Abstract
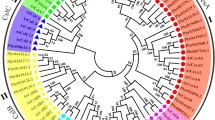
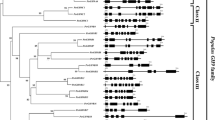
The CESA gene superfamily of Arabidopsis and other seed plants comprises the CESA family, which encodes the catalytic subunits of cellulose synthase, and eight families of CESA-like (CSL) genes whose functions are largely unknown. The CSL genes have been proposed to encode processive β-glycosyl transferases that synthesize noncellulosic cell wall polysaccharides. BLAST searches of EST and shotgun genomic sequences from the moss Physcomitrella patens (Hedw.) B.S.G. were used to identify genes with high similarity to vascular plant CESAs, CSLAs, CSLCs, and CSLDs. However, searches using Arabidopsis CSLBs, CSLEs, and CSLGs or rice CSLFs or CSLHs as queries identified no additional CESA superfamily members in P. patens, indicating that this moss lacks representatives of these families. Intron insertion sites are highly conserved between Arabidopsis and P. patens in all four shared gene families. However, phylogenetic analysis strongly supports independent diversification of the shared families in mosses and vascular plants. The lack of orthologs of vascular plant CESAs in the P. patens genome indicates that the divergence of mosses and vascular plants predated divergence and specialization of CESAs for primary and secondary cell wall syntheses and for distinct roles within the rosette terminal complexes. In contrast to Arabidopsis, the CSLD family is highly represented among P. patens ESTs. This is consistent with the proposed function of CSLDs in tip growth and the central role of tip growth in the development of the moss protonema.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, et al (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Appenzeller L, Doblin M, Barreiro R, et al (2004) Cellulose synthesis in maize: isolation and expression analysis of the cellulose synthase (CesA) gene family. Cellulose 11:287–299
Baldauf SL (2003) Phylogeny for the faint of heart: a tutorial. Trends Genet 19:345–351
Bonetta DT, Facette M, Raab TK, et al (2002) Genetic dissection of plant cell-wall biosynthesis. Biochem Soc Trans 30:298–301
Burn JE, Hocart CH, Birch RJ, et al (2002) Functional analysis of the cellulose synthase genes CesA1, CesA2, and CesA3 in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 129:797–807
Burton RA, Shirley NJ, King BJ, et al (2004) The CesA gene family of barley: quantitative analysis of transcripts reveals two groups of co-expressed genes. Plant Physiol 134:224–236
Burton RA, Wilson SM, Hrmova M, et al (2006) Cellulose synthase-like CslF genes mediate the synthesis of cell wall (1,3;1,4)-β-d-glucans. Science 311:1940–1942
Carafa A, Duckett JG, Knox JP, et al (2005) Distribution of cell-wall xylans in bryophytes and tracheophytes: new insights into basal interrelationships of land plants. New Phytol 168:231–240
Charnock SJ, Henrissat B, Davies GJ (2001) Three-dimensional structures of UDP-sugar glycosyltransferases illuminate the biosynthesis of plant polysaccharides. Plant Physiol 125:527–531
Coutinho PM, Deleury E, Dalvies GJ, et al (2003) An evolving hierarchical family classification of glycosyltransferases. J Mol Biol 328:307–317
Cove D (2005) The moss Physcomitrella patens. Annu Rev Genet 39:339–358
Cutler S, Somerville C (1997) Cellulose synthesis: cloning in silico. Curr Biol 7:R108–R111
Desprez T, Vernhettes S, Fagard M, et al (2002) Resistance against herbicide isoxaben and cellulose deficiency caused by distinct mutations in same cellulose synthase isoform CESA6. Plant Physiol 128:482–490
Dhugga KS, Barreiro R, Whitten B, et al (2004) Guar seed β-mannan synthase is a member of the cellulose synthase super gene family. Science 303:363–366
Djerbi S, Lindskog M, Arvestad L, et al (2005) The genome sequence of black cottonwood (Populus tremula) reveals 18 conserved cellulose synthase (CesA) genes. Planta 221:739–746
Doblin MS, De Melis L, Newbigin E, et al (2001) Pollen tubes of Nicotiana alata express two genes from different b-glucan synthase families. Plant Physiol 125:2040–2052
Doblin MS, Kurek I, Jacob-Wilk D, et al (2002) Cellulose biosynthesis in plants: from genes to rosettes. Plant Cell Physiol 43:1407–1420
Doblin MS, Vergara CE, Read S, et al (2003) Plant cell wall biosynthesis: making the bricks. In: Rose JKC (ed) The plant cell wall. Blackwell, Oxford, pp. 183–222
Ewing RM, Ben Kahla A, Poirot O, et al (1999) Large-scale statistical analyses of rice ESTs reveal correlated patterns of gene expression. Genome Res 9:950–959
