Abstract
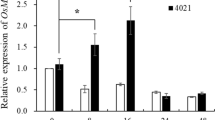
A banana somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinase (SERK) gene, designated as MaSERK1, was isolated from Musa acuminata cv. Mas (AA). It encoded a protein of 628 amino acids with above 82% identities to reported SERKs of coconut, rice, maize, Arabidopsis, carrot, and Medicago truncatula. MaSERK1 was expressed weakly in male flower clusters, but not in male flower-derived nonembryogenic calli, but it was highly expressed in male flower-derived embryogenic calli and embryogenic cell suspensions (ECS). During subculture of ECS, MaSERK1 expression and frequency of somatic embryogenesis were influenced by the duration of subculture, wherein expression decreased within 0 to 6 days of subculture, increased to highest levels at 12 days following subculture, and dropped thereafter. The frequency of somatic embryogenesis of ECS positively correlated with MaSERK1 transcript levels. Moreover, MaSERK1 expression in leaves of Musa paradisiaca L. cv. Dongguan Dajiao (ABB), known to be resistant to Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense race 4 (FOC race 4), was induced by exogenous salicylic acid (SA) or inoculation with FOC race 4. However, MaSERK1 expression levels in leaves of Mucus spp. cv. Pisang awak (ABB), known to be susceptible to FOC race 4, did not change following either treatment. These results suggested that MaSERK1 not only could serve as a molecular marker for banana somatic embryogenesis, but also played a role in disease resistance response in banana.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- D:
-
Day
- ECS:
-
Embryogenic cell suspensions
- FOC:
-
Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense
- LRR:
-
Leucine-rich repeat
- PCV:
-
Packed cell volume
- R:
-
Resistance
- RACE:
-
Rapid amplification of cDNA ends
- RLK:
-
Receptor-like kinase
- SA:
-
Salicylic acid
- SERK:
-
Somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinase
References
Albrecht C, Russinova E, Hecht V, Baaijens E, de Vries S (2005) The Arabidopsis thaliana somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinases 1 and 2 control male sporogenesis. Plant Cell 17:3337–3349
Asif MH, Dhawan P, Nath P (2000) A simple procedure for the isolation of high quality RNA from ripening banana fruit. Plant Mol Biol Rep 18:109–115
Baudino S, Hansen S, Brettschneider R, Hecht V, Dresselhaus T, Lörz H, Dumas C, Rogowsky P (2001) Molecular characterization of two novel maize LRR receptor-like kinases, which belong to the SERK gene family. Planta 213:1–10
Chinchilla D, Zipfell C, Robatzekl S, Kemmerling B, Nürnberger T, Jones JDG, Felix G, Boller T (2007) A flagellin-induced complex of the receptor FLS2 and BAK1 initiates plant defence. Nature 448:497–501
Côte FX, Domergue R, Monmarson S, Schwendiman J, Teisson C, Escalant JV (1996) Embryogenic cell suspensions from the male flower of Musa AAA cv. Grande Naine. Physiol Plant 97:285–290
Diévart A, Clark SE (2004) LRR-containing receptors regulating plant development and defense. Development 131:251–261
Escalant JV, Teisson C, Côte FX (1994) Amplified somatic embryogenesis from male flowers of triploid banana and plantain cultivars (Musa spp.). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 30:181–186
Hecht V, Vielle-Calzada JP, Hartog MV, Schmidt EDL, Boutilier K, Grossniklaus U, de Vries SC (2001) The Arabidopsis somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase 1 gene is expressed in developing ovules and embryos and enhances embryogenic competence in culture. Plant Physiol 127:803–816
Heese A, Hann DR, Gimenez-Ibanez S, Jones AME, He K, Li J, Schroeder JI, Peck SC, Rathjen JP (2007) The receptor-like kinase SERK3/BAK1 is a central regulator of innate immunity in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:12217–12222
Hofmann K, Bucher P, Falquet L, Bairoch A (1999) The PROSITE database: its status in 1999. Nucleic Acids Res 27:215–219
Hu H, Xiong L, Yang Y (2005) Rice SERK1 gene positively regulates somatic embryogenesis of cultured cell and host defense response against fungal infection. Planta 222:107–117
Huang BZ, Xu L, Yang H, Tang X, Wei Y, Qiu J, Guan Q (2005) Preliminary results of fields evaluation of banana germplasm resistant to Fusarium wilt disease. Guangdong Agr Sci 6:9–10
Ito Y, Takaya K, Kurata N (2005) Expression of SERK family receptor-like protein kinase genes in rice. Biochim Biophys Acta 1730:253–258
Kobe B, Deisenhofer J (1995) Proteins with leucine-rich repeats. Curr Opin Struct Biol 5:409–416
Mak C, Mohamed AA, Liew KW, Ho YW (2004) Early screening technique for Fusarium wilt resistance in banana micropropagated plants. In: Mohan JS, Swennen R (eds) Banana improvement: cellular, molecular biology, and induced mutations. Enfield (NH) USA, Science Publishers, Inc, pp 219–227
Nakai K, Kanehisa M (1992) A knowledge base for predicting protein localization sites in eukaryotic cells. Genomics 14:897–911
