Abstract
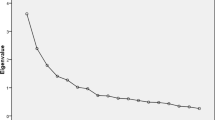
Objective The aim of this study was to develop and validate a questionnaire for assessing HIV-infected patients’ satisfaction with pharmaceutical care received in Nigerian HIV clinics. Method Questionnaire’s items were selected based on similar published studies and designed on a 5- point Likert response scale. Face and content validity, feasibility, factorial validity, reliability, and construct validity were evaluated. The instrument’s feasibility was assessed in a secondary health care facility (St. Charles Borromeo Hospital Onitsha) and validated in a tertiary health care facility (University of Nigeria Teaching Hospital Enugu). Factor analysis used principal components and varimax rotation. Reliability was established using internal consistency with Cronbach’s alpha. Convergent and discriminant validity were determined using Spearman’s rho correlation. Results A self-administered 16-item questionnaire in 5-point Likert response scale format was developed. Questionnaire evaluated cumulative experience of patients with comprehensive pharmaceutical care practice in pharmacies of HIV clinics. Eighty questionnaires were collected for pilot test while four hundred questionnaires were retrieved for the validity test. Factor analysis resulted in four factors: ‘Interpersonal/Professional relationship with pharmacist’, ‘patient counseling’, ‘drug information’ and ‘managing therapy’, with a cumulative variance of 56.7%. Cronbach’s alpha for the whole questionnaire was 0.85, and 0.81, 0.66, 0.67 and 0.72 for the four factors, respectively. Four items used for convergent and discriminant validity showed convergence between the related items and variance between the unrelated items. Conclusion The questionnaire developed is a reliable and valid instrument for assessing patient satisfaction with pharmaceutical care in HIV clinics in Nigeria. Further research is needed to expand the instruments’ robustness.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). AIDS epidemic update. [Online] 2007. [Cited 2008 Jan]. Available from: http://data.unaids.org/pub/EPISlides/2007/2007_epiupdate_en.pdf.
McNeil DG. U.N. Agency to say it overstated extent of HIV cases by millions. New York Times. [Online] 2007. [Cited 2009 March]. Available from: http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9C01EEDF103BF933A15752C1A9619C 8B63&sec=&spon=&pagewanted=2.
Helper C, Strand L. Opportunities and responsibilities in pharmaceutical care. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1990;43:533–4.
Aguwa CN, Ukwe CV, Ekwunife OI. Effect of pharmaceutical care programme on blood pressure and quality of life in a Nigerian pharmacy. Pharm World Sci. 2008;30:107–10.
Gourley GK, Gourley DR, La Monica RE, Reed P, Solomon DK, Washington E. Development and validation of the pharmaceutical care satisfaction questionnaire. Am J Manag Care. 2001;7(5):461–6.
Schoomer JC, Kucukarslan SN. Measuring patient satisfaction with pharmaceutical services. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 1997;54:2721–32.
Volume CI, Farris KB, Kassam R. Pharmaceutical care research and education project (PREP): patient outcomes. J Am Pharm Assoc. 2001;41:411–20.
Larson LN, Rovers J, Mackeigan LD. Patient satisfaction with pharmaceutical care: update of a validated instrument. J Am Pharm Assoc. 2002;42:44–50.
Cerda JM, Gimeno GS, Boquet EM, Villalaba EM, Aminana MA. HIV infected patients’ perceived satisfaction with an outpatient pharmaceutical care unit (OPCU). Farm Hosp. 2005;29:134–9.
Traverso ML, Salamano M, Botta C, Colautti M, Palchik V, Perez B. Questionnaire to assess patient satisfaction with pharmaceutical care in Spanish language. Int J Qual Health Care. 2007;9(4):217–24.
Ware JE, Hays RD. Methods for measuring patient satisfaction with specific medical encounters. Med Care. 1988;26:393–402.
Global HIV/AIDS Initiative Nigeria (GHAIN). Pharmaceutical care in HIV/AIDS. Seminar presentation in training program.
Nwana OC. Introduction to educational research for students–teachers. Ibadan: Heinemann Educational Books Limited; 1981.
Trochim WMK, Donnelly JP. The research methods knowledge base. Mason: Ceegage Learning; 2008.
Marquez-Peiro JF, Perez-Peiro C. Evaluation of patient satisfaction in outpatient pharmacy. Farm Hosp. 2008;32(2):71–6.
Streiner DL, Norman GR. Health measurement scales: a practical guide to development and use. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1995.
Rose LE, Kim MT, Dennison CR, Hill MN. The contexts of adherence for African Americans with high blood pressure. J Adv Nurs. 2000;32:587–94.
Gifford AL, Bormann JE, Shiverly MJ, Wright BC, Richman DD, Bozzette SA. Predictors of self-reported adherence and plasma HIV concentrations in patients on multidrug antiretroviral regimens. JAIDS. 2000;23(5):386–95.
Machtinger EL, Bangsberg DR (2005) Adherence to HIV antiretroviral therapy. HIV Insite knowledge base chapter. [Online]. [cited 2008 Sept 13]. Available from: http://hivinsite.ucsf.edu/InSite?page=kb-03-02-09#.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank all pharmacists of the HIV/AIDS clinics of the University of Nigeria Teaching Hospital, Ituku-Ozalla and Saint Charles Borromeo Hospital, Onitsha for their assistance during the course of the work.
Funding
None.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
See Table 4.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Njilele, A.C., Ukwe, C.V., Okonta, J.M. et al. Development of a patient satisfaction questionnaire for HIV/AIDS patients in Nigeria. Int J Clin Pharm 34, 98–104 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11096-011-9596-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11096-011-9596-9