Fagard M, Desnos T, Desprez T, et al (2000) PROCUSTE1 encodes a cellulose synthase required for normal cell elongation specifically in roots and dark-grown hypocotyls of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 12:2409–2423
Favery B, Ryan E, Foreman J, et al (2001) KOJAK encodes a cellulose synthase-like protein required for root hair cell morphogenesis in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev 15:79–89
Frei E, Preston RD (1968) Non-cellulosic structural polysaccharides in algal cell walls. III. Mannan in siphoneous green algae. Proc Roy Soc B 169:127–145
Gardiner JC, Taylor NG, Turner SR (2003) Control of cellulose synthase complex localization in developing xylem. Plant Cell 15:1740–1748
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hamann T, Osborne E, Youngs HL, et al (2004) Global expression analysis of CESA and CSL genes in Arabidopsis. Cellulose 11:279–286
Hazen SP, Scott-Craig JS, Walton JD (2002) Cellulose synthase-like genes of rice. Plant Physiol 128:336–340
Hebant C (1977) The conducting tissues of bryophytes. J. Cramer, Vaduz, pp 157
Hebsgaard SM, Korning PG, Tolstrup N, et al (1996) Splice site prediction in Arabidopsis thaliana pre-mRNA by combining local and global sequence information. Nucl Acids Res 24:3439–3452
Holland N, Holland D, Helentjaris T, et al (2000) A comparative analysis of the plant cellulose synthase (CesA) gene family. Plant Physiol 123:1313–1323
Joshi CP, Bhandari S, Ranjan P, et al (2004) Genomics of cellulose biosynthesis in poplars. New Phytol 164:53–61
Keegstra K, Walton J (2006) β-glucans–brewer’s bane, dietician’s delight. Science 311:1872–1873
Kurek I, Kawagoe Y, Jacob-Wilk D, et al (2002) Dimerization of cotton fiber cellulose synthase catalytic subunits occurs via oxidation of the zinc-binding domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:11109–11114
Lang D, Eisinger J, Reski R, et al (2005) Representation and high-quality annotation of the Physcomitrella patens transcriptome demonstrates a high proportion of proteins involved in metabolism in mosses. Plant Biol 7:238–250
Lewis LA, McCourt RM (2004) Green algae and the origin of land plants. Am J Bot 91:1535–1556
Liang X, Joshi CP (2004) Molecular cloning of ten distinct hypervariable regions from the cellulose synthase gene superfamily in aspen trees. Tree Physiol 24:543–550
Liepman AH, Wilkerson CG, Keegstra K (2005) Expression of cellulose synthase-like (Csl) genes in insect cells reveals that CslA family members encode mannan synthases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:2221–2226
Matsunaga T, Ishii T, Matsumoto S, et al (2004) Occurrence of the primary cell wall polysaccharide rhamnogalacturonan II in pteridophytes, lycophytes, and bryophytes: implications for the evolution of vascular plants. Plant Physiol 134:339–351
Nairn CJ, Haselkorn T (2005) Three loblolly pine CesA genes expressed in developing xylem are orthologous to secondary cell wall CesA genes of angiosperms. New Phytol 166:907–915
Neill AA (2005) A cellulose synthase-like (CslD) gene from Coleochaete scutata. Thesis. University of Rhode Island
Nishiyama T, Fujita T, Shin-I T, et al (2003) Comparative genomics of Physcomitrella patens gametophytic transcriptome and Arabidopsis thaliana: implication for land plant evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:8007–8012
Nobles DR Jr, Brown RM Jr (2004) The pivotal role of cyanobacteria in the evolution of cellulose synthases and cellulose synthase-like proteins. Cellulose 11:437–448
Nobles DR, Romanovicz DK, Brown RM Jr (2001) Cellulose in cyanobacteria: origin of vascular plant cellulose synthase? Plant Physiol 127:529–542
Pear JR, Kawagoe Y, Schreckengost WE, et al (1996) Higher plants contain homologs of the bacterial celA genes encoding the catalytic subunit of cellulose synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:12637–12642
Peng L, Kawagoe Y, Hogan P, et al (2002) Sitosterol-b-glucoside as primer for cellulose synthesis in plants. Science 295:147–150
Perrin RM (2001) Cellulose: how many cellulose synthases to make a plant? Curr Biol 11:R213–R216
Popper ZA, Fry SC (2003) Primary cell wall composition of bryophytes and charophytes. Ann Bot (Lond) 91:1–12
Read SM, Bacic T (2002) Prime time for cellulose. Science 295:59–60
Reiss HD, Schnepf E, Herth W (1984) The plasma membrane of the Funaria caulonema tip cell: morphology and distribution of particle rosettes, and the kinetics of cellulose synthesis. Planta 160:428–435
Richmond T (2000) Higher plant cellulose synthases. Genome Biol 1:3001.1–3001.6
Richmond TA, Somerville CR (2000) The cellulose synthase superfamily. Plant Physiol 124:495–498
