Purpose
The aims of this study were 1) to demonstrate a new modeling strategy that uses experimental computational models built by the synthetic method and 2) to study the consequences of spatial alignment, or lack thereof, of P-glycoprotein (Pgp) and CYP3A4 on the transport and metabolism of drug-like compounds and the influence of competitive inhibition by metabolites on the transport and metabolism of those compounds.
Methods
The synthetic method of modeling and simulation was used to construct discrete-event, discrete-space models. Within a framework designed for experimentation, object-oriented software components were assembled into devices representing the efflux transport and metabolism mechanisms within cell monolayers in Caco-2 transwell systems.
Results
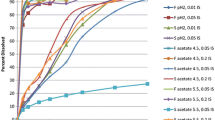
Conditions for transport and metabolism synergism (and lack thereof) were identified. Simulations showed how spatial alignment altered the coordinated influences of Pgp and CYP3A4 on absorption of a series of drug-like compounds. Within those experiments, when the metabolites were also substrates of Pgp, the metabolite levels produced were insufficient to give evidence of a competitive inhibitory effect on either transport or metabolism.
Conclusions
The results provide evidence of the potential value of using this class of models to improve our understanding of how complex cellular processes influence the transport and absorption of compounds, and the consequences of interventions.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A:
-
apical
- ANOVA:
-
analysis of variance
- B:
-
basolateral
- cyp :
-
the in silico counterpart to CYP3A4
- ER:
-
extraction ratio
- ISTS:
-
in silico transwell system
- Pgp:
-
P-glycoprotein
- pgp :
-
the in silico counterpart to P-glycoprotein
References
L. Z. Benet C. L. Cummins C. Y. Wu (2004) ArticleTitleUnmasking the dynamic interplay between efflux transporters and metabolic enzymes Int. J. Pharm. 277 3–9 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.ijpharm.2002.12.002 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXktFOis7k%3D Occurrence Handle15158963
G. M. Grass (1997) ArticleTitleSimulation models to predict oral drug absorption from in vitro data Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 23 199–219 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0169-409X(96)00436-X Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXktlKltQ%3D%3D
Y. Liu C. A. Hunt (2005) ArticleTitleStudies of intestinal drug transport using an in silico epitheliomimetic device Biosystems 82 154–167 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.biosystems.2005.06.008 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXhtFKnurnE Occurrence Handle16135397
V. J. Wacher L. Salphati L. Z. Benet (2001) ArticleTitleActive secretion and enterocytic drug metabolism barriers to drug absorption Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 46 89–102 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0169-409X(00)00126-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXitVOhs7c%3D Occurrence Handle11259835
V. J. Wacher C. Y. Wu L. Z. Benet (1995) ArticleTitleOverlapping substrate specificities and tissue distribution of cytochrome P450 3A and P-glycoprotein: implications for drug delivery and activity in cancer chemotherapy Mol. Carcinog. 13 129–134 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXnt1ams7k%3D Occurrence Handle7619215
E. G. Schuetz W. T. Beck J. D. Schuetz (1996) ArticleTitleModulators and substrates of P-glycoprotein and cytochrome P4503A coordinately up-regulate these proteins in human colon carcinoma cells Mol. Pharmacol. 49 311–318 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XhtFOgtrc%3D Occurrence Handle8632764
K. T. Kivisto M. Niemi M. F. Fromm (2004) ArticleTitleFunctional interaction of intestinal CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 18 621–626 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1472-8206.2004.00291.x Occurrence Handle15548232
E. Wang K. Lew M. Barecki C. N. Casciano R. P. Clement W. W. Johnson (2001) ArticleTitleQuantitative distinctions of active site molecular recognition by P-glycoprotein and cytochrome P450 3A4 Chem. Res. Toxicol. 14 1596–1603 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXosFOqtLg%3D Occurrence Handle11743742
K. Ito H. Kusuhara Y. Sugiyama (1999) ArticleTitleEffects of intestinal CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein on oral drug absorption—theoretical approach Pharm. Res. 16 225–231 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXhvFylsbk%3D Occurrence Handle10100307
P. B. Watkins (1997) ArticleTitleThe barrier function of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein in the small bowel Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 27 161–170 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0169-409X(97)00041-0 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXmtlejt74%3D Occurrence Handle10837556
J. H. Hochman M. Chiba J. Nishime M. Yamazaki J. H. Lin (2000) ArticleTitleInfluence of P-glycoprotein on the transport and metabolism of indinavir in Caco-2 cells expressing cytochrome P-450 3A4 J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 292 310–318 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXhslGkug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10604964
P. Schmiedlin-Ren K. E. Thummel J. M. Fisher M. F. Paine K. S. Lown P. B. Watkins (1997) ArticleTitleExpression of enzymatically active CYP3A4 by Caco-2 cells grown on extracellular matrix-coated permeable supports in the presence of 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 Mol. Pharmacol. 51 741–754 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXjt1ehtr0%3D Occurrence Handle9145912
C. L. Crespi B. W. Penman M. Hu (1996) ArticleTitleDevelopment of Caco-2 cells expressing high levels of cDNA-derived cytochrome P4503A4 Pharm. Res. 13 1635–1641 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1016428304366 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XnsVKrtLc%3D Occurrence Handle8956327
G. E. P. Ropella, C. A. Hunt, and S. Sheikh-Bahaei. Methodological considerations of heuristic modeling of biological systems, The 9th World Multi-Conference on Systemics, Cybernetics and Informatics, Orlando, FL, 2005.
