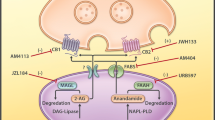
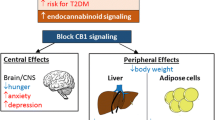
Abstract
The endogenous endocannabinoid system encompasses a family of natural signaling lipids (“endocannabinoids”) functionally related to Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, the psychoactive ingredient of marijuana (cannabis), along with proteins that modulate the endocannabinoids, including enzymes, transporters, and receptors. The endocannabinoid system’s ubiquitous regulatory actions in health and disease underscore its importance to mammalian (patho)physiology and suggest discrete targets through which it may be modulated for therapeutic gain. Medications based on the endocannabinoid system are an important focus of contemporary translational research, particularly with respect to substance abuse and obesity, two prevalent disorders with a pathogenic component of endocannabinoid system hyperactivity. Pressing health care needs have made the rational design of targeted CB1 cannabinoid-receptor modulators a promising route to future medications with significant therapeutic impact against psychobehavioral and metabolic disturbances having a reward-supported appetitive component.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Pertwee RG: Cannabinoid pharmacology: the first 66 years. Br J Pharmacol 2006, 147:S163–S171.
Matias I, Di Marzo V: Endocannabinoid synthesis and degradation, and their regulation in the framework of energy balance. J Endocrinol Invest 2006, 29(3 Suppl):15–26.
Onaivi ES, Ishiguro H, Gong JP, et al.: Discovery of the presence and functional expression of cannabinoid CB2 receptors in brain. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2006, 1074:514–536.
Pertwee RG: The pharmacology of cannabinoid receptors and their ligands: an overview. Int J Obes (Lond) 2006, 30(Suppl 1):S13–S18.
Demuth DG, Molleman A: Cannabinoid signaling. Life Sci 2006, 78:549–563.
Liu I, Wang L, Harvey-White J, et al.: A biosynthetic pathway for anandamide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006, 103:13345–13350.
Di Marzo V, Petrosino S: Endocannabinoids and the regulation of their levels in health and disease. Curr Opin Lipidol 2007, 18:129–140.
Bari M, Battista N, Fezza F, et al.: New insights into endocannabinoid degradation and its therapeutic potential. Mini Rev Med Chem 2006, 6:257–268.
Ho WS, Randall MD: Endothelium-dependent metabolism by endocannabinoid hydrolases and cyclooxygenases limits vasorelaxation to anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol. Br J Pharmacol 2007, 150:641–651.
Hashimotodani Y, Ohno-Shosaku T, Kano M: Endocannabinoids and synaptic function in the CNS. Neuroscientist 2007, 13:127–137.
Pacher P, Bátaki S, Kunos G: The endocannabinoid system as an emerging target of pharmacotherapy. Pharmacol Rev 2006, 58:389–462.
Tucci SA, Halford JC, Harrold JA, et al.: Therapeutic potential of targeting the endocannabinoids: implications for the treatment of obesity, metabolic syndrome, drug abuse and smoking cessation. Curr Med Chem 2006, 13:2669–2680.
Khanapure SP, Garvey DS, Janero DR, et al.: Eicosanoids in inflammation: biosynthesis, pharmacology, and therapeutic frontiers. Curr Top Med Chem 2007, 7:311–340.
Kaczocha M, Hermann A, Glaser ST, et al.: Anandamide uptake is consistent with rate-limited diffusion and is regulated by the degree of its hydrolysis by fatty acid amide hydrolase. J Biol Chem 2006, 281:9066–9075.
Makie K: Cannabinoid receptors as therapeutic targets. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2006, 46:101–122.
Pavlopoulos S, Thakur GA, Nikas SP, et al.: Cannabinoid receptors as therapeutic targets. Curr Pharm Des 2006, 12:1751–1769.
Bingham B, Jones PG, Uveges AJ, et al.: Species-specific in vitro pharmacological effects of the cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2) selective ligand AM1241 and its resolved enantiomers. Br J Pharmacol 2007, 151:1061–1070.
Di Marzo V, Bifulco M, De Petrocellis L: The endocannabinoid system and its therapeutic exploitation. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2004, 3:771–784.