Richmond TA, Somerville CR (2001) Integrative approaches to determining Csl function. Plant Mol Biol 47:131–143
Robert S, Mouille G, Höfte H (2004) The mechanism and regulation of cellulose synthesis in primary walls: lessons from cellulose-deficient Arabidopsis mutants. Cellulose 11:351–364
Roberts AW, Roberts E (2004) Cellulose synthase (CesA) genes in algae and seedless plants. Cellulose 11:419–435
Roberts AW, Roberts EM, Delmer DP (2002) Cellulose synthase (CesA) genes in the green alga Mesotaenium caldariorum. Eukaryot Cell 1:847–855
Samuga A, Joshi CP (2004) Cloning and characterization of cellulose synthase-like gene, PtrCSLD2 from developing xylem of aspen trees. Physiol Plant 120:631–641
Saxena IM, Brown RM Jr, Fevre M, et al (1995) Multidomain architecture of β-glycosyl transferases: implications for mechanism of action. J Bacteriol 177:1419–1424
Schaefer D, Zryd J-P (2004) Principles of targeted mutagenesis in the moss Physcomitrella patens. In: Wood AJ, Oliver MJ, Cove DJ (eds) New frontiers in bryology: physiology, molecular biology and functional genomics. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp. 37–49
Scheible W-R, Eshed R, Richmond T, et al (2001) Modifications of cellulose synthase confer resistance to isoxaben and thiazolidinone herbicides in Arabidopsis Ixr1 mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:10079–10084
Schmiedel G, Schnepf E (1980) Polarity and growth of caulonema tip cells of the moss Funaria hygrometrica. Planta 147:405–413
Schween G, Gorr G, Hohe A, et al (2003) Unique tissue-specific cell cycle in Physcomitrella. Plant Biol 5:50–58
Somerville C, Bauer S, Brininstool G, et al (2004) Toward a systems approach to understanding plant cell walls. Science 306:2206–2211
Tanaka K, Murata K, Yamazaki M, et al (2003) Three distinct rice cellulose synthase catalytic subunit genes required for cellulose synthesis in the secondary wall. Plant Physiol 133:73–83
Taylor NG, Scheible W-R, Cutler S, et al (1999) The irregular xylem3 locus of Arabidopsis encodes a cellulose synthase required for secondary cell wall synthesis. Plant Cell 11:769–779
Taylor NG, Laurie S, Turner SR (2000) Multiple cellulose synthase catalytic subunits are required for cellulose synthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 12:2529–2539
Taylor NG, Howells RM, Huttly AK, et al (2003) Interactions among three distinct CesA proteins essential for cellulose synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:1450–1455
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, et al (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucl Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Thornton J (2002) Gene family phylogenetics: tracing protein evolution on trees. In: DeSalle R, Giribet G, Wheeler W (eds) Molecular systematics and evolution: theory and practice. Birkhauser, Geneva, pp 191–207
Tsekos I (1999) The sites of cellulose synthesis in algae: diversity and evolution of cellulose-synthesizing enzyme complexes. J Phycol 35:635–655
Tusnády GE, Simon I (1998) Principles governing amino acid composition of integral membrane proteins: applications to topology prediction. J Mol Biol 283:489–506
Vergara CE, Carpita NC (2001) β-D-Glycan synthases and the CesA gene family: lessons to be learned from the mixed-linkage (1→3),(1→4)β-D-glucan synthase. Plant Mol Biol 47:145–160
Wang X, Cnops G, Vanderhaeghen R, et al (2001) AtCSLD3, a cellulose synthase-like gene important for root hair growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 126:575–586
Yoon HS, Hackett JD, Ciniglia C, et al (2004) A molecular timeline for the origin of photosynthetic eukaryotes. Mol Biol Evol 21:809–818
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the National Research Initiative of the USDA Cooperative State Research, Education and Extension Service, Grant 2003-35304-13233, and NSF ADVANCE Institutional Transformation Award SBE-0245039. We gratefully acknowledge the use of cDNA libraries from the University of Leeds and EST clones from the University of Leeds and the RIKEN Biological Resources Center. We also thank Chessa Goss for excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Accession numbers: DQ417756, DQ417757, DQ898284–6, DQ898147–54, DQ902545–51.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roberts, A.W., Bushoven, J.T. The cellulose synthase (CESA) gene superfamily of the moss Physcomitrella patens . Plant Mol Biol 63, 207–219 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-006-9083-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-006-9083-1