G. E. P. Ropella, C. A. Hunt, and D. A. Nag. Using heuristic models to bridge the gap between analytic and experimental models in biology, SpringSim’05, San Diego, CA, 2005.
N. Gilbert S. Bankes (2002) ArticleTitlePlatforms and methods for agent-based modeling Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99 IssueIDSuppl. 3 7197–7198 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XjvVygs7Y%3D Occurrence Handle12011398
A. Walter J. Gutknecht (1986) ArticleTitlePermeability of small nonelectrolytes through lipid bilayer membranes J. Membr. Biol. 90 207–217 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XksFKnt7c%3D Occurrence Handle3735402
T. X. Xiang B. D. Anderson (1993) ArticleTitleDiffusion of ionizable solutes across planar lipid bilayer membranes: boundary-layer pH gradients and the effect of buffers Pharm. Res. 10 1654–1661 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1018989107129 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXit12qsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle8290481
C. L. Cummins L. M. Mangravite L. Z. Benet (2001) ArticleTitleCharacterizing the expression of CYP3A4 and efflux transporters (P-gp, MRP1, and MRP2) in CYP3A4-transfected Caco-2 cells after induction with sodium butyrate and the phorbol ester 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate Pharm. Res. 18 1102–1109 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1010914624111 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXnt1ektrY%3D Occurrence Handle11587480
L. Steels R. Brooks (1995) The Artificial Life Route to Artificial Intelligence: Building Embodied, Situated Agents Erlbaum Hillsdale, NJ
M. E. Andersen (2003) ArticleTitleToxicokinetic modeling and its applications in chemical risk assessment Toxicol. Lett. 138 9–27 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXmsVGgtw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle12559690
D. Noble (2002) ArticleTitleThe rise of computational biology Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3 459–463 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nrm810 Occurrence Handle12042768
H. Kitano (2002) ArticleTitleComputational systems biology Nature 420 206–210 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nature01254 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xos1Gnsbo%3D Occurrence Handle12432404
L. Z. Benet C. L. Cummins (2001) ArticleTitleThe drug efflux–metabolism alliance: biochemical aspects Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 50 IssueIDSuppl 1 S3–S11 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXntVWkurk%3D Occurrence Handle11576692
S. J. Mouly M. F. Paine P. B. Watkins (2004) ArticleTitleContributions of CYP3A4, P-glycoprotein, and serum protein binding to the intestinal first-pass extraction of saquinavir J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 308 941–948 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXhvVWntLY%3D Occurrence Handle14718607
J. H. Hochman M. Chiba M. Yamazaki C. Tang J. H. Lin (2001) ArticleTitleP-glycoprotein-mediated efflux of indinavir metabolites in Caco-2 cells expressing cytochrome P450 3A4 J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 298 323–330 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXksFChu78%3D Occurrence Handle11408558
M. F. Paine L. Y. Leung H. K. Lim K. Liao A. Oganesian M.Y. Zhang K. E. Thummel P. B. Watkins (2002) ArticleTitleIdentification of a novel route of extraction of sirolimus in human small intestine: roles of metabolism and secretion J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 301 174–186 Occurrence Handle10.1124/jpet.301.1.174 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xis1Kqsr4%3D Occurrence Handle11907172
C. L. Cummins W. Jacobsen L. Z. Benet (2002) ArticleTitleUnmasking thedynamic interplay between intestinal P-glycoprotein and CYP3A4 J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 300 1036–1045 Occurrence Handle10.1124/jpet.300.3.1036 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XitVelsLs%3D Occurrence Handle11861813
B. P. Zeigler (1997) Objects and Systems: Principled Design with Implementations in C++ and Java Springer New York
Acknowledgments
This research was funded in part by the CDH Research Foundation (R21CDH00101; CAH is a trustee of the CDH Research Foundation) and CAH. We thank Glen Ropella for his many contributions; we thank Robert Spear and Betty-ann Hoener; we also thank the members of the Biosystems Group for helpful discussion and commentary,with special thanks going to Jesse Engelberg, Pearl Johnson, Sean Kim, Tai Ning Lam, Amina Qutub, and JonTang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Hunt, C.A. Mechanistic Study of the Cellular Interplay of Transport and Metabolism Using the Synthetic Modeling Method. Pharm Res 23, 493–505 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-006-9505-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-006-9505-4