. Oncol Rep 24:997–1004
Ninomiya I, Ohta T, Fushida S, Endo Y, Hashimoto T, Yagi M, Fujimura T, Nishimura G, Tani T, Shimizu K, Yonemura Y, Heizmann CW, Schäfer BW, Sasaki T, Miwa K (2001) Increased expression of S100A4 and its prognostic significance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol 18:715–720
Nakamura N, Takenaga K (1998) Hypomethylation of the metastasis-associated S100A4 gene correlates with gene activation in human colon adenocarcinoma cell lines. Clin Exp Metastasis 16:471–479
Tulchinsky E, Grigorian M, Tkatch T, Georgiev G, Lukanidin E (1995) Transcriptional regulation of the mts1 gene in human lymphoma cells: the role of DNA-methylation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1261:243–248
Bjørnland K, Winberg JO, Odegaard OT, Hovig E, Loennechen T, Aasen AO, Fodstad O, Maelandsmo GM (1999) S100A4 involvement in metastasis: deregulation of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases in osteosarcoma cells transfected with an anti-S100A4 ribozyme. Cancer Res 59:4702–4708
Ford HL, Salim MM, Chakravarty R, Aluiddin V, Zain SB (1995) Expression of Mts1, a metastasis-associated gene, increases motility but not invasion of a nonmetastatic mouse mammary adenocarcinoma cell line. Oncogene 11:2067–2075
Zhang HY, Zheng XZ, Xuan XY, Wang XH, Wang F, Li SS (2010) Expression of S100A4 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its relation to tumor invasion and metastasis. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 30:1541–1544
Sengupta N, MacDonald TT (2007) The role of matrix metalloproteinases in stromal/epithelial interactions in the gut. Physiology (Bethesda) 22:401–409
Saleem M, Kweon MH, Johnson JJ, Adhami VM, Elcheva I, Khan N, Bin Hafeez B, Bhat KM, Sarfaraz S, Reagan-Shaw S, Spiegelman VS, Setaluri V, Mukhtar H (2006) S100A4 accelerates tumorigenesis and invasion of human prostate cancer through the transcriptional regulation of matrix metalloproteinase 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:14825–14830
Schmidt-Hansen B, Ornås D, Grigorian M, Klingelhöfer J, Tulchinsky E, Lukanidin E, Ambartsumian N (2004) Extracellular S100A4(mts1) stimulates invasive growth of mouse endothelial cells and modulates MMP-13 matrix metalloproteinase activity. Oncogene 23:5487–5495
Sherbet GV, Lakshmi MS (1998) S100A4 (MTS1) calcium binding protein in cancer growth, invasion and metastasis. Anticancer Res 18:2415–2421
Andersen H, Mejlvang J, Mahmood S, Gromova I, Gromov P, Lukanidin E, Kriajevska M, Mellon JK, Tulchinsky E (2005) Immediate and delayed effects of E-cadherin inhibition on gene regulation and cell motility in human epidermoid carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol 25:9138–9150
Yonemura Y, Endou Y, Kimura K, Fushida S, Bandou E, Taniguchi K, Kinoshita K, Ninomiya I, Sugiyama K, Heizmann CW, Schafer BW, Sasaki T (2000) Inverse expression of S100A4 and E-cadherin is associated with metastatic potential in gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res 6:4234–4242
Kimura K, Endo Y, Yonemura Y, Heizmann CW, Schafer BW, Watanabe Y, Sasaki T (2000) Clinical significance of S100A4 and E-cadherin-related adhesion molecules in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Oncol 16:1125–1131
Keirsebilck A, Bonné S, Bruyneel E, Vermassen P, Lukanidin E, Mareel M, van Roy F (1998) E-cadherin and metastasin (mts-1/S100A4) expression levels are inversely regulated in two tumor cell families. Cancer Res 58:4587–4591
Conacci-Sorrell M, Zhurinsky J, Ben-Ze’ev A (2002) The cadherin-catenin adhesion system in signaling and cancer. J Clin Invest 109:987–991
Grigorian M, Andresen S, Tulchinsky E, Kriajevska M, Carlberg C, Kruse C, Cohn M, Ambartsumian N, Christensen A, Selivanova G, Lukanidin E (2001) Tumor suppressor p53 protein is a new target for the metastasis-associated Mts1/S100A4 protein: functional consequences of their interaction. J Biol Chem 276:22699–22708
Parker C, Lakshmi MS, Piura B, Sherbet GV (1994) Metastasis-associated mts1 gene expression correlates with increased p53 detection in the B16 murine melanoma. DNA Cell Biol 13:343–351
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Cao (the University of Hong Kong) for providing the EC-1 cell line.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, HY., Zheng, XZ., Wang, XH. et al. S100A4 mediated cell invasion and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via the regulation of MMP-2 and E-cadherin activity. Mol Biol Rep 39, 199–208 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-0726-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-0726-1