Abstract
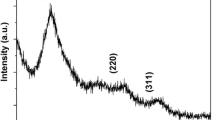
The precursor of ZnO has been prepared by refluxing in ethanol at 70°C for 4 h using ZnAc2·H2O as the initial agent. Then ZnO has been prepared from the reaction of LiOH·H2O and the precursor. The ZnO is modified by mercaptoacetic acid (MAA) and detected by SEM and XRD. These ZnO particles have single phase, like-sphere and size of 4.6 nm. The modified effectivity of MAA for the quantum dots (QDs) has been investigated with UV-visible and fluorescence analysis, and the mechanism and property of ZnO light emitting have been discussed under given conditions. The reasons why the fluorescent emission peak of surface defects disappear and the exciton emission peak increase are that MAA effectively covers the surface defects of ZnO and stably coats ZnO particles. At the same time, the effect of the added amount of the MAA, temperature and electrolyte on light-emitting properties of modified product has also been studied. The result shows that the modified ZnO QDs have good fluorescence property, stability and suitable capability of resisting electrolyte. These results are important for biological analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Govorov A O. Optical and electronic properties of quantum dots with magnetic impurities. Comptes Rendus Physique, 2008, 9(8): 857–873
Smith A M, Duan H W, Mohs A M, Nie S M. Bioconjugated quantum dots for in vivo molecular and cellular imaging. Adv Drug Deli Rev, 2008, 60(11): 1226–1240
Santos B S, Farias P M A, Fontes A, Brasil Jr A G, Jovino C N, Neto A G C, Silva D C N, de Menezes F D, Ferreira R. Semiconductor nanocrystals obtained by colloidal chemistry for biological applications. Appl Surf Sci, 2008, 255(3): 796–798
Li H B, Wang X Q. Single QD-micelles coated with gemini surfactant for selective recognition of a cation and an anion in aqueous solutions. Sens Actu B: Chem, 2008, 134(1): 238–244
Kim D G, Tomihira K K, Okahara S, Nakayama M k. Highly efficient preparation of size-controlled CdS quantum dots with high photolu minescence yield. J Crys Grow, 2008, 310(18): 4244–4247
Zheng J J, Zheng Z H, Gong W W, Hu X B, Gao W, Ren X G, Zhao H F. Stable, small, and water-soluble Cu-doped ZnS quantum dots prepared via femtosecond laser ablation. Chem Phys Lett, 2008, 465(4–6): 275–278
Narayanan S, Sinha S S, Verma P K, Pal S K. Ultrafast energy transfer from 3-mercaptopropionic acid-capped CdSe/ZnS QDs to dye-labelled DNA Chem. Phy Lett, 2008, 463(1–3): 160–165
Liu M M, Xu L, Cheng W Q, Zeng Y, Yan Z Y. Surface-modified CdS quantum dots as luminescent probes for sulfadiazine determination. Spectrochim Acta Part A: Mole Biomole Spectrosc, 2008,70(5): 1198–1202
Hong D D, Rhee J I. Use of CdSe/ZnS luminescent quantum dots incorporated within sol-gel matrix for urea detection. Anal Chim Acta, 2008, 626(1): 53–61
Magnanini R, Tarricone L, Parisini A, Longo M, Gombia E. Investigation of GaAs/InGaP superlattices for quantum well solar cells. Thin Solid Films, 2008, 516(20): 6734–6738
Hazdra P, Voves J, Oswald J, Kuldová K, Hospodková A, Hulicius E. Optical characterisation of MOVPE grown vertically correlated InAs/GaAs QDs. Microelectro J, 2008, 39(8): 1070–1074
Kaizu T K, Takahasi M T, Yamaguchi K, Mizuki J. In situ determination of Sb distribution in Sb/GaAs(001) layer for high-density InAs quantum dot growth. J Crys Grow, 2008, 310(15): 3436–3439
Idowu M, Lamprecht E, Nyokong T. Interaction of water-soluble thiol capped CdTe quantum dots and bovine serum albumin. J Photochem Photobiol: Chem, 2008,198(1): 7–12
Anderson R E, Warren C W. Systematic investigation of preparing biocompatible, single and small ZnS-capped CdSe quantum dots with amphiphilic polymers. ACS Nano, 2008, 2(7): 1341–1352
Li L, Guo L, Zhang Z, Tang J, Xie J. Recent advances of aptamer sensors. Sci China Ser B-Chem, 2008, 51(3): 193–204
Reithmaier J P, Forchel A. Recent advances in semiconductor quantum-dot lasers. Comptes Rendus Physique, 2003, 4(6): 611–619
Xu H, Yan C. Preparation and application of water-soluble quantum dots (in Chinese). Prog Chem, 2005,17(5): 800–808
Sato M k, Kawata A T, Morito S Z, Sato Y, Yamaguchi I. Preparation and properties of polymer/zinc oxide nanocomposites using functionalized zinc oxide QDs. Euro Polym J, 2008, 44(11): 3430–3438
Patra M K, Manoth M, Singh V K, Gowd G S, Choudhry V S, Vadera S R, Kumar N. Synthesis of stable dispersion of ZnO quantum dots in aqueous medium showing visible emission from bluish green to yellow. J Luminescence, 2009, 129(3), 320–324
Norberg N S, Gamelin D R. Influence of surface modification on the luminescence of colloidal ZnO nanocrystals. J Phys Chem B, 2005, 109(44): 20810–20816
Yang Y, Li Y Q, Fu S Y, Xiao H M. Transparent and light-emitting epoxy nanocomposites containing ZnO quantum dots as encapsulating materials for solid state lighting. J Phys Chem C, 2008, 112(28): 10553–10558
Monticone S, Tufeu R, Kanaev A V. Complex nature of the UV and visible fluorescence of colloidal ZnO nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B, 1998, 102: 2854–2862
Guo L. Highly monodisperse polymer-capped ZnO nanoparticles: Preparation and optical properties. Appl Phys Lett, 2000,76(20): 2901–2903
Shan G Y, Lu Q, An L M, Wang X. Electrons transfer between mercaptoacetic acid and ZnO nanocrystal thin film. Chem Res Chin U, 2005, 21(2): 201–204
Meulenkamp E A. Size dependence of the dissolution of ZnO nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B, 1998, 102: 7764–7769
Yan Y, Zhang W, Fan J, Ji X. New approach to prepare Q-CdS nanoparticles: Polymer dispersion method (in Chinese). Acta Chim Sin, 2005, 63(14): 1303–1306
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 202171042) and the Natural Science Foundation of Southwest Petroleum University (Grant No. 2007XJZ044)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhuang, J., Liu, M. & Liu, H. MAA-modified and luminescence properties of ZnO quantum dots. Sci. China Ser. B-Chem. 52, 2125–2133 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-009-0198-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-009-0198-5