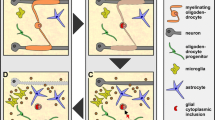
Abstract
Oligodendrocytes met neurotrophins in the early 1990s of the last century. Since then, their relationship underwent functional ups and downs partially dependent on the developmental stage of the oligodendroglial cells and the species, from which the cells were derived. This review provides a brief overview of oligodendroglial cells and neurotrophins, characterizes neurotrophin signaling during oligodendroglial development, and discusses the significance of proneurotrophins and sortilin for oligodendroglial death and survival. Furthermore, data are provided that TrkA, the tyrosine kinase competent NGF receptor, is localized to caveolincontaining microdomains on the oligodendroglial plasma membrane; an interplay of caveolin and NGF signaling via TrkA might be of functional importance. Finally, experimental evidence of studies is presented which support the idea that neurotrophins are promising candidates for improving oligodendroglial regeneration and remyelination.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, S. J., & Dawbarn, D. (2006). Clinical 4relevance of the neurotrophins and their receptors. Clinical Science, 110, 175–191.
Althaus, H. H. (2004). Remyelination in multiple sclerosis: a new role for neurotrophins? Progress in Brain Research, 146, 415–432.
Althaus, H. H., & Klöppner, S. (2006). Mature pig oligodendrocytes rapidly process human recombinant pro-nerve growth factor and do not undergo cell death. Journal of Neurochemistry, 98, 506–517.
Althaus, H. H., & Richter-Landsberg, C. (2000). Glial cells as targets and producers of neurotrophins. International Review of Cytology, (vol. 197, pp. 203–277). San Diego: Academic.
Althaus, H. H., Bürgisser, P., Klöppner, S., et al. (1987). Oligodendrocytes ensheath carbon fibers and produce myelin in vitro. In Glial-Neuronal Communication in Development and Regeneration. NATO ASI Series H 2 pp. 780–798. Berlin: Springer.
Althaus, H. H., Hempel, R., Klöppner, S., Engel, J., Schmidt-Schultz, T., Kruska, L., et al. (1997). Nerve growth factor signal transduction in mature pig oligodendrocytes. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 50, 729–742.
Althaus, H. H., Klöppner, S., Schmidt-Schultz, T., & Schwartz, P. (1992). Nerve growth factor induces proliferation and enhances fiber regeneration in oligodendrocytes isolated from adult pig brain. Neuroscience Letters, 135, 219–223.
Althaus, H. H., Kruska, L., Klöppner, S., & Heumann, R. (1994). Oligodendrocytes isolated from pig or rat, are both target cells for growth factors and cytokines, but respond to a different spectrum. 1st Europ. Meeting on Glial Cell Function in Health and Disease, p.50
Althaus, H. H., Montz, H., Neuhoff, V., & Schwartz, P. (1984). Isolation and cultivation of mature oligodendroglial cells. Naturwissenschaften, 71, 309–315.
Althaus, H. H., Mursch, K., & Klöppner, S. (2001). Differential response of mature TrkA/p75NTR expressing human and pig oligodendrocytes: aging, does it matter. Microscopy Research and Technique, 52, 689–699.
Barde, Y.-A., Edgar, D., & Thoenen, H. (1982). Purification of a new neurotrophic factor from mammalian brain. EMBO Journal, 1, 549–553.
Baron, W., Colognato, H., & FFrench-Constant, C. (2005). Integrin-growth factor interactions as regulators of oligodendroglial development and function. Glia, 49, 467–479.
Barres, B. A., Schmid, R., Sendnter, M., & Raff, M. C. (1993). Multiple extracellular signals are required for long-term oligodendrocyte survival. Development, 118, 283–295.
Barres, B. A., Raff, M. C., Gaese, F., Bartke, I., Dechant, G., & Barde, Y. (1994). A crucial role for neurotrophin-3 in oligodendrocyte development. Nature, 367, 371–375.
Baumann, N., & Pham-Dinh, D. (2001). Biology of oligodendrocyte and myelin in the mammalian central nervous system. Physiological Reviews, 81, 871–927.
Beattie, M. S., Harrington, A. W., Lee, R., et al. (2002). ProNGF induces p75-mediated death of oligodendrocytes following spinal cord injury. Neuron, 36, 375–386.
Benarroch, E. E. (2005). Neuro-astrocyte interactions: partnership for normal function and disease in the central nervous system. Mayo Clinic Proceedings, 80, 1326–1338.
Berninger, B., & Poo, M. M. (1998). Fast actions of neurotrophic factors. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 6, 324–330.
Berry, M., Hubbard, P., & Butt, A. M. (2002). Cytology and lineage of NG2-positive glia. Journal of Neurocytology, 31, 457–467.
