Abstract
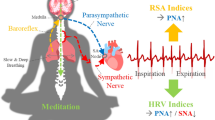
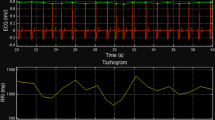
Respiratory sinus arrhythmia (RSA) is largely mediated by the autonomic nervous system through its modulating influence on the heart beats. We propose a robust algorithm for quantifying instantaneous RSA as applied to heart beat intervals and respiratory recordings under dynamic breathing patterns. The blood volume pressure-derived heart beat series (pulse intervals, PIs) are modeled as an inverse Gaussian point process, with the instantaneous mean PI modeled as a bivariate regression incorporating both past PIs and respiration values observed at the beats. A point process maximum likelihood algorithm is used to estimate the model parameters, and instantaneous RSA is estimated via a frequency domain transfer function evaluated at instantaneous respiratory frequency where high coherence between respiration and PIs is observed. The model is statistically validated using Kolmogorov–Smirnov goodness-of-fit analysis, as well as independence tests. The algorithm is applied to subjects engaged in meditative practice, with distinctive dynamics in the respiration patterns elicited as a result. The presented analysis confirms the ability of the algorithm to track important changes in cardiorespiratory interactions elicited during meditation, otherwise not evidenced in control resting states, reporting statistically significant increase in RSA gain as measured by our paradigm.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
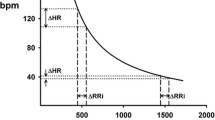
Note that for a fair comparison across subjects, the RSA gain was normalized by the standard deviation of the corresponding RP.
References
Barbieri R, Brown EN (2006) Analysis of heartbeat dynamics by point process adaptive filtering. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 53(1):4–12
Barbieri R, Waldmann RA, Di Virgilio V, Triedman JK, Bianchi AM, Cerutti S, Saul JP (1996) Continuous quantification of baroreflex and respiratory control of heart rate by use of bivariate autoregressive techniques. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol 1:264–277
Barbieri R, Bianchi AM, Triedman JK, Mainardi LT, Cerutti S, Saul JP (1997) Model dependency of multivariate autoregressive spectral analysis. IEEE Eng Med Bio Mag 16(5):74–85
Barbieri R, Matten EC, Alabi ARA, Brown EN (2005) A point-process model of human heartbeat intervals: new definitions of heart rate and heart rate variability. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288(1):H424–H435
Baselli G, Bolis D, Cerutti S, Freschi C (1985) Autoregressive modeling and power spectral estimate of RR interval time series in arrhythmic patients. Comput Biomed Res 18(6):510–530
Berntson GG, Bigger JT, Eckberg DL, Grossman P et al (1997) Heart rate variability: origins, methods, and interpretive caveats. Psychophysiology 34(6):623–648
Blain G, Meste O, Bermon S (2005) Influences of breathing patterns on respiratory sinus arrhythmia in humans during exercise. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288(2):H887
Brown EN, Barbieri R, Ventura V, Kass RE, Frank LM (2002) The time rescaling theorem and its application to neural spike train data analysis. Neural Comput 14(2):325–346
Chen Z, Brown E, Barbieri R (2009) Assessment of autonomic control and respiratory sinus arrhythmia using point process models of human heart beat dynamics. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 56(7):1791–1802
Chhikara RS, Folks JL (1989) The inverse gaussian distribution: theory, methodology, and applications. Marcel Dekker, Inc. New York
Denver JW, Reed SF, Porges SW (2007) Methodological issues in the quantification of respiratory sinus arrhythmia. Biol Psychol 74(2):286–294
Ditto B, Eclache M, Goldman N (2006) Short-term autonomic and cardiovascular effects of mindfulness body scan meditation. Ann Behav Med 32(3):227–234
Eckberg DL (1983) Human sinus arrhythmia as an index of vagal cardiac outflow. J Appl Physiol 54:961–966
Eckberg DL (2003) The human respiratory gate. J Physiol 548(2):339–352
Elstad M, Toska K, Chon KH, Raeder EA, Cohen RJ (2001) Respiratory sinus arrhythmia: opposite effects on systolic and mean arterial pressure in supine humans. J Physiol 536(1):251–259
Faes L, Porta A, Cucino R, Cerutti S, Antolini R, Nollo G (2004) Causal transfer function analysis to describe closed loop interactions between cardiovascular and cardiorespiratory variability signals. Biol Cybern 90(6):390–399
Garland EL, Gaylord SA, Boettiger CA, Howard MO (2010) Mindfulness training modifies cognitive, affective, and physiological mechanisms implicated in alcohol dependence: results of a randomized controlled pilot trial. J Psychoactive Drugs 42(2):177–192
Gilad O, Swenne CA, Davrath LR, Akselrod S (2005) Phase-averaged characterization of respiratory sinus arrhythmia pattern. Am J Physiol Heart Circul Physiol 288(2):H504
Goedhart AD, Van Der Sluis S, Houtveen JH, Willemsen G, De Geus EJC (2007) Comparison of time and frequency domain measures of RSA in ambulatory recordings. Psychophysiology 44(2):203–215
Grossman P, Kollai M (1993) Respiratory sinus arrhythmia, cardiac vagal tone, and respiration: within- and between-individual relations. Psychophysiology 30(5):486–495
Grossman P, Svebak S (1987) Respiratory sinus arrhythmia as an index of parasympathetic cardiac control during active coping. Psychophysiology 24(2):228–235