Citron ML, Herman TS, Vreeland F, et al.: Antiemetic efficacy of levonantradol compared to delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol for chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. Cancer Treat Rep 1985, 69:109–112.
Ibrahim MM, Rude ML, Stagg NJ, et al.: CB2 cannabinoid receptor mediation of antinociception. Pain 2006, 122:36–42.
Rhem J, Taylor B, Room R: Global burden of disease from alcohol, illicit drugs and tobacco. Drug Alcohol Rev 2006, 25:503–513.
Camí J, Farré M: Drug addiction. N Engl J Med 2003, 349:975–986.
Maldonado R, Valverde O, Berrendero F: Involvement of the endocannabinoid system in drug addiction. Trends Neurosci 2006, 29:225–232.
Fattore L, Spano MS, Deiana S, et al.: An endocannabinoid mechanism in relapse to drug seeking: a review of animal studies and clinical perspectives. Brain Res Rev 2007, 53:1–16.
Le Foll B, Goldberg SR: Cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist as promising new medications for drug dependence. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2005, 312:875–883.
Pierce RC, Kumaresan V: The mesolimbic dopamine system: the final common pathway for the reinforcing effect of drugs of abuse? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2006, 30:215–238.
Fattore L, Deiana S, Spano MS, et al.: Endocannabinoid system and opioid addiction: behavioural aspects. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2005, 81:343–359.
Ledent C, Valverde O, Cossu G, et al.: Unresponsiveness to cannabinoids and reduced addictive effects of opiates in CB1 receptor knockout mice. Science 1999, 283:401–404.
Vinod KY, Hungund BL: Endocannabinoid lipids and mediated system: implications for alcoholism and neuropsychiatric disorders. Life Sci 2005, 77:1569–1583.
Colombo G, Serra S, Vacca G, et al.: Endocannabinoid system and alcohol addiction: pharmacological studies. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2005, 81:369–380.
Hoenica J, Ponce G, Jimenez-Arriero MA, et al.: Association in alcoholic patients between psychopathic traits and the addictive effect of allelic forms of the CNR1 and FAAH endocannabinoid genes, and the 3’ region of the DRD2 gene. Neurotox Res 2007, 11:51–60.
Rimonabant to reduce alcohol consumption. US National Institutes of Health website. http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct/show/NCT0075205. Accessed July 2007.
Castañé A, Berrendero F, Maldonado R: The role of the cannabinoid system in nicotine addiction. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2005, 81:381–386.
Cohen C, Kodas E, Griebel G: CB1 receptor antagonists for the treatment of nicotine addiction. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2005, 81:387–395.
SR141716 Zimulti (rimonabant) NDA 21-888. Briefing information for FDA advisory committee meeting. http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/07/briefing/2007-4306b1-01-sponsor-backgrounder.htm. Accessed July 2007.
Runyon SP, Carroll FI: Dopamine transporter ligands: recent developments and therapeutic potential. Curr Top Med Chem 2006, 6:1825–1843.
Kahlig KM, Galli A: Regulation of dopamine transporter function and plasma membrane expression by dopamine, amphetamine, and cocaine. Eur J Pharmacol 2003, 479:153–158.
Arnold JC: The role of endocannabinoid transmission in cocaine addiction. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2005, 81:396–406.
Lile JA: Pharmacological determinants of the reinforcing effects of psychostimulants: relation to agonist substitution treatment. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 2006, 14:20–33.
Makriyannis A, Mechoulam R, Piomelli D: Therapeutic opportunities through modulation of the endocannabinoid system. Neuropharmacology 2005, 48:1068–1071.
Sink KS, McLaughlin PJ, Wood JA, et al.: The novel cannabinoid CB1 receptor neutral antagonist AM4113 suppresses food intake and food-reinforced behavior but does not induce signs of nausea in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 2007, In press.
Klein S, Allison DB, Heymsfield SB, et al.: Waist circumference and cardiometabolic risk: a consensus statement from Shaping America’s Health: Association for Weight Management and Obesity Prevention; NAASO, The Obesity Society; the American Society for Nutrition; and the American Diabetes Association. Am J Clin Nutr 2007, 85:1197–1202.