Bhakar, A. L., Howell, J. L., Paul, C. E., et al. (2003). Apoptosis induced by p75NTR overexpression requires Jun kinase-dependent phosphorylation of Bad. Journal of Neuroscience, 23, 11373–11381.
Bierl, M. A., & Isaacson, L. G. (2007). Increased NGF proforms in aged sympathetic neurons and their targets. Neurobiology of Aging, 28, 122–134.
Bilderback, T. R., Gazula, V.-R., Lisanti, M. P., & Dobrowsky, R. T. (1999). Caveolin interacts with TrkA and p75NTR and regulates neurotrophin signalling pathways. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 274, 257–263.
Blesch, A. (2006). Neurotrophic factors in neurodegeneration. Brain Pathology, 16, 295–303.
Blöchl, A., & Blöchl, R. (2007). A cell-biological model of p75NTR signalling. Journal of Neurochemistry, 102, 289–305.
Bruno, M. A., & Cuello, A. C. (2006). Activity-dependent release of precursor nerve growth factor, conversion to mature nerve growth factor, and its degradation by a protease cascade. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103, 6735–6740.
Butt, A. M., Ibrahim, M., Ruge, F. M., & Berry, M. (1995). Biochemical subtypes of oligodendrocytes in the anterior medullary velum of the rat as revealed by the monoclonal antibody Rip. Glia, 14, 185–197.
Buttigieg, H., Kawaja, M., & Fahnestock, M. (2007). Neurotrophic activity of proNGF in vivo. Experimental Neurology, 204, 832–835.
Cao, Q., Xu, X.-M., deVries, W. H., et al. (2005). Functional recovery in traumatic spinal cord injury after transplantation of multineurotrophin-expressing glial-restricted precursor cells. Journal of Neuroscience, 25, 6947–6957.
Carmen, J., Magnus, T., Cassiani-Ingoni, R., Sherman, L., Rao, M. S., & Mattson, M. R. (2007). Revisiting the astrocyte-oligodendrocyte relationship in the adult CNS. Progress in Neurobiology, 82, 151–162.
Casaccia-Bonnefil, P., Carter, B. D., Dobrowsky, R. T., & Chao, M. V. (1996). Death of oligodendrocytes mediated by the interaction of nerve growth factor with its receptor p75. Nature, 383, 716–719.
Casper, K. B., & McCarthy, K. D. (2006). GFAP-positive progenitor cells produce neurons and oligodendrocytes throughout the CNS. Molecular and Cellular Neurosciences, 31, 676–684.
Chan, J. R., Watkins, T. A., Cosgaya, J. M., et al. (2004). NGF controls axonal receptivity to myelination by Schwann cells or oligodendrocytes. Neuron, 43, 183–191.
Chandran, S., Compston, A., Jauniaux, E., Gilson, J., Blakemore, W., & Svendsen, C. (2004). Differential generation of oligodendrocytes from human and rodent embryonic spinal cord neural precursors. Glia, 47, 314–324.
Chang, A., Nishiyama, A., Peterson, J., Prineas, J., & Trapp, B. D. (2000). NG2-positive oligodendrocyte progenitor cells in adult human brain and multiple sclerosis lesions. Journal of Neuroscience, 20, 6404–6412.
Chao, M. V., & Hempstead, B. L. (1995). p75 and Trk: a two-receptor system. Trends in Neuroscience, 18, 321–326.
Cohen, R. I., Marmur, R., Norton, W. T., Mehler, M. F., & Kessler, J. A. (1996). Nerve growth factor and neurotrophin-3 differentially regulate the proliferation and survival of developing rat brain oligodendrocytes. Journal of Neuroscience, 16, 6433–6442.
Coulson, E. J. (2006). Does the p75 neurotrophin receptor mediate A beta-induced toxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neurochemistry, 98, 654–660.
Coulson, E. J., Reid, K., Shipham, K. M., Morley, S., Kilpatrick, T. J., & Bartlett, P. F. (2004). The role of neurotransmission and the Copper domain in p75 neurotrophin receptor death signa- ling. Progress in Brain Research, 146, 41–62.
Dai, X., Qu, P., & Dreyfus, C. F. (2001). Neuronal signals regulate neurotrophin expression in oligodendrocytes of the basal forebrain. Glia, 34, 234–239.
Deadwyler, G. D., Pouly, S., Antel, J. P., & deVries, G. H. (2000). Neuregulins and ErbB receptor expression in adult human oligodendrocytes. Glia, 32, 304–312.
