Abstract
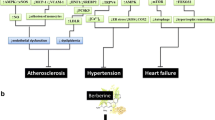
Coptis Chinensis is a traditional Chinese medicine herb that has the effect of clearing heat and drying dampness, purging fire to eliminate toxin. Berberine is the main alkaloid of Coptis Chinensis, and, recent researches showed that berberine had the effect of anti-atherosclerosis. This paper reviewed the anti-atherosclerosis mechanism of berberine, which may be related to regulating lipids, anti-inflammation, decompression, reducing blood sugar, and inhibiting vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang J, Lin J. Advance on study in anti-tumor mechanism of berberine. China J Chin Mater Med (Chin) 2007;32:881–883,934.
Cheng YX, Zhong GQ. Study progress of berberine in treating cardiovascular disease. Med Recapitul (Chin) 2007;13:780–781.
He GH, Liu Y, Ai ZB, Zhang XD, Wang YF. Effects of berberine on carotid artery atherosclerosis in rabbits. Neur Injury Funct Reconstruct (Chin) 2006;1:42–44.
He GH, Ai ZB, Liu Y, Wang YF, Li CY, Zheng H, et al. The effect of berberine on the thickness of intima and chemoattraction of macrophage cells in rabbits. J Apopl Nerv Dis (Chin) 2006;23:94–96.
He GH, Zhou L, Wang YF, Ai ZB. The effect of berberine on the angiotensin II receptor type 1 in the prevention of carotid artery atherosclerosis in rabbits. Chin J Arterioscler (Chin) 2006;14:1035–1037.
Ai ZB, He GH, Liu Y, Wang YF, Zhang XD, Li CY, et al. The experimental study on carotid artery atherosclerosis in rabbit by berberine. J Apopl Nerv Dis (Chin) 2005;22:138–140.
Zhou L, He GH, Li CY, Wang YF, Ai ZB. The effect of berberine on angiotensin of carotid artery atherosclerosis in rabbits. Stroke Nerv Dis (Chin) 2006;13:212–218.
Zuo YF, Guo Y, Jiang X, Li FM, Wang QZ. Effects of berberine on atherosclerosis and plasma levels of lipid in atherosclerotic rabbits. Chin J Cerebrovasc Dis (Chin) 2006;3:204–207.
Li JZ. A study of carotid atherosclerotic plaques and serum lipoproteins in the patients with cerebral infarction. Chin J Disdiagn (Chin) 2001;1:1147–1148.
Hansson GK, Robertson AK, Söderberg-Nauclér C. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Ann Rev Pathol 2006;1:297–329.
Griendling KK, Alexander RW. Oxidative stress and cardiovascular disease. Circulation 1997;96:3264–3265.
Crouse JR 3rd, Byington RP, Bond MG, Espeland MA, Craven TE, Sprinkle JW, et al. Pravastatin, lipids, and atherosclerosis in carotid arteries (PLAC-II). Am J Cardiol 1 1995;75:45.
Kong W, Wei J, Abidi P, Inaba S, Lin MH, Li C, et al. Berberine is a novel cholesterol-lowering drug working through a unique mechanism distinct from statins. Nat Med 2004;10:1344–1351.
Wei J, Jiang JD, Wu JD, Wang SK, Wang ZZ, Pan HN, et al. Research on the effective improvement of hyperlipidemia by berberine. Chin J Diabetes (Chin) 2005;13:49–51.
Brusq JM, Amcellin N, Grondin P, Guillard R, Martin S, Saintillan Y, et al. Inhibition of lipid synthesis through activation of AMP kinase: an additional mechanism for the hypolipidemic effects of berberine. J Lipid Res 2006;47:1281–1288.
Heieh YS, Kuo WH, Lin TW. Protective effects of berberine against low-density lipoprotein (LDL) oxidation and oxidized LDL-induced cytotoxicity on endothelial cells. J Agric Food Chem 2007;55:10435–10437.
Ross R. Atherosclerosis—an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med 1999;340:115–126.
Guo L, Ding SW. Experimental study of complex Herba Siegesbeckiae mixtura anti-atherosclerotic on endothelial injury of atherosclerosis. J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2001;19:105–106.
Guo LL, Wang J. Status and suggestions about antiatherosclerosis by traditional Chinese medicine. China J Chin Mater Med (Chin) 2007;32:93–96.
Kuo CL, Chi CW, Liu TY. The anti-inflammatory potential of berberine in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett 2004;23:127–137.
Hsiang CY, Wu SL, Cheng SE, Ho TY. Acetaldehyde-induced interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha production is inhibited by berberine through nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway in HepG2 cells. J Biomed Sci 2005;12:791–801.
Yang J, Wang HD, Lu DX, Wang YP, Qi RB, Li J. Effects of neutral sulfate berberine on LPS-induced cardiomyocyte TNF-alpha secretion, abnormal calcium cycling, and cardiac dysfunction in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2006;27:173–178.
Duan H, Zhang HK, Liu JJ, Nie WJ, Ma Y. Effect of berberine on IL-6 of carotid artery after balloon injury in rabbits. J Med Forum (Chin) 2006;10:6–9.
Fukuda K, Hibiya Y, Mutoh M, Koshiji M, Akao S, Fujiwara H. Inhibition of activator protein 1 activity by berberine in human hepatoma cells. Planta Med 1999;65:381–382.
