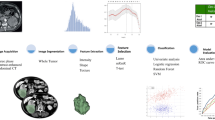
Abstract
We present a new image quantification and classification method for improved pathological diagnosis of human renal cell carcinoma. This method combines different feature extraction methodologies, and is designed to provide consistent clinical results even in the presence of tissue structural heterogeneities and data acquisition variations. The methodologies used for feature extraction include image morphological analysis, wavelet analysis and texture analysis, which are combined to develop a robust classification system based on a simple Bayesian classifier. We have achieved classification accuracies of about 90% with this heterogeneous dataset. The misclassified images are significantly different from the rest of images in their class and therefore cannot be attributed to weakness in the classification system.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Esgiar, A. N., Naguib, R. N. G., Sharif, B. S., Bennett, M. K., & Murray, A. (1998). Microscopic image analysis for quantitative measurement and feature identification of normal and cancerous colonic mucosa. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology Biomedicine, 2, 197–203.
Vermeulena, P. B., Gasparinib, G., Foxc, S. B., Toid, M., Martine, L., Mcculloche, P., Pezzellaf, F., Vialeg, G., Weidnerh, N., Harrisc, A. L., & Dirix, L. Y. (1996). Quantification of angiogenesis in solid human tumors: an international consensus on the methodology and criteria of evaluation. European Journal of Cancer, 32(14), 2474–2484.
Roula, M. A., Diamond, J., Bouridane, A., Miller, P., & Amira, A. (2002). A multispectral computer vision system for automatic grading of prostatic neoplasia. Proc. IEEE Int. Symp. On Biomed. Imaging, 193–196.
Thiran, J. P., & Macq, B. (1996). Morphological feature extraction for the classification of digital images of cancerous tissues. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 43(10), 1011–1020.
Diamond, J., Anderson, N., Bartels, P., Montironi, R., & Hamilton, P. (2004). The use of morphological characteristics and texture analysis in the identification of tissue composition in prostatic neoplasia. Human Pathology, 35, 1121–1131.
Walker, R. F., Jackway, P. T., Lovell, B., & Longstaff, I. D. (1994). Classification of cervical cell nuclei using morphological segmentation and textural feature extraction. Proc of the 2nd Australian and New Zealand Conference on Intelligent Information Systems, 297–301.
Esgiar, A. N., Naguib, R. N. G., Sharif, B. S., Bennett, M. K., & Murray, A. (2002). Fractal analysis in the detection of colonic cancer images. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology Biomedicine, 6, 54–58.
Depeursinge, A., Sage, D., Hidki, A., Platon, A., Poletti, P.-A., Unser, M., & Muller, H. (2007). Lung Tissue Classification Using Wavelet Frames”, 29th Annual International,Conference of the IEEE EMBS, 6259–6262.
Waheed, S., Moffitt, R. A., Chaudry, Q., Young, A. N., & Wang, M. D. (2007). Computer Aided Histopathological Classification of Cancer Subtypes. IEEE BIBE 2007, 503–508.
Weeks, A. R., & Hague, G. E. (1997). Color Segmentation in the HSI Color Space Using the k-means Algorithm. Proceedings of the SPIE—Nonlinear Image Processing, 8, 143–154.
Hauta-Kasari, M., Parkkinen, J., & Jaaskelainen, T. (1996). Generalized co-occurrence matrix for multispectral texture analysis. 13th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, 2, 785–789.
Arivazhagan, S., & Ganesan, L. (2003). Texture classification using wavelet transform. Pattern Recogn Lett, 24(9–10), 1513–1521.
Unser, M., & Aldroubi, A. (1996). A review of wavelets in biomedical applications. Proceedings of the IEEE, 84(4), 626–638.
Fernandez, M., & Mavilio, A. (2002). Texture analysis of medical images using the wavelet transform. AIP Conference Proceedings, 630, 164–168 October.
Acknowledgement
This research was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (R01CA108468, P20GM072069, and U54CA119338) to M.D.W., Georgia Cancer Coalition (Distinguished Cancer Scholar Award to M.D.W.), Hewlett Packard, and Microsoft Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudry, Q., Raza, S.H., Young, A.N. et al. Automated Renal Cell Carcinoma Subtype Classification Using Morphological, Textural and Wavelets Based Features. J Sign Process Syst Sign Image Video Technol 55, 15–23 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-008-0214-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-008-0214-6