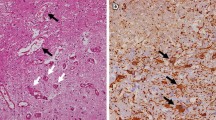
Abstract
Radiation therapy is widely used in the treatment of primary malignant brain tumors and metastatic tumors of the brain with either curative or palliative intent. The limitation of cancer radiation therapy does not derive from the inability to ablate tumor, but rather to do so without excessively damaging the patient. Among the varieties of radiation-induced brain toxicities, it is the late delayed effects that lead to severe and irreversible neurological consequences. Following radiation exposure, late delayed effects within the CNS have been attributable to both parenchymal and vascular damage involving oligodendrocytes, neural progenitors, and endothelial cells. These reflect a dynamic process involving radiation-induced death of target cells and subsequent secondary reactive neuroinflammatory processes that are believed to lead to selective cell loss, tissue damage, and functional deficits. The progressive, late delayed damage to the brain after high-dose radiation is thought to be caused by radiation-induced long-lived free radicals, reactive oxygen species, and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Experimental studies suggest that radiation-induced brain injury can be successfully mitigated and treated with several well established drugs in wide clinical use which exert their effects by blocking pro-inflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen species. This review highlights preclinical and early clinical data that are translatable for future clinical trials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leung W, Hudson MM, Strickland DK et al (2000) Late effects of treatment in survivors of childhood acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol 18:3273–3279
Kim JH, Khil MS, Kolozsvary A et al (1999) Fractionated radiosurgery for 9L gliosarcoma in the rat brain. Radiat Res 45:1035–1040
van der Kogel AJ (1991) Central nervous system injury in small animal models. In: Gutin RH, Leibel SA, Sheline GE (eds) Radiation injury to the nervous system. Raven Press, New York, pp 91–111
Hopewell JW (1998) Radiation injury to the central nervous system. Med Ped Oncol 1(Suppl):1–9
Tofilon PJ, Fike JR (2000) The radioresponse of the central nervous system: a dynamic process. Radiat Res 153:357–370
Hopewell JW, van der Kogel AJ (1999) Pathophysiological mechanisms leading to the development of late radiation-induced damage to the central nervous system. Front Radiat Ther Oncol 33:265–275
Kamiryo T, Kassell NF, Thai QA et al (1996) Histological changes in the normal rat brain after gamma irradiation. Acta Neurochir 138:451–459
French-Constant C, Raff MC (1986) The oligodendrocyte type-2 astrocyte cell lineage is specialized for myelination. Nature 323:335–338
Vrdoljak E, Bill CA, van der Kogel AJ et al (1992) Radiation-induced apoptosis of oligodendrocytes in vitro. Int J Radiat Biol 62:475–480
Calvo W, Hopewell JW, Reinhold HS et al (1988) Time-and dose-related changes in the white matter of the rat brain after single doses of X-rays. Br J Radiol 61:1043–1052
Coderre JA, Morris GM, Micca PL et al (2006) Late effects of radiation on the central nervous system: role of vascular endothelial damage and glial stem cell survival. Radiat Res 166:495–503
Schuller BW, Binns PJ, Riley KJ et al (2006) Selective irradiation of the vascular endothelium has no effect on the survival of murine intestinal crypt stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:3787–3792
Raju U, Gumin GJ, Tofilon PJ (2000) Radiation-induced transcription factor activation in rat cerebral cortex. Int J Radiat Biol 76:1045–1053
Belka C, Budach W, Kortmann RD et al (2001) Radiation-induced CNS toxicity-molecular and cellular mechanisms. Brit J Cancer 85:1233–1239
Tsao MN, Li YQ, Lu G et al (1999) Upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with radiation-induced blood–spinal cord barrier disruption. J Neuropath Exp Neurol 58:1051–1060
Logan A, Berry M (1993) Transforming growth factor β1 and basic fibroblast growth factor in the injured CNS. Trends Pharmacol Sci 14:337–343
Chiang CS, Hong JH, Stadler A et al (1997) Delayed molecular responses to brain irradiation. Int J Radiat Biol 72:45–53