Dechant, G., & Barde, Y.-A. (2002). The neurotrophin receptor p75(NTR): novel functions and implications for diseasesofv the nervous system. Nature Neuroscience, 5, 1131–1136.
Domeniconi, M., Hempstead, B. L., & Chao, M. V. (2007). Pro-NGF secreted by astrocytes promotes motor neuron cell death. Molecular and Cellular Neurosciences, 34, 271–279.
Dowling, P., Ming, X., Raval, S., et al. (1999). Up-regulated p75(NTR) neurotrophin receptor on glial cells in MS plaques. Neurology, 53, 1676–1682.
Dreetz Gjerstad, M., Tandrup, T., Koltzenburg, M., & Jakobsen, J. (2002). Predominant neuronal B-cell loss in L5 DRG of p75 receptor deficient mice. Journal of Anatomy, 200, 81–87.
Du, Y. Z., & Dreyfus, C. F. (2002). Oligodendrocytes as providers of growth factors. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 68, 647–654.
Du, Y., Fischer, T. Z., Lee, L. N., Lercher, L. D., & Dreyfus, C. F. (2003). Regionally specific effects of BDNF on oligodendrocytes. Developmental Neuroscience, 25, 116–126.
Du, Y., Fischer, T. Z., Clinton-Luke, P., Lercher, L. D., & Dreyfus, C. F. (2006). Distinct effects of p75 in mediating actions of neurotrophins on basal forebrain oligodendrocytes. Molecular and Cellular Neurosciences, 31, 366–375.
Engel, J., Althaus, H. H., & Kristjansson, G. I. (1994). NGF increases [Ca2+]i in regenerating mature oligodendroglial cells. NeuroReport, 5, 397–400.
Engel, U., & Wolswijk, G. (1996). Oligodendrocyte-type-2 astrocyte (O-2A) progenitor cells derived from adult spinal cord: In vitro characteristics and response to PDGF, bFGF and NT-3. Glia, 16, 16–26.
Espinosa de los Monteros, A., Zhang, M., & deVellis, J. (1993). O2A progenitor cells transplanted into neonatal rat brain develop into oligodendrocytes but not astrocytes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 90, 50–54.
Fahnestock, M., Michalski, B., Xu, B., & Coughlin, M. D. (2001). The precursor pro-nerve growth factor is the predominant form of nerve growth factor in brain and is increased in Alzheimer’s disease. Molecular and Cellular Neurosciences, 18, 210–220.
Fahnestock, M., Yu, G., Michalski, B., et al. (2004a). The nerve growth factor precursor proNGF exhibits neurotrophic activity but is less active than mature nerve growth factor. Journal of Neurochemistry, 89, 581–592.
Fahnestock, M., Yu, G., & Coughlin, M. D. (2004b). ProNGF: a neurotrophic or an apoptotic molecule? Progress in Brain Research, 146, 101–110.
Farhadi, H. F., Mowla, S. J., Petrecca, K., Morris, S. J., Seidah, N. G., & Murphy, R. A. (2000). Neurotrophin-3 sorts to the constitutive secretory pathway of hippocampal neurons and is diverted to the regulated secretory pathway by coexpression with brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Journal of Neuroscience, 20, 4059–4068.
Fayard, B., Loeffler, S., Weis, J., Vögelin, E., & Krüttgen, A. (2005). The secreted brain-derived neurotrophic factor precursor pro-BDNF binds to TrkB and p75NTR but not to TrkA or TrkC. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 80, 18–28.
Fedoroff, S., & Vernadakis, A. (1986). Astrocytes, Vol.I-III. Orlando: Academic.
Filipovic, R., & Zecevic, N. (2008). The effect of CXCL1 on human fetal oligodendrocyte progenitor cells. Glia, 56, 1–15.
Fuccillo, M., Joyner, A. L., & Fishell, G. (2006). Morphogen to mitogen: the multiple roles of hedgehog signalling in vertebrate neural development. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 7, 772–783.
Gao, L., & Miller, R. H. (2006). Specification of optic nerve oligodendrocyte precursors by retinal ganglion cell axons. Journal of Neuroscience, 26, 7619–7628.
Girard, C., Bemelmans, A.-P., Dufour, N., et al. (2005). Grafts of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin 3-transduced primate Schwann cells lead to functional recovery of the demyelinated mouse spinal cord. Journal of Neuroscience, 25, 7924–7933.
Grinspan, J. (2002). Cells and signaling in oligodendrocyte development. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, 61, 297–306.
Haroutunian, V., & Davis, K. L. (2007). Introduction to the special section: Myelin and oligo- dendrocyte abnormalities in schizophrenia. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology, 10, 499–502.
