Abstract
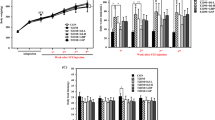
The effect of fermented mushroom of Coprinus comatus rich in trace elements, including vanadium, chromium, zinc, magnesium, copper, iron, and nickel, on glycemic metabolism was studied in this paper. Alloxan-induced hyperglycemic mice were used in the study. The blood glucose, glycohemoglobin, and glycogen synthesis of the mice were analyzed, respectively. At the same time, the gluconeogenesis of the normal mice was also determined. After the mice were administered (ig) with C. comatus rich in vanadium (CCRV), the blood glucose and the glycohemoglobin of alloxan-induced hyperglycemic mice decreased (p < 0.05, p < 0.01), glycogen synthesis of alloxan-induced hyperglycemic mice elevated (p < 0.01), the gluconeogenesis of the normal mice was inhibited (p < 0.01), and the sugar tolerance of the normal mice was improved. However, the same result did not occur in other groups. Vanadium at lower doses in combination with C. comatus induced significant effect on glycemic metabolism in mice.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Han C, Li J, Hui Q (2008) Determination of trace elements in Jinqi a traditional Chinese medicine. Biol Trace Elem Res.122:122–126.
A.B. Chausmer(1998).Zinc, insulin and diabetes. J. Am. Coll. Nutr.17 : 109–115.
R.A. Anderson, N. Cheng, and N. A. Bryden et al. (1997) Elevated intakes of supplemental chromium improve glucose and insulin variables in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes.46:1786–1791.
K. Kimura, (1996) Role of essential trace elements in the disturbance of carbohydrate metabolism. Nippon Rinsho.54:79–84.
M. Korc, (1983) Manganese action on pancreatic protein synthesis in normal and diabetic rats. Am. J. Physiol.245: 628–634.
A.D. Mooradian and J.E. Morely, (1987) Micronutrient status in diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Clin. Nutr.45:877–895
E.L.Novelli, N.L.Rodrigues and B.O.Ribas, (1988) Effect of nickel chloride on streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.66: 663–665.
J. Gil, M. Miralpeix, J. (1988) Carreras, R. Bartrons. Insulin-like effects of vanadate on glucokinase activity and fructose 2,6-bisphosphate levels in the liver of diabetic rats. J Biol Chem.263:1868–1871.
Y. Shechter. (1990) Insulin-mimetic effects of vanadate. Possible implications for future treatment of diabetes. Diabetes. 39: 1–5.
Han C, Cui B, Wang Y (2008) Vanadium uptake by biomass of Coprinus comatus and their effect on hyperglycemic mice. Biol Trace Elem Res. 124:35–39.
Domingo J L (2002) Vanadium and tungsten derivatives as antidiabetic agents: a review of their toxic effects. Biol Trace Elem Res 88:97–112.
A.H. Zargar, N.A. Shah and S.R.Masoodi et al (1998) Copper zinc and magnesium levels in non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Postgrad. Med. J.74: 665–668.
J. Cartana and L .Arola (1992) Nickel-induced hyperglycaemia: the role of insulin and glucagon. Toxicology.71:181–192.
S. Swaminathan, V.A. Fonseca, M.G. Alam and S.V. Shah, (2007) The role of iron in diabetes and its complications. Diabetes Care.30:1926–1933.
Swanston-Flatt SK, Day C, Bailey CJ, Flatt PR. (1989a) Evaluation of traditional plant treatments for diabetes: studies in streptozotocin diabetic mice. Acra Diaberologiu Larinu 26:51–55.
Kiho T, Tsujimura Y, Sakushima M, Usui S, Ukai S. (1994) Polysaccharides in fungi. XXXIII. Hypoglycemic activity of an acidic polysaccharide (AC) from Tremella fuciformis. Yakugaku Zasshi (in Japanese) 114: 308–315.
Kiho T, Sobue S, Ukai S (1994)Structural features and hypoglycemic activities of two polysaccharides from a hot-water extract of Agrocybe cylindracea. Carbohydr Res 251:81–7.
Kalac P, Niznamska M, Bevilaqua D, Staskova I.( 1996) Concentrations of mercury, copper, cadmium and lead in fruiting bodies of edible mushrooms in the vicinity of a mercury smelter and a copper smelter. Sci Total Enxiron 177: 251–258.
Kalac P, Svoboda L (2000) A review of trace element concentrations in edible mushrooms. Food Chem 69: 273–281.
Malinowska E, Szefer P, Falandaysz J (2004) Metals bioaccumulation by bay bolete, Xerocomus badius, from selected sites in Poland. Food Chem 84: 405–416.
Han C, Yuan J, wang Y. (2006) Hypoglycemic activity of fermented mushroom of Coprinus comatus rich in vanadium. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 20(3):191–196.
Zhou G, Han C,(2008). The co-effect of vanadium and fermented mushroom of Coprinus comatus on glycaemic metabolism. Biol Trace Elem Res. 124(1):20–27.
Y You, Z Lin (2003) Antioxidant effect of Ganoderma polysaccharide peptide. Acta Pharm Sinica 38: 85–88.
D Keppler, K Decker (1974) Glycogen. Methods of Enzymatic Analysis. In:H.U Bergmeyer, ed. New York: Academic Press, pp 11– 17.
D.B Duncan (1957) Multiple range tests for correlated and heteroscedastic means. Biometrics 13: 164–176.
K Sakurai,M Katoh, K Someno, Y Fujimoto (2001)Apoptosis and mitochondrial damage in INS-1 cells treated with alloxan. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 24: 876–882.
Lelley J. (1983) Investigations on the culture of the ink cap, Coprinus coniurus (Mull ex Fr) Gray. Mushroom Journul 129:14.
Bailey CJ, Turner SL, Jakeman K, Hayes WA.( 1984) Effect of Coprinus comatus on plasma glucose concentrations in mice.Planta Medica 50:525–26.
Acknowledgment
This project was supported by Science and Technology Program of Shandong Education Department of China (J08LH62) and projects for Young Scientist from IPCAS (08CX043004) and a NNSF grant (30800301).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, Y., Han, L., Yuan, C. et al. Comparison of Hypoglycemic Activity of Trace Elements Absorbed in Fermented Mushroom of Coprinus comatus . Biol Trace Elem Res 131, 177–185 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-009-8352-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-009-8352-7