Schnackenberg CS (2002) Oxygen radicals in cardiovascular-renal disease. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2:121–125
Simonian NA, Coyle JT (1996) Oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Ann Rev Pharmacol 36:83–106
Ehara S, Ueda M, Naruko T et al (2001) Elevated levels of oxidized low density lipoprotein show a positive relationship with the severity of acute coronary syndromes. Circulation 103:1955–1960
Robbins MEC, Zhao W (2004) Chronic oxidative stress and radiation-induced late normal tissue injury: a review. Int J Radiat Biol 80:251–259
Lo YY, Wong JM, Cruz TF (1996) Reactive oxygen species mediate cytokine activation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinases. J Biol Chem 271:15703–15707
Watanabe Y, Suzuki O, Haruyama T et al (2003) Interferon-gamma induces reactive oxygen species and endoplasmic reticulum stress at the hepatic apoptosis. J Cell Biochem 89:244–253
Dringen R, Gutterer JM, Hirrlinger J (2000) Glutathione metabolism in brain. Eur J Biochem 267:4912–4916
Smith KJ, Kapoor R, Felts PA (1999) Demyelination: the role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Brain Pathol 9:69–92
Guan J, Stewart J, Ware JJ et al (2006) Effects of dietary supplements on the space radiation-induced reduction in total antioxidant status in CBA mice. Radiat Res 165:373–378
Li Y-Q, Ballinger JR, Nordal RA et al (2001) Hypoxia in radiation-induced blood–spinal cord barrier breakdown. Cancer Res 61:3348–3354
Lyubimova N, Hopewell JW (2004) Experimental evidence to support the hypothesis that damage to vascular endothelium plays the primary role in the development of late radiation-induced CNS injury. Br J Radiol 77:488–492
Nordal RA, Nagy A, Pintilie M et al (2004) Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 target genes in central nervous system radiation injury: a role for vascular endothelial growth factor. Clin Cancer Res 10:3342–3353
Gonzalez J, Kumar AJ, Conrad CA et al (2007) Effect of Bevacizumab on radiation necrosis of the brain. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 67:323–326
Winkler F, Kozin SV, Tong RT et al (2004) Kinetics of vascular normalization by VEGFR2 blockade governs brain tumor response to radiation: role of oxygenation, angiopoietin-1, and matrix metalloproteinases. Cancer Cell 6:553–563
Raber J, Rola R, LeFevour A et al (2004) Radiation-induced cognitive impairments are associated with changes in indicators of hippocampal neurogenesis. Radiat Res 162:39–47
Madsen TM, Kristjansen PE, Bolwig TG et al (2003) Arrested neuronal proliferation and impaired hippocampal function following fractionated brain irradiation in the adult rat. Neurosci 119:635–642
Fike JR, Rola R, Limoli CL (2007) Radiation response of neural precursor cells. Neurosurg Clin N Am 18:115–127
Mizumastu S, Monje M, Morhardt R et al (2003) Extreme sensitivity of adult neurogenesis to low doses of x-irradiation. Cancer Res 63:4021–4027
Saxe MD, Battaglia F, Wang JW et al (2006) Ablation of hippocampal neurogenesis impairs contextual fear conditioning and synaptic plasticity in the dentate gyrus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 14:17501–17506
Lynch MA (2004) Long term potentiation and memory. Physiol Rev 84:87–136
Bruel-Jungerman E, Davis S, Rampon C et al (2006) Long-term potentiation enhances neurogenesis in the adult dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 26:5888–5893
Shi L, Adams MM, Long A et al (2006) Spatial learning and memory deficits after whole-brain irradiation are associated with changes in NMDA receptor subunits in the hippocampus. Radiat Res 166:892–899
Armstrong CL, Gyato K, Awadalla AW et al (2004) A critical review of the clinical effects of therapeutic irradiation damage to the brain: the roots of controversy. Neuropsych Rev 14:65–86
Monje M, Palmer T (2003) Radiation injury and neurogenesis. Curr Opin Neurol 16:129–134
Monje ML, Mizumatsu S, Fike JR et al (2003) Irradiation induces neural precursor-cell dysfunction. Nat Med 8:955–962
Lonn EM, Yusuf S, Jha P et al (1994) Emerging role of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in cardiac and vascular protection. Circulation 90:2056–2069
