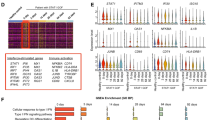
Abstract
Antidepressive drugs offer considerable symptomatic relief in mood disorders and, although commonly discovered by screening with single biological targets, most interact with multiple receptors and signaling pathways. Antidepressants require a treatment regimen of several weeks before clinical efficacy is achieved in patient populations. While the biochemical mechanisms underlying the delayed temporal profile remain unclear, molecular adaptations over time are likely involved. The selective serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor, venlafaxine, offers a dual antidepressive action. Its pharmacological behavior, however, is unknown at the genetic level, and it is difficult to monitor in human brain samples. Because the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis is often severely disrupted in mood disorders, lymphocytes may serve as models of neuropsychiatric conditions. As such, we examined the role of venlafaxine on the gene expression profile of human lymphocytes. DNA microarray was used to measure the expression patterns of multiple genes in human lymphocytes from depressed patients treated with this mood stabilizer. In this self-controlled study, RNAs of control and treated samples were purified, converted into cDNA and labeled with either Cy3 or Cy5, mixed and hybridized to DNA microarrays containing human oligonucleotides corresponding to more than 8,000 genes. Genes that were differentially regulated in response to treatment were selected for follow up on the basis on novelty, gene identity, and level of over-expression/repression, and selected transcripts were profiled by real-time PCR (data have been normalized to β-actin). Using software analysis of the microarray data, a number of transcripts were differentially expressed between control and treated samples, of which only 57 were found to significantly vary with the “P” value of 0.05 or lower as a result of exposure to venlafaxine. Of these, 31 genes were more highly expressed and 26 transcripts were found to be significantly less abundant. Most selected genes were verified with QRT-PCR to alter. As such, independent verification using QRT-PCR demonstrated the reliability of the method. Genes implicated in ionic homeostasis were differentially expressed, as were genes associated with cell survival, neural plasticity, signal transduction, and metabolism. Understanding how gene expression is altered over a clinically relevant time course of administration of venlafaxine may provide insight into the development of antidepressant efficacy as well as the underlying pathology of mood disorders. These changes in lymphocytes are thought to occur in the brain, and a “neuro-immune system” is proposed by this study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Pacher V. Kecskeméti (2004) ArticleTitleCardiovascular side effects of new antidepressants and antipsychotics: new drugs, old concerns? Curr. Pharm. Des 10 2463–2475 Occurrence Handle10.2174/1381612043383872 Occurrence Handle15320756 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXlslWjsbs%3D
E. A. Muth J. T. Haskins J. A. Moyer G. E. Husbands S. T. Nielsen E. B. Sigg (1986) ArticleTitleAntidepressant biochemical profile of the novel bicyclic compound Wy−45,030, an ethyl cyclohexanol derivative Biochem. Pharmacol 35 4493–4497 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0006-2952(86)90769-0 Occurrence Handle3790168 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXpsF2ksw%3D%3D
B. A. Faraj Z. L. Olkowski R. T. Jackson (1994) ArticleTitleExpression of a high-affinity serotonin transporter in human lymphocytes Int. J. Immunopharmacol 16 561–567 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0192-0561(94)90107-4 Occurrence Handle7928004 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXksFSlsbc%3D
R. Ader D. L. Felten N. Cohen (1991) Psychoneuroimmunology EditionNumber2 Academic Press New York
E. M. Smith F. S. Galin R. D. LeBoeuf D. H. Coppenhaver D. V. Harbour J. E. Blalock (1990) ArticleTitleNucleotide and amino acid sequence of lymphocyte-derived corticotropin: endotoxin induction of a truncated peptide Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87 1057–1060 Occurrence Handle1689057 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXhslamtbs%3D
J. E. Blalock (1994) ArticleTitleThe immune system: our sixth sense Immunologist 2 8–15 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXis1ygsrk%3D
J. E. Blalock E. M. Smith (1980) ArticleTitleHuman leukocyte interferon: structural and biological relatedness to adrenocorticotropic hormone and endorphins Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77 5972–5974 Occurrence Handle6160589 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3MXhtlyrtw%3D%3D
D. Felten S. Felten D. Bellinger D. Ackerman K. Madden (1987) ArticleTitleNoradrenergic sympathetic neural interactions with immune system: structure and function Immunol. Rev 100 225–226 Occurrence Handle3326822 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXntlejuw%3D%3D
M. J. Schwarz S. Chiang N. Muller M. Ackenheil (2001) ArticleTitleT-helper-1 and T-helper-2 responses in psychiatric disorders Brain Behav. Immun 15 340–370 Occurrence Handle10.1006/brbi.2001.0647 Occurrence Handle11782103 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xit1ymsw%3D%3D
M. Maes E. Bosmans J. Calabrese R. Smith H. Y. Meltzer (1995) ArticleTitleInterleukin−2 and interleukin−6 in schizophrenia and mania: effects of neuroleptics and mood stabilizers J. Psychiatr. Res 29 141–152 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-3956(94)00049-W Occurrence Handle7666381 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqA1MrotVE%3D
M. Irwin (1999) ArticleTitleImmune correlation of depression Adv. Exp. Med. Biol 46 1–24
