Abstract
Purpose
To describe comorbidities in breast cancer patients at diagnosis and examine factors associated with self-reported comorbidities 30 months post-diagnosis.
Methods
Nine hundred forty one of 1,171 women had a medical record abstract and a follow-up survey in the Health, Eating, Activity and Lifestyle Study.
Results
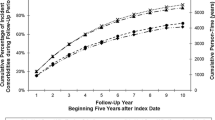
We compared our breast cancer cohort to a contemporaneous nationally-representative sample of age, race/ethnicity and education matched women without cancer (n = 865). Breast cancer patients did not have substantially more comorbidities than women without breast cancer. Women with a hospital record of congestive heart failure significantly less often received chemotherapy or radiation following breast conserving surgery. In multivariate analysis, women who received chemotherapy alone (OR = 3.2; 95% CI: 1.5–6.8), chemotherapy plus radiation (OR = 1.9; 95% CI: 1.02–3.7) or radiation plus tamoxifen (OR = 1.9; 95% CI: 1.1–3.2) were significantly more likely to report at least one new comorbid condition following breast cancer diagnosis than women who received no chemotherapy, tamoxifen or radiation. Overall, women who received adjuvant therapy were more likely to have new comorbidities.
Conclusions
Comorbidities were not substantially different in breast cancer patients than the non-cancer matched controls. Future research should focus on efforts to minimize comorbidities related to chemotherapy and other combination therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Cancer Society.Cancer Facts and Figures. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2007.
Greenfield S, Blanco DM, Elashoff RM, Ganz PA. Patterns of care related to age of breast cancer patients. J Am Med Assoc. 1987;20:2766–70. doi:10.1001/jama.257.20.2766.
Yancik R, Wesley MN, Ries LAG, Havlik RJ, Edwards BK, Yates JW. Effect of age and comorbidity in postmenopausal breast cancer patients age 55 years and older. J Am Med Assoc. 2001;285:885–92. doi:10.1001/jama.285.7.885.
Ballard-Barbash R, Potosky AL, Harlan LC, Nayfield SG, Kessler LG. Factors associated with surgical and radiation therapy for early stage breast cancer in older women. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996;88:716–26. doi:10.1093/jnci/88.11.716.
Harlan LC, Clegg LX, Trimble EL. Trends in surgery and chemotherapy for women diagnosed with ovarian cancer in the United States. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:3488–94. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.01.061.
Gross CP, McAvay GJ, Guo Z, Tinetti ME. The impact of chronic illnesses on the use and effectiveness of adjuvant chemotherapy for colon cancer. Cancer. 2007;109:2410–9. doi:10.1002/cncr.22726.
Balasubramanian BA, Gandhi SK, Demissie K, et al. Use of adjuvant systemic therapy for early breast cancer among women 65 years of age and older. Cancer Control. 2007;14:63–68.
West DW, Satariano WA, Ragland DR. Hiatt RA. Comorbidity and breast cancer survival: a comparison between black and white women. Ann Epidemiol. 1996;6:413–9. doi:10.1016/S1047-2797(96)00096-8.
McTiernan A, Rajan KB, Tworoger SS, et al. Adiposity and sex hormones in postmenopausal breast cancer survivors. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:1961–6. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.07.057.
Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. Journal of Chronic Diseases. 1987;40:373–83. doi:10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8.
http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/elec_prods/subject/nhanes3.htm.
Satariano WA, Ragland DR. The effect of comorbidity on 3-year survival of women with primary breast cancer. Ann Intern Med. 1994;120:104–10.
Yancik R, Wesley MN, Ries LA, Havlik RJ, Edwards BK, Yates JW. Effect of age and comorbidity in postmenopausal breast cancer patients aged 55 years and older. J Am Med Assoc. 2001;285:885–92. doi:10.1001/jama.285.7.885.
Lipscombe LL, Goodwin PJ, Zinman B, McLaughlin JR, Hux JF. Diabetes mellitus and breast cancer: a retrospective population based cohort study. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006;98:349–56. doi:10.1007/s10549-006-9172-5.
Michels KB, Hankinson SE, Solomon CG, et al. Type 2 diabetes and subsequent incidence of breast cancer in the nurses’ health study. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:1752–8. doi:10.2337/diacare.26.6.1752.
Cristofanilli M, Yamamura Y, Kau SW, et al. Thyroid hormone and breast cancer. Cancer. 2005;103:1122–8. doi:10.1002/cncr.20881.
Klabunde CN, Reeve BB, Harlan LC, Davis WW, Potosky AL. Do patients consistently report comorbid conditions over time? Med Care. 2005;43:391–400. doi:10.1097/01.mlr.0000156851.80900.d1.
http://consensus.nih.gov/2000/2000AdjuvantTherapyBreastCancer114html.htm.
Hurria A, Brogan K, Panageas KS, et al. Patterns of toxicity in older patients with breast cancer receiving adjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Research and Treatmen. 2005;92:151–6. doi:10.1007/s10549-005-1410-8.
Geiger AM, Gischberg GM, Chen W, Bernsein L. Stroke risk and tamoxifen therapy for breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004;96:1528–36.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funding source
N01-PC-35139, N01-PC-35142, N01-PC-35138
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harlan, L.C., Klabunde, C.N., Ambs, A.H. et al. Comorbidities, therapy, and newly diagnosed conditions for women with early stage breast cancer. J Cancer Surviv 3, 89–98 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11764-009-0084-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11764-009-0084-3