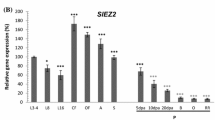
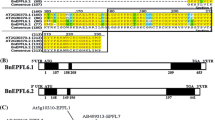
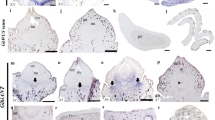
Abstract
We have isolated a plant NOTCHLESS (NLE) homolog from the wild potato species Solanum chacoense Bitt., encoding a WD-repeat containing protein initially characterized as a negative regulator of the Notch receptor in animals. Although no Notch signaling pathway exists in plants, the NLE gene is conserved in animals, plants, and yeast. Overexpression of the plant ScNLE gene in Drosophila similarly affected bristle formation when compared to the overexpression of the endogenous Drosophila NLE gene, suggesting functional conservation. Expression analyses showed that the ScNLE gene was fertilization-induced and primarily expressed in ovules after fertilization, mainly in the integumentary tapetum (endothelium). Significant expression was also detected in the shoot apex. Promoter deletion analysis revealed that the ScNLE promoter had a complex modulatory architecture with both positive, negative, and tissue specific regulatory elements. Transgenic plants with reduced levels of ScNLE transcripts displayed pleitotropic phenotypes including a severe reduction in seed set, consistent with ScNLE gene expression pattern.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DAP:
-
Days after pollination
- HAP:
-
Hours after pollination
References
Acosta-Garcia G, Vielle-Calzada JP (2004) A classical arabinogalactan protein is essential for the initiation of female gametogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:2614–2628
Acton TB, Zhong H, Vershon AK (1997) DNA-binding specificity of Mcm1: operator mutations that alter DNA-binding and transcriptional activities by a MADS box protein. Mol Cell Biol 17:1881–1889
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ (1999) Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science 284:770–776
Bowman JL, Drews GN, Meyerowitz EM (1991) Expression of the Arabidopsis floral homeotic gene AGAMOUS is restricted to specific cell types late in flower development. Plant Cell 3:749–758
Busi MV, Bustamante C, D’angelo C, Hidalgo-Cuevas M, Boggio SB, Valle EM, Zabaleta E (2003) MADS-box genes expressed during tomato seed and fruit development. Plant Mol Biol 52:801–815
Bussiere F, Ledu S, Girard M, Heroux M, Perreault J-P, Matton DP (2003) Development of an efficient cis-trans-cis ribozyme cassette to inactivate plant genes. Plant Biotechnol J 1:423–435
Cebolla A, Vinardell JM, Kiss E, Olah B, Roudier F, Kondorosi A, Kondorosi E (1999) The mitotic inhibitor ccs52 is required for endoreduplication and ploidy-dependent cell enlargement in plants. Embo J 18:4476–4484
Chaudhury AM, Ming L, Miller C, Craig S, Dennis ES, Peacock WJ (1997) Fertilization-independent seed development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:4223–4228
Clarke AE (1940) Fertilization and early embryo development in the potato. Am Potato J 17:20–25
Conlan RS, Hammond-Kosack M, Bevan M (1999) Transcription activation mediated by the bZIP factor SPA on the endosperm box is modulated by ESBF-1 in vitro. Plant J 19:173–181
Conner J, Liu Z (2000) LEUNIG, a putative transcriptional corepressor that regulates AGAMOUS expression during flower development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:12902–12907
Deng XW, Caspar T, Quail PH (1991) cop1: a regulatory locus involved in light-controlled development and gene expression in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev 5:1172–1182
Diaz I, Martinez M, Isabel-Lamoneda I, Rubio-Somoza I, Carbonero P (2005) The DOF protein, SAD, interacts with GAMYB in plant nuclei and activates transcription of endosperm-specific genes during barley seed development. Plant J 42:652–662
Diaz I, Vicente-Carbajosa J, Abraham Z, Martinez M, Isabel-La Moneda I, Carbonero P (2002) The GAMYB protein from barley interacts with the DOF transcription factor BPBF and activates endosperm-specific genes during seed development. Plant J 29:453–464
Dnyansagar VR, Cooper DC (1960) Development of the seed of Solanum phureja. Am J Bot 47:176–186
Germain H, Rudd S, Zotti C, Caron S, O’brien M, Chantha SC, Lagace M, Major F, Matton DP (2005) A 6374 unigene set corresponding to low abundance transcripts expressed following fertilization in Solanum chacoense Bitt, and characterization of 30 receptor-like kinases. Plant Mol Biol 59:515–532