Kluger J. The science of appetite. Time. June 11, 2007. http://www.time.com/magazine/article/0,9171,1627006,00.html. Accessed July 2007.
Cook S, Bloom S: The obesity pipeline: current strategies in the development of anti-obesity drugs. Nature Rev 2006, 5:919–931.
Pagotto U, Marsicano G, Cota D, et al.: The emerging role of the endocannabinoid system in endocrine regulation and energy balance. Endocr Rev 2006, 27:73–100.
Bellocchio L, Mancini G, Vicennati V, et al.: Cannabinoid receptors as therapeutic targets for obesity and metabolic diseases. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2006, 6:586–591.
Cota D, Tschöp MH, Horvath TL, et al.: Cannabinoids, opioids and eating behavior: the molecular face of hedonism? Brain Res Rev 2006, 51:85–107.
Henness S, Robinson DM, Lyseng-Williamson KA: Rimonabant. Drugs 2006, 66:2109–2119.
Patel PN, Pathak R: Rimonabant: a novel selective cannabinoid-1 receptor antagonist for treatment of obesity. Am J Health Syst Pharm 2007, 64:481–489.
Rimonabant regulatory update in the United States. Sanofi-Aventis website. http://en.sanofi-aventis.com/Images/070629_rimonabant-US_en_tcm24-17003.pdf. Accessed July 2007.
Ward SJ, Dykstra LA: The role of CB1 receptors in sweet versus fat reinforcement: effect of CB1 receptor deletion, CB1 receptor antagonism (SR141716A) and CB1 receptor agonism (CP-55940). Behav Pharmacol 2005, 16:381–388.
Sipe JC, Waalen J, Gerber A, Beutler E: Overweight and obesity associated with a missense polymorphism in fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). Int J Obes (Lond) 2005, 29:755–759.
Aberle J, Fedderwitz I, Klages N, et al.: Genetic variation in two proteins of the endocannabinoid system and their influence on body mass index and metabolism under low fat diet. Horm Metab Res 2007, 39:395–397.
Fegley D, Gaetani S, Duranti A, et al.: Characterization of the fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor cyclohexyl carbamic acid 3’-carbamoyl-3-yl ester (URB597): effects of anandamide and oleoylethanolamide deactivation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2005, 313:352–358.
Serrano A, Del Arco I, Javier Pavón F, et al.: The cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist SR141716A (rimonabant) enhances the metabolic benefits of long-term treatment with oleoylethanolamide in Zucker rats. Neuropharmacology 2007, In press.
Salamone JD, McLaughlin PJ, Sink K, et al.: Cannabinoid CB1 receptor inverse agonists and neutral antagonists: effects on food intake, food-reinforced behavior and food aversions. Physiol Behav 2007, 91:383–388.
Siegfried Z, Kanyas K, Latzer Y, et al.: Association study of cannabinoid receptor gene (CNR1) alleles and anorexia nervosa: differences between restricting and binging/purging subtypes. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2004, 125:126–130.
Montelone P, Matias I, Martiadis V, et al.: Blood levels of the endocannabinoid anandamide are increased in anorexia nervosa and in binge-eating disorder, but not in bulimia nervosa. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005, 30:1216–1221.
Kapur A, Hurst DP, Fleischer D, et al.: Mutation studies of Ser7.39 and ser2.60 in the human CB1 cannabinoid receptor: evidence for a serine-induced bend in CB1 transmembrane helix 7. Mol Pharmacol 2007, 71:1512–1524.
Williams J, Wood J, Pandarinathan L, et al.: Quantitative method for the profiling of the endocannabinoid metabolome by LC-atmosphere pressure chemical ionization-MS. Anal Chem 2007, 79:5582–5593.
Espinola-Klein C, Rupprecht HJ, Bickel C, et al.: Impact of metabolic syndrome on atherosclerosis burden and cardiovascular prognosis. Am J Cardiol 2007, 99:1623–1628.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Janero, D.R., Makriyannis, A. Targeted modulators of the endogenous cannabinoid system: Future medications to treat addiction disorders and obesity. Curr Psychiatry Rep 9, 365–373 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-007-0047-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-007-0047-1