Grossman P, Taylor EW (2007) Toward understanding respiratory sinus arrhythmia: relations to cardiac vagal tone, evolution and biobehavioral functions. Biol Psychol 74(2):263–285
Grossman P, Karemaker J, Wieling W (1991) Prediction of tonic parasympathetic cardiac control using respiratory sinus arrhythmia: the need for respiratory control. Psychophysiology 28(2):201–216
Heitmann A, Huebner T, Schroeder R, Perz S, Voss A (2011) Multivariate short-term heart rate variability: a pre-diagnostic tool for screening heart disease. Med Biol Eng Comput 49(1):41–50
Hirsch JA, Bishop B (1981) Respiratory sinus arrhythmia in humans: how breathing pattern modulates heart rate. Am J Physiol 241:H620–H629
Jo JA, Blasi A, Valladares E, Juarez R, Baydur A, Khoo MCK (2005) Determinants of heart rate variability in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome during wakefulness and sleep. Am J Physiol Heart Circul Physiol 288(3):H1103
Kabat-Zinn J (1990) Full catastrophe living: using the wisdom of your body and mind to face stress, pain, and illness. Delta Trade Paperbacks. ISBN 9780385303125. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=i4AedPJKtYYC
Katona PG, Jih F (1975) Respiratory sinus arrhythmia: noninvasive measure of parasympathetic cardiac control. J Appl Physiol 39(5):801
Kluge KA, Harper RM, Schechtman VL, Wilson AJ, Hoffman HJ, Southall DP (1988) Spectral analysis assessment of respiratory sinus arrhythmia in normal infants and infants who subsequently died of sudden infant death syndrome. Pediatr Res 24(6):677–682
Lazar SW, Kerr CE, Wasserman RH, Gray JR, Greve DN, Treadway MT, McGarvey M, Quinn BT, Dusek JA, Benson H, L RS, I MC, Fischl B (2005) Meditation experience is associated with increased cortical thickness. Neuroreport 16(17):1893–1897
Lehrer P, Sasaki Y, Saito Y (1999) Zazen and cardiac variability. Psychosom Med 61(6):812–821
Loader C (1999) Local regression and likelihood. Springer, Berlin
Malik M, Bigger JT, Camm AJ, Kleiger RE, Malliani A, Moss AJ, Schwartz PJ (1996) Heart rate variability standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. Am Heart Assoc Circ 93(5):1043–1065
Melillo P, Fusco R, Sansone M, Bracale M, Pecchia L (2011) Discrimination power of long-term heart rate variability measures for chronic heart failure detection. Med Biol Eng Comput 49:67–74
Mukkamala R, Mathias JM, Mullen TJ, Cohen RJ, Freeman R (1999) System identification of closed-loop cardiovascular control mechanisms: diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 276(3):R905
Mulder LJM (1992) Measurement and analysis methods of heart rate and respiration for use in applied environments. Biol Psychol 34(2–3):205–236
Orini M, Bail ó n R, Enk R, Koelsch S, Mainardi L, Laguna P (2010) A method for continuously assessing the autonomic response to music-induced emotions through HRV analysis. Med Biol Eng Comput 48(5):423–433
Ortner CNM, Kilner S, Zelazo PD (2007) Mindfulness meditation and reduced emotional interference on a cognitive task. Motiv Emot 31(4):271–283
Peng CK, Henry IC, Mietus JE, Hausdorff JM, Khalsa G, Benson H, Goldberger AL (2004) Heart rate dynamics during three forms of meditation. Int J Cardiol 95(1):19–27
Peressutti C, Martín-González J, M García-Manso J, Mesa D (2010) Heart rate dynamics in different levels of zen meditation. Int J Cardiol 145(1):142–146
Piskorski J, Guzik P (2011) Asymmetric properties of long-term and total heart rate variability. Med Biol Eng Comput 49(11):1289–1297
Ross SM (2007) Introduction to probability models, 9th edn. Academic Press, Massachusetts
Saul JP, Cohen RJ (1994) Respiratory sinus arrhythmia. In: Vagal control of the heart: experimental basis and clinical implications. Futura Publishing Co. Inc., Armonk, pp 511–536
Saul JP, Berger RD, Chen MH, Cohen RJ (1989) Transfer function analysis of autonomic regulation. II. Respiratory sinus arrhythmia. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 256(1):H153–H161
Sin PYW, Galletly DC, Tzeng YC (2010) Influence of breathing frequency on the pattern of respiratory sinus arrhythmia and blood pressure: old questions revisited. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 298(5):H1588
Thomas RJ, Mietus JE, Peng CK, Goldberger AL (2005) An electrocardiogram-based technique to assess cardiopulmonary coupling during sleep. Sleep 28(9):1151–1161
Tibshirani R, Hastie T (1987) Local likelihood estimation. J Am Stat Assoc 82(398):559–567
Voss A, Schulz S, Baer KJ (2010) Linear and nonlinear analysis of autonomic regulation of heart rate variability in healthy first-degree relatives of patients with schizophrenia, pp 5395–5398
Womack BF (1971) The analysis of respiratory sinus arrhythmia using spectral analysis and digital filtering. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 18:399–409
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) under Grant R01-HL084502, Grant R01-DA015644, Grant DP1-OD003646, Grant K01-AT00694-01.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kodituwakku, S., Lazar, S.W., Indic, P. et al. Point process time–frequency analysis of dynamic respiratory patterns during meditation practice. Med Biol Eng Comput 50, 261–275 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-012-0866-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-012-0866-z