T. B. Herbert S. Cohen (1993) ArticleTitleDepression and immunity: A meta-analytic review Psychol. Bull 113 472–486 Occurrence Handle10.1037/0033-2909.113.3.472 Occurrence Handle8316610 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyA3czisVI%3D
J. R. Calabrese M. A. Kling P. W. Gold (1987) ArticleTitleAlterations in immunocompetence during stress, bereavement, and depression: focus on neuroendocrine regulation Am. J. Psychiatr 144 1123–1134 Occurrence Handle3307461 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiiA38zmsFI%3D
S. J. Schleifer S. E. Keller A. T. Meyerson M. J. Raskin K. L. Davis M. Stein (1984) ArticleTitleLymphocyte function in major depressive disorder Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 41 484–486 Occurrence Handle6609689 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiuB3c3it1Q%3D
M. Irwin T. L. Smith J. C. Gillin (1987) ArticleTitleLow natural killer cytotoxicity in major depression Life. Sci 41 2127–2133 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0024-3205(87)90531-5 Occurrence Handle3669915 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BieD3sfgtFw%3D
Á. Zvara G. Szekeres Z. Janka J. Z. Kelemen C. Cimmer M. Sántha L. G. Puskás (2005) ArticleTitleOver-expression of dopamine D(2) receptor and inwardly rectifying potassium channel genes in drug-naive schizophrenic peripheral blood lymphocytes as potential diagnostic markers Dis. Markers 21 61–69 Occurrence Handle15920292 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXksVGjtb4%3D
E. J. Meredith A. Chamba M. J. Holder N. M. Barnes J. Gordon (2005) ArticleTitleClose encounters of the monoamine kind: immune cells betray their nervous disposition Immunology 115 289–295 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1365-2567.2005.02166.x Occurrence Handle15946246 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXlvFCmsrg%3D
L. G. Puskás Á. Zvara L. Hackler SuffixJr. T. Micsik P. Hummelen Particlevan (2002) ArticleTitleProduction of bulk amounts of universal RNA for DNA microarrays Biotechniques 33 898–904 Occurrence Handle12398199
L. G. Puskás L. Hackler SuffixJr. G. Kovács Z. Kupihár Á. Zvara T. Micsik P. Hummelen Particlevan (2002) ArticleTitleRecovery of cyanine-dye nucleotide triphosphates Anal. Biochem 305 279–281 Occurrence Handle12054458
A. Onody Á. Zvara L. Hackler SuffixJr. L. Vígh P Ferdinándy L. G. Puskás (2003) ArticleTitleEffect of classic preconditioning on the gene expression pattern of rat hearts: a DNA microarray study FEBS Lett 536 35–40 Occurrence Handle12586334 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXhtVGhtLg%3D
K. Kitajka L. G. Puskás Á. Zvara L. Hackler SuffixJr. G Barcelo-Coblijn Y. K. Yeo T. Farkas (2002) ArticleTitleThe role of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in brain: modulation of rat brain gene expression by dietary n-3 fatty acids Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99 2619–2624 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.042698699 Occurrence Handle11880617 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xit1CrsLk%3D
W. S. Cleveland (1974) ArticleTitleRobust locally weighted regression and smoothing scatterplots J. Am. Statist. Assoc 74 829–836
Y. H. Yang S. Dudoit P. Luu D. M. Lin V. Peng J. Ngai T. P. Speed (2002) ArticleTitleNormalization for cDNA microarray data: a robust composite method addressing single and multiple slide systematic variation Nucleic Acids Res 30 15 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xnslaru7g%3D
M. W. Pfaffl (2001) ArticleTitleA new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR Nucleic Acids Res 29 45 Occurrence Handle10.1093/nar/29.9.e45
M. S. Rajeevan D. G. Ranamukhaarachchi S. D. Vernon E. R. Unger (2001) ArticleTitleUse of real-time quantitative PCR to validate the results of cDNA array and differential display PCR technologies Methods 25 443–451 Occurrence Handle10.1006/meth.2001.1266 Occurrence Handle11846613 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XhtFelt7c%3D
S. Yoshida B. M. Yashar S. Hiriyanna A. Swaroop (2002) ArticleTitleMicroarray analysis of gene expression in the aging human retina Invest. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci 43 2554–2560
A. Palotás L. G. Puskás K. Kitajka M. Palotás J. Molnár M. Pákáski Z. Janka B. Penke J. Kálmán (2004) ArticleTitleThe effect of citalopram on gene expression profile of Alzheimer lymphocytes Neurochem. Res 29 1563–1570 Occurrence Handle15260135
Fehér, L. Z., Kálmán, J., Puskás, L. G., Gyülvészi, G., Kitajka, K., Penke, B., Palotás, M., Samarova, E. I., Molnár, J., Zvara, Á., Matin, K., Bódi, N., Hugyecz, M., Pákáski, M., Bjelik, A., Juhász, A., Bogáts, G., Janka, Z., and Palotás, A. 2005. Impact of haloperidol and risperidone on gene expression profile in the rat cortex. Neurochem. Int. 47:271–280
R. L. Wilder (1995) ArticleTitleNeuroendocrine–immune system interaction and autoimmunity Annu. Rev. Immunol 13 307–338 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.iy.13.040195.001515 Occurrence Handle7612226 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXltFamtbY%3D
G. A. V. Rook (1994) ArticleTitleHormones, peripherally activated prohormones and regulation of immunity Annu. Rev. Immunol 20 125–163
Palotás, A., Kálmán, J., Puskás, L. G., Kemény, L., Janka, Z., and Penke, B. 2005. Calcium, and the Alzheimer’s Ca2+- tastrophe. in Coleman, R. M. (ed), Trends in Neurochemistry Research, Nova Science Publishers, Inc
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kálmán, J., Palotás, A., Juhász, A. et al. Impact of Venlafaxine on Gene Expression Profile in Lymphocytes of the Elderly with Major Depression – Evolution of Antidepressants and the Role of the “Neuro-Immune” System. Neurochem Res 30, 1429–1438 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-005-8513-9
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-005-8513-9