Crawford DC, Chobanian AV, Brecher P (1994) Angiotensin II induces fibronectin expression associated with cardiac fibrosis in the rat. Cir Res 74:727–739
Nakajima M, Hutchinson HG, Fujinaga M et al (1995) The angiotensin II type 2 (AT2) receptor antagonizes the growth effects of the AT1 receptor: gain-of-function study using gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:10663–10667
Liu YH, Yang XP, Sharov VG et al (1997) Effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonists in rats with heart failure: role of kinins and angiotensin II type 2 receptors. J Clin Invest 99:1926–1935
Griendling KK, Minieri CA, Ollerenshaw JD et al (1994) Angiotensin II stimulates NADPH and NADPH oxidase activity in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res 74:1141–1148
Tojo A, Onozato ML, Kobayashi N et al (2002) Angiotensin II and oxidative stress in Dahl salt-sensitive rat with heart failure. Hypertension 40:834–839
Mehta JL, Hu B, Chen J et al (2003) Pioglitazone inhibits LOX-1 expression in human coronary artery endothelial cells by reducing intracellular superoxide radical generation. Arterioscl Thromb Vasc Biol 23:2203–2208
Robbins MEC, Diz DI (2006) Pathogenic role of the rennin-angiotensin system (RAS) in modulating radiation-induced late effects. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 64:6–12
Ward WF, Solliday HH, Moteni A et al (1983) Radiation injury in a rat lung. Angiotensin converting enzyme activity. Radiat Res 96:294–300
Ward WF, Kim YT, Molteni A et al (1988) Radiation-induced pulmonary endothelial dysfunction in rats: modification by an inhibitor of angiotensin converting enzyme. Int J Rad Oncol Biol Phys 15:135–140
Moulder JE, Fish BL, Cohen EP (1993) Treatment of radiation nephropathy with ACE inhibitors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 27:93–99
Moulder JE, Fish BL, Cohen EP (1998) Radiation nephropathy is treatable with an angiotensinII type 1 (AT1) receptor antagonist. Radiother Oncol 46:307–315
Moulder JE, Fish BL, Regner KR et al (2002) Angiotensin II blockade reduces radiation-induced proliferation in experimental radiation nephropathy. Radiat Res 157:500–505
Kim JH, Brown SL, Kolozsvary A et al (2004) Modification of radiation injury by Ramipril, inhibitor of angiotensin-converting enzyme, on optic neuropathy in the rat. Radiat Res 161:137–142
Ryu S, Kolozsvary A, Jenrow KA et al (2007) Mitigation of radiation-induced optic neuropathy in rats by ACE inhibitor ramipril: importance of rampril dose and treatment. J Neuro-Oncol 82:119–124
Jenrow K, Liu J, Kolozsvary A et al (2007) Ramipril mitigates radiation-induced impairment of dentate gyrus neurogenesis. Abstract 4132. 13th International congress of radiation research
Diomede L, Albani D, Sottocorno M et al (2001) In vivo anti-inflammatory effect of statins is mediated by non-sterol mevalonate products. Arterioscler Throm Vasc Biol 21:1327–1332
Shishehbor MH, Bremen ML et al (2003) Statins promote potent systemic anti-oxidant effects through specific inflammatory pathways. Circulation 108:426–431
Haendeler J, Hoffman J, Zeiher A et al (2004) Antioxidant effects of statins via S-nitrosylation and activation of thioredoxin in endothelial cells. Circulation 110:856–861
Chen J, Zhang ZG, Li Y et al (2003/2005) Statins induce angiogenesis, neurogenesis, and synaptogenesis after stroke. Ann Neurol 53:743–751 Erratum in: Ann Neurol. 58:818
Lu D, Goussev A, Chen J et al (2004) Atorvastatin reduces neurological deficit and increases synaptogenesis, angiogenesis, and neuronal survival in rats subjected to traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 21:21–32
Lu D, Qu C, Goussev A et al (2007) Statins increase neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus, reduce delayed neuronal death in the hippocampal CA3 region, and improve spatial learning in rat after traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 24:1132–1146
Williams JP, Hernady E, Johnston CJ et al (2004) Effect of administration of lovastatin on the development of late pulmonary effects after whole-lung irradiation in a murine model. Radiat Res 161:560–567