Nolan KE, Irwanto RR, Rose RJ (2003) Auxin up-regulates MtSERK1 expression in both Medicago truncatula root-forming and embryogenic cultures. Plant Physiol 133:218–230
Pegg KG, Moore NY, Bentley S (1996) Fusarium wilt of banana in Australia: a review. Aust J Agric Res 47:637–650
Pei X, Li S, Jiang Y, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Jia S (2006) Isolation, characterization and phylogenetic analysis of the resistance gene analogues (RGAs) in banana (Musa spp.). Plant Sci 172:1166–1174
Qi YX, Xie YX, Zhang X, Pu JJ, Zhang HQ (2006) The identification of pathogen causing banana Fusarium wilt in Hainan. Biotechnol Bull s1:316–319
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning, a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory Press, New York
Santos MO, Romano E, Yotoko KSC, Tinoco MLP, Dias BBA, Aragão FJL (2005) Characterisation of the cacao somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinase (SERK) gene expressed during somatic embryogenesis. Plant Sci 168:723–729
Santos MO, Romano E, Vieira LS, Baldoni AB, Aragão FJL (2008) Suppression of SERK gene expression affects fungus tolerance and somatic embryogenesis in transgenic lettuce. Plant Biol. doi:10.1111/j.1438-8677.2008.00103.x
Santy PE, Andrew JK, Blondy CC, Eduardo CC (2007) Structure and phylogenetic analysis of Pto-type disease resistance gene candidates in banana. Mol Genet Genomics 278:443–453
Schmidt EDL, Guzzo F, Toonen MAJ, de Vries SC (1997) A leucine-rich repeat containing receptor-like kinase marks somatic plant cells competent to form embryos. Development 124:2049–2062
Shah K, Vervoort J, de Vries SC (2001) Role of threonines in the Arabidopsis thaliana somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase 1 activation loop in phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 276:41263–41269
Somleva MN, Schmidt EDL, de Vries SC (2000) Embryogenic cells in Dactylis glomerata L. (Poaceae) explants identified by cell tracking and by SERK expression. Plant Cell Rep 19(1):718–726
Song D, Li G, Song F, Zheng Z (2008) Molecular characterization and expression analysis of OsBISERK1, a gene encoding a leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase, during disease resistance responses in rice. Mol Biol Rep 35(2):275–283
Strosse H, Schoofs H, Panis B, Andre E, Reyniers K, Swennen R (2006) Development of embryogenic cell suspensions from shoot meristematic tissue in bananas and plantains (Musa spp). Plant Sci 170:104–112
Tao Y, Yuan F, Leister RT, Ausubel FM, Katagiri F (2000) Mutational analysis of the Arabidopsis nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeat resistance gene RPS2. Plant Cell 12:2541–2554
Thomas C, Meyer D, Himber C, Steinmetz A (2004) Spatial expression of a sunflower SERK gene during induction of somatic embryogenesis and shoot organogenesis. Plant Physiol Biochem 42(1):35–42
Walker JC (1994) Structure and function of the receptor-like protein kinases of higher plants. Plant Mol Biol 26:1599–1609
Wei YR, Huang XL, Li J, Huang X, Li Z, Li XJ (2005) Establishment of embryogenic cell suspension culture and plant regeneration of edible banana Musa acuminata cv. Mas (AA). Chin J Biotechnol 21(1):58–65
Yoshimura S, Yamanouchi U, Katayose Y, Toki S, Wang ZX, Kono I, Kurata N, Yano M, Iwata N, Sasaki T (1998) Expression of Xa1, a bacterial blight-resistance gene in rice, is induced by bacterial inoculation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:1663–1668
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (30400287), Ministry of Education of China for doctorial study (20050558040), Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (011126, 06023159, 06300470), Programs for Science and Technology Development of Guangdong (2006B20101014), and Programs for Science and Technology Development of Guangzhou (2006Z3-E0281).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Figure 1
Multiple full-length amino acid sequence alignment of MaSERK1 with reported somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinases (SERKs). Putative domains were indicated on the top of the sequences. The eleven subdomains of protein kinase domain were marked with Roman numbers. The asterisks indicated sequence identity. Percentages indicated amino acid identity to MaSERK1. The accession number for SERKs are as follows: CnSERK: AAV58833; OsSERK1: AAU88198; OsBISERK1: AAR26543; ZmSERK1: CAC37638; ZmSERK2: CAC37639; AtSERK1: CAB42254; AtSERK2: AAK68073; AtSERK3: AAK68074; DcSERK: AAB61708; and MtSERK1: AAN64293. Cn = Cocos nucifera; Os = Oryza sativa; Zm = Zea mays; At = Arabidopsis thaliana; Dc = Daucus carota; Mt = Medicago truncatula (PDF 51 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, X., Lu, XY., Zhao, JT. et al. MaSERK1 Gene Expression Associated with Somatic Embryogenic Competence and Disease Resistance Response in Banana (Musa spp.). Plant Mol Biol Rep 28, 309–316 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-009-0150-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-009-0150-z