Cai GH, Zhong LC, Shan J, Jiang H, Jiao B. Effect of berberine on arachidonic acid metabolism in rabbit platelets and endothelial cells. Thromb Res 2002;106:223–227.
Jankowski P, Bilo G, Kawecka-Jaszcz K. The pulsatile component of blood pressure: its role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Blood Press 2007;16:238–245.
Delcker A, Diener HC, Wilhelm H. Influence of vascular risk factors for atherosclerotic carotid plaque progression. Stroke 1995;26:2016–2022.
Jiang Y, Shi SN, Wang HY. A study of carotid in elderly by color doppler ultrasound. Chin J Ultra Med (Chin) 2000;16:758–759.
Lu H, Cassis LA, Daugherty A. Atherosclerosis and arterial blood pressure in mice. Curr Drug Targets 2007;8:1181–1189.
Zhang LS. Clinical usage of berberine. Chin Rem Clin (Chin) 2004;41:78.
Lau CW, Yao XQ, Chen ZY, Ko WH, Huang Y. Cardiovascular actions of berberine. Cardiovasc Drug Rev 2001;19:234–244.
Ko WH, Yao XQ, Lau CW, Law WI, Chen ZY, Kwok W, et al. Vasorelaxant and antiproliferative effects of berberine. Eur J Pharmacol 2000;399:187–196.
Li ZH, Zhang T, Ge ZM. Molecular biological mechanism of hyperglycosemia accelerating AS. Chin J Arterioscler (Chin) 2006;14:633–635.
Yin J, Xing H, Ye J. Efficacy of berberine in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 2008;57:712–717.
Liu L, Deng Y, Yu S, Lu S, Xie L, Liu X. Berberine attenuates intestinal disaccharidases in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Pharmazie 2008;63:384–388.
Zhou JY, Zhou SW, Zhang KB, Tang JL, Guang LX, Ying Y, et al. Chronic effects of berberine on blood, liver glucolipid metabolism and liver PPARs expression in diabetic hyperlipidemic rats. Biol Pharm Bull 2008;31:1169–1176.
Yi P, Lu FE, Xu LJ, Chen G, Dong H, Wang KF. Berberine reverses free-fatty-acid-induced insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through targeting IKKbeta. World J Gastroenterol 2008;14:876–883.
Gao CL, Zhang JQ, Huang QL. Experimental study on berberine raised insulin sensitivity in insulin resistance rat models. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 1997;17:162.
Ko BS, Choi SB, Park SK, Jang JS, Kim YE, Park S. Insulin sensitizing and insulinotropic action of berberine from Cortidis Rhizoma. Biol Pharm Bull 2005;28:1431–1437.
Turner N, Li JY, Gosby A, Sabrina WC, Cheng Z, Myyoshi H, et al. Berberine, and its more biologically available derivative dihydroberberine, inhibit mitochondrial respiratory complex I: a mechanism for the action of berberine to activate AMPK and improve insulin action. Diabetes 2008;57:1414–1418.
Gorenne I, Kavurma M, Scott S, Bennett M. Vascular smooth muscle cell senescence in atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res 2006;72:9–17.
Tanabe H, Suzuki H, Mizukami H, Inoue M. Double blockade of cell cycle progression by coptisine in vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Pharmacol 2005;70:1176–1184.
Lee S, Lim HJ, Park HY, Lee KS, Park JH, Jang Y. Berberine inhibits rat vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration in vitro and improves neointima formation after balloon injury in vivo. Berberine improves neointima formation in a rat model. Atherosclerosis 2006;186:29–37.
Liang KW, Ting CT, Yin SC, Chen YT, Lin SJ, Liao JK, et al. Berberine suppresses MEK/ERK-dependent Egr-1 signaling pathway and inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell regrowth after in vitro mechanical injury. Biochemical Pharmacol 2006;71:806–817.
Liang KW, Yin SC, Ting KW, Lin SJ, Hsueh CM, Chen CY, et al. Berberine inhibits platelet-derived growth factor-induced growth and migration partly through an AMPK-dependent pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol 2008;590:343–354.
Huang CG, Chu ZL, Wei SJ, Jiang H, Jiao B. Effect of berberine on arachidonic acid metabolism in rabbit platelets and endothelial cells. Thromb Res 2002;106:223–227.
Jin XL, Shao Y, Wang MJ, Chen LJ, Jin GZ. Tetrahydroprot-oberberines inhibit lipid peroxidation and scavenge hydroxyl free radicals. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2000;21:447–480.
Fang FZ, Dai DZ, Wang ZZ, Wang SK, Weng SY. Inhibition of chlorobenzyl-tetrahydroberberine on the H2O2-induced apoptosis and proliferation of endothelial cells. Chin J Clin Pharmacol Ther (Chin) 2002;7:200–204.
Xi GM, He GH, Huang CF, Luo GJ. Effect of berberine on ICAM-1 and E-selectin of cerebral infarction. Stroke Nerv Dis (Chin) 2003;20:273.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, M., Wang, J. & Liu, Lt. Advance of studies on anti-atherosclerosis mechanism of berberine. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 16, 188–192 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-010-0188-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-010-0188-7