Haydont V, Gilliot O, Rivera S et al (2007) Successful mitigation of delayed intestinal radiation injury uring pravastatin is not associated with acute injury improvement or tumor protection. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 68:1471–1482
Wang J, Boerma M, Fu Q et al (2007) Simvastatin ameliorates radiation enteropathy development after localized fractionated irradiation by a protein C-independent mechanism. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 68:1483–1490
Jenrow K, Liu J, Kolozsvary A et al Atorvastatin reduces impairment of dentate gyrus neurogenesis after whole brain radiation in rats (In preparation)
Li D, Chen H, Romeo F et al (2002) Statins modulate oxidized low density lipoprotein-mediated adhesion molecule expression in human coronary artery endothelial cells: role of LOX-1. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 13:601–605
Lefaix JL, Delanian S, Vozenin MC et al (1999) Striking regression of subcutaneous fibrosis induced by high doses of gamma rays using a combination of pentoxyfylline and alpha-tocopherol : an experimental study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 43:839–847
Delanian S, Lefaix JL (2004) The radiation-induced fibroatrophic process: therapeutic perspective via the antioxidant pathway. Radiother Oncol 73:119–131
He YY, Hsu CY, Ezrin AM et al (1993) Polyethylene glycol-conjugated superoxide dismutase in focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Am J Physiol 265:H252-H256
Imaizumi S, Woolworth V, Fishman RA et al (1990) Liposome-entrapped superoxide dismutase reduces cerebral infarction in cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 21:1312–1317
Doctrow SR, Huffman K, Marcus CB et al (1996) Salen manganese complexes: combined superoxide dismutase/catalase mimics with broad pharmacological efficacy. In: Sies H (ed) Antioxidants in “disease mechanisms and therapeutic strategies”, advances in pharmacology. Academic Press, NY, pp. 247–269
Baker K, Marcus CB, Huffman K et al (1998) Synthetic combined superoxide dismutase/catalase mimetics are protective as a delayed treatment in a rat stroke model: a key role for reactive oxygen species in ischemic brain injury. J Pharmacol Exper Therapeut 284:215–221
Liu R, Liu IY, Bi X et al (2003) Reversal of age-related learning deficits and brain oxidative stress in mice with superoxide dismutase/catalase mimetics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:8526–8531
Greenberger JS, Epperly MW, Gretton J et al (2003) Radioprotective gene therapy. Curr Gene Ther 3:183–195
Yan S, Brown SL, Kolozsvary A et al (2007) Mitigation of radiation-induced skin injury by AAV mediated MnSOD gene therapy (Submitted)
Hicklin DJ, Ellis LM (2005) Role of the VEGF pathway in tumor growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol 23:1011–1057
van Bruggen N, Thigbodeaux H, Palmer JT et al (1999) VEGF antagonism reduces edema formation and tissue damage after ischemia/reperfusion injury in the mouse brain. J Clin Invest 104:1613–1620
Dibbens JA, Miller DL, Damert A et al (1999) Hypoxic regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA stability requires the cooperation of multiple RNA elements. Mol Biol Cell 10:907–919
Liu W, Ahmad SA, Reinmuth N et al (2000) Endothelial cell survival and apoptosis in tumor vasculature. Apoptosis 5:323–328
Yang JC, Haworth L, Sherry RM et al (2003) A randomized trial of bevacizumab, an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody, for metastatic renal caner. N Engl J Med 349:2335–2345
Ferrara N, Hillan KJ, Gerber HP et al (2004) Discovery and development of bevacizumab, an anti-VEGF antibody for treating cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:391–400
Holash J, Davis S, Papadopoulos N et al (2002) VEGF-Trap: a VEGF blocker with potent antitumor effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:11393–11398
Acknowledgement
The study was in part supported by NIH NIAID 5U19AI067734-020005 (JHK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.H., Brown, S.L., Jenrow, K.A. et al. Mechanisms of radiation-induced brain toxicity and implications for future clinical trials. J Neurooncol 87, 279–286 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-008-9520-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-008-9520-x