Gillaspy G, Ben-David H, Gruissem W (1993) Fruits: a developmental perspective. Plant Cell 5:1439–1451
Goldberg RB, Barker SJ, Perez-Grau L (1989) Regulation of gene expression during plant embryogenesis. Cell 56:149–160
Guitton AE, Berger F (2005) Loss of function of MULTICOPY SUPPRESSOR OF IRA 1 produces nonviable parthenogenetic embryos in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 15:750–754
Higo K, Ugawa Y, Iwamoto M, Korenaga T (1999) Plant cis-acting regulatory DNA elements (PLACE) database: 1999. Nucleic Acids Res 27:297–300
Honma T, Goto K (2000) The Arabidopsis floral homeotic gene PISTILLATA is regulated by discrete cis-elements responsive to induction and maintenance signals. Development 127:2021–2030
Hu W, Wang Y, Bowers C, Ma H (2003) Isolation, sequence analysis, and expression studies of florally expressed cDNAs in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 53:545–563
Huang H, Mizukami Y, Hu Y, Ma H (1993) Isolation and characterization of the binding sequences for the product of the Arabidopsis floral homeotic gene AGAMOUS. Nucleic Acids Res 21:4769–4776
Huck N, Moore JM, Federer M, Grossniklaus U (2003) The Arabidopsis mutant feronia disrupts the female gametophytic control of pollen tube reception. Development 130:2149–2159
Joshi CP, Zhou H, Huang X, Chiang VL (1997) Context sequences of translation initiation codon in plants. Plant Mol Biol 35:993–1001
Kadesch T (2000) Notch signaling: a dance of proteins changing partners. Exp Cell Res 260:1–8
Kapil RN, Tiwari SC (1978) The integumentary tapetum. Bot Rev 44:457–490
Kerschen A, Napoli CA, Jorgensen RA, Muller AE (2004) Effectiveness of RNA interference in transgenic plants. FEBS Lett 566:223–228
Kim MK, Choi JW, Jeon JH, Franceschi VR, Davin LB, Lewis NG (2002) Specimen block counter-staining for localization of GUS expression in transgenic arabidopsis and tobacco. Plant Cell Rep 21:35–39
Kimble J, Simpson P (1997) The LIN-12/Notch signaling pathway and its regulation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 13:333–361
Kohler C, Hennig L, Bouveret R, Gheyselinck J, Grossniklaus U, Gruissem W (2003) Arabidopsis MSI1 is a component of the MEA/FIE Polycomb group complex and required for seed development. Embo J 22:4804–4814
Lagacé M, Chantha SC, Major G, Matton DP (2003) Fertilization induces strong accumulation of a histone deacetylase (HD2) and of other chromatin-remodeling proteins in restricted areas of the ovules. Plant Mol Biol 53:759–769
Lantin S, O’brien M, Matton DP (1999) Pollination, wounding and jasmonate treatments induce the expression of a developmentally regulated pistil dioxygenase at a distance, in the ovary, in the wild potato Solanum chacoense Bitt. Plant Mol Biol 41:371–386
Larkin JC, Oppenheimer DG, Pollock S, Marks MD (1993) Arabidopsis GLABROUS1 gene requires downstream sequences for function. Plant Cell 5:1739–1748
Le Bras S, Cohen-Tannoudji M, Guyot V, Vandormael-Pournin S, Coumailleau F, Babinet C, Baldacci P (2002) Transcript map of the Ovum mutant (Om) locus: isolation by exon trapping of new candidate genes for the DDK syndrome. Gene 296:75–86
Lease KA, Wen J, Li J, Doke JT, Liscum E, Walker JC (2001) A mutant Arabidopsis heterotrimeric G-protein beta subunit affects leaf, flower, and fruit development. Plant Cell 13:2631–2641
Lee JY, Baum SF, Alvarez J, Patel A, Chitwood DH, Bowman JL (2005) Activation of CRABS CLAW in the Nectaries and Carpels of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17:25–36
Lu P, Porat R, Nadeau JA, O’neill SD (1996) Identification of a meristem L1 layer-specific gene in Arabidopsis that is expressed during embryonic pattern formation and defines a new class of homeobox genes. Plant Cell 8:2155–2168
Marton ML, Cordts S, Broadhvest J, Dresselhaus T (2005) Micropylar pollen tube guidance by egg apparatus 1 of maize. Science 307:573–576
Matton DP, Maes O, Laublin G, Xike Q, Bertrand C, Morse D, Cappadocia M (1997) Hypervariable domains of self-incompatibility RNases mediate allele-specific pollen recognition. Plant Cell 9:1757–1766
Neer EJ, Schmidt CJ, Nambudripad R, Smith TF (1994) The ancient regulatory-protein family of WD-repeat proteins. Nature 371:297–300
O’Brien M, Kapfer C, Major G, Laurin M, Bertrand C, Kondo K, Kowyama Y, Matton DP (2002) Molecular analysis of the stylar-expressed Solanum chacoense small asparagine-rich protein family related to the HT modifier of gametophytic self-incompatibility in Nicotiana. Plant J 32:985–996
