Abstract
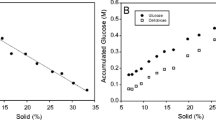
As technologies for utilizing biomass for fuel and chemical production continue to improve, enzymatic hydrolysis can be run at still higher solids concentrations. For hydrolyses that initially contain little or no free water (10–40% total solids, w/w), the saccharification of insoluble polymers into soluble sugars involves changes of volume, density, and proportion of insoluble solids. This poses a new challenge when determining the degree of hydrolysis (conversion yield). Experiments have shown that calculating the yield from the resulting sugar concentration in the supernatant of the slurry and using the assumed initial volume leads to significant overestimations of the yield. By measuring the proportion of insoluble solids in the slurry as well as the sugar concentration and specific gravity of the aqueous phase, it is possible to precisely calculate the degree of conversion. The discrepancies between the different ways of calculating yields are demonstrated along with a nonlaborious method for approximating yields in high solids hydrolysis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jørgensen, H., Kristensen, J. B., & Felby, C. (2007). Biofuels, Bioproducts and Biorefining, 1, 119–134.
Zacchi, G., & Axelsson, A. (1989). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 34, 223–233. doi:10.1002/bit.260340211.
Larsen, J., Petersen, M. Ø., Thirup, L., Li, H. W., & Iversen, F. K. (2008). Chemical Engineering & Technology, 31, 765–772. doi:10.1002/ceat.200800048.
Cara, C., Moya, M., Ballesteros, I., Negro, M. J., Gonzalez, A., & Ruiz, E. (2007). Process Biochem, 42, 1003–1009. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2007.03.012.
Varga, E., Klinke, H. B., Reczey, K., & Thomsen, A. B. (2004). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 88, 567–574. doi:10.1002/bit.20222.
Rosgaard, L., Andric, P., Dam-Johansen, K., Pedersen, S., & Meyer, A. S. (2007). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 143, 27–40. doi:10.1007/s12010-007-0028-1.
Jørgensen, H., Vibe-Pedersen, J., Larsen, J., & Felby, C. (2007). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 96, 862–870. doi:10.1002/bit.21115.
Lin, Y., & Tanaka, S. (2006). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 69, 627–642. doi:10.1007/s00253-005-0229-x.
Sluiter, A., Ruiz, R., Scarlata, C., Sluiter, J., & Templeton, D. (2008). National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden, CO, USA. Retrieved Aug. 8, 2008, from http://www.nrel.gov/biomass/analytical_procedures.html#lap-009.
Wood, T., & Bhat, K. M. (1988). Methods for measuring cellulase activities. In: Wood, W. A. and Kellogg, S. T. (eds.) Biomass—part A: cellulose and hemicellulose (pp. 87–112). San Diego: Academic.
Brown, L., & Torget, R. (1996). National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden, CO, USA. Retrieved Aug. 8, 2008, from http://www.nrel.gov/biomass/analytical_procedures.html#lap-009.
Acknowledgements
DONG Energy, Denmark, is gratefully thanked for the hydrothermally pretreated wheat straw. Novozymes A/S, Bagsværd, Denmark is gratefully thanked for the enzymes. The project is financially supported by the Danish Research Agency contract 2104-05-0008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kristensen, J.B., Felby, C. & Jørgensen, H. Determining Yields in High Solids Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Biomass. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 156, 127–132 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-008-8375-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-008-8375-0