Ohad N, Margossian L, Hsu YC, Williams C, Repetti P, Fischer RL (1996) A mutation that allows endosperm development without fertilization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:5319–5324
Osterlund MT, Hardtke CS, Wei N, Deng XW (2000) Targeted destabilization of HY5 during light-regulated development of Arabidopsis. Nature 405:462–466
Pandey S, Assmann SM (2004) The Arabidopsis putative G protein-coupled receptor GCR1 interacts with the G protein alpha subunit GPA1 and regulates abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell 16:1616–1632
Papi M, Sabatini S, Bouchez D, Camilleri C, Costantino P, Vittorioso P (2000) Identification and disruption of an Arabidopsis zinc finger gene controlling seed germination. Genes Dev 14:28–33
Plesch G, Stormann K, Torres JT, Walden R, Somssich IE (1997) Developmental and auxin-induced expression of the Arabidopsis prha homeobox gene. Plant J 12:635–647
Porat R, Lu P, O’neill SD (1998) Arabidopsis SKP1, a homologue of a cell cycle regulator gene, is predominantly expressed in meristematic cells. Planta 204:345–351
Rotman N, Rozier F, Boavida L, Dumas C, Berger F, Faure JE (2003) Female control of male gamete delivery during fertilization in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Biol 13:432–436
Royet J, Bouwmeester T, Cohen SM (1998) Notchless encodes a novel WD40-repeat-containing protein that modulates Notch signaling activity. Embo J 17:7351–7360
Shiu SH, Bleecker AB (2001) Receptor-like kinases from Arabidopsis form a monophyletic gene family related to animal receptor kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:10763–10768
Sieburth LE, Meyerowitz EM (1997) Molecular dissection of the AGAMOUS control region shows that cis elements for spatial regulation are located intragenically. Plant Cell 9:355–365
Singh M, Bhalla PL, Xu H, Singh MB (2003) Isolation and characterization of a flowering plant male gametic cell-specific promoter. FEBS Lett 542:47–52
Smith TF, Gaitatzes C, Saxena K, Neer EJ (1999) The WD repeat: a common architecture for diverse functions. Trends Biochem Sci 24:181–185
Tanksley SD (2004) The genetic, developmental, and molecular bases of fruit size and shape variation in tomato. Plant Cell 16(Suppl):S181–189
Tilly JJ, Allen DW, Jack T (1998) The CArG boxes in the promoter of the Arabidopsis floral organ identity gene APETALA3 mediate diverse regulatory effects. Development 125:1647–1657
Van Nocker S, Ludwig P (2003) The WD-repeat protein superfamily in Arabidopsis: conservation and divergence in structure and function. BMC Genom 4:50
Wigge PA, Weigel D (2001) Arabidopsis genome: life without notch. Curr Biol 11:R112–114
Williams EJ (1955) Seed failure in the Chippewa variety of Solanum tuberosum. Bot Gaz 10:10–15
Yamagishi K, Nagata N, Yee KM, Braybrook SA, Pelletier J, Fujioka S, Yoshida S, Fischer RL, Goldberg RB, Harada JJ (2005) TANMEI/EMB2757 encodes a WD repeat protein required for embryo development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 139:163–173
Yanagisawa S (2004) Dof domain proteins: plant-specific transcription factors associated with diverse phenomena unique to plants. Plant Cell Physiol 45:386–391
Yu L, Gaitatzes C, Neer E, Smith TF (2000) Thirty-plus functional families from a single motif. Protein Sci 9:2470–2476
Acknowledgements
We are indebt to Dr. Stephen Cohen from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory, Heidelberg, Germany, where part of the work was realized in his laboratory on Drosophila transgenic experiments. We also thank Roselyne Labbé, Édtih Lafleur and Éric Chevalier for technical assistance. This work was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) and from the Canada Research Chair program. S. C. Chantha is the recipient of Ph.D. fellowships from NSERC and from Le Fonds Québécois de la Recherche sur la Nature et les Technologies (FQRNT, Québec). D. P. Matton holds a Canada Research Chair in Functional Genomics and Plant Signal Transduction.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chantha, SC., Emerald, B.S. & Matton, D.P. Characterization of the plant Notchless homolog, a WD repeat protein involved in seed development. Plant Mol Biol 62, 897–912 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-006-9064-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-006-9064-4