Hardy, R., & Reynolds, R. (1991). Proliferation and differentiation potential of rat forebrain oligodendroglial progenitors both in vitro and in vivo. Development, 111, 1061–1080.
Heinrich, M., Gorath, M., & Richter-Landsberg, C. (1999). Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) modulated early differentiation of oligodendrocytes in rat brain corical cultures. Glia, 28, 244–255.
Hennigan, A., O’Callaghan, R. M., & Kelly, A. M. (2007). Neurotrophins and their receptors: roles in plasticity, neurodegeneration and neuroprotection. Biochemical Society Transactions, 35, 424–427.
Hermans-Borgmeyer, I., Hermey, G., Nykjaer, A., & Schaller, C. (1999). Expression of the 100- kDa neurotensin receptor sortilin during mouse embryonal development. Molecular Brain Research, 65, 216–219.
Heumann, R. (1994). Neurotrophin signalling. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 4, 668–679.
Huang, C.-S., Zhou, J., Feng, A. K., et al. (1999). Nerve growth factor signalling in caveolae- like domains at the plasma membrane. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 274, 36707–36714.
Huang, E. J., & Reichardt, L. F. (2001). Neurotrophins: roles in neuronal development and function. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 24, 677–736.
Ibañez, C. F. (2002). Jekyll-Hyde neurotrophins: the story of proNGF. Trends in Neuroscience, 25, 284–286.
Johe, K. K., Hazel, T. G., Müller, T., Dugich-Djordjevic, M. M., & McKay, R. D. G. (1996). Single factors direct the differentiation of stem cells from the fetal and adult central nervous system. Genes & Development, 10, 3129–3140.
Jones, K. R., & Reichardt, L. F. (1990). Molecular cloning of a human gene that is a member of the nerve growth factor family. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 87, 8060–8064.
Kagawa, T., Wada, T., & Ikenaka, K. (2001). Regulation of oligodendrocyte development. Microscopy Research and Technique, 52, 740–745.
Kahn, M. A., Kumar, S., Liebe, D., Chang, R., Parada, L. F., & deVellis, J. (1999). Mice lacking NT-3, and its receptor TrkC, exhibit profound deficiencies in CNS glial cells. Glia, 26, 153–165.
Karadottir, R., & Attwell, D. (2007). Neurotransmitter receptors in the life and death of oligodendrocytes. Neuroscience, 145, 1426–1438.
Kassmann, C. M., Lappe-Siefke, C., Baes, M., et al. (2007). Axonal loss and neuroinflammation caused by peroxisome-deficient oligodendrocytes. Nature Genetics, 39, 969–976.
Kavanaugh, B., Beesley, J., Itoh, T., Itoh, A., Grinspan, J., & Pleasure, D. (2000). Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) diminishes susceptibility of the oligodendroglial lineage to AMPA glutamate receptor-mediated excitotoxicity. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 60, 725–732.
Kim, S. U., & Yong, V. W. (1990). Growth factors in human glial cells in culture. In G. Jeserich, H. H. Althaus, & T. V. Waehneldt (Eds.) Cellular and molecular biology of myelination, NATOASI Series H Vol.43 (pp. 255–279). Berlin: Springer.
Klopfleisch, S. (2007). Inhibition der oligodendrogliären Cholesterinsynthese via Simvastatin: Negative Folgen für eine Remyelinisation? PhD thesis, University of Osnabrueck, Germany
Krause, S., Schindowski, K., Zechel, S., & von Bohlen, & Halbach, O. (2007). Expression of trkB and trkC receptors and their ligands brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 in the murine amygdala. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 86, 411–421
Krenz, N., & Weaver, L. C. (2000). Nerve growth factor in glia and inflammatory cells of the injured rat spinal cord. Journal of Neurochemistry, 74, 730–739.
Krüttgen, A., Möller, J. C., Heymach, J. V., & Shooter, E. M. (1998). Neurotrophins induce release of neurotrophins by the regulated secretory pathway. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 95, 9614–9619.
Kumar, S., & DeVellis, J. (1996). Neurotrophin activates signal transduction in oligodendroglial cells: expression of functional TrkC receptor isoforms. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 44, 490–498.
Kumar, S., Pena, L. A., & de Vellis, J. (1993). CNS glial cells express neurotrophin receptors whose levels are regulated by NGF. Molecular Brain Research, 7, 163–168.
Kumar, S., Kahn, M. A., Dirk, L., & deVellis, J. (1998). NT-3 mediated TrkC receptor activation promotes proliferation and cell survival of rodent progenitor oligodendrocyte cells in vitro and in vivo. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 54, 754–765.
Kumar, A., Sinha, R. A., Tiwari, M., et al. (2006). Increased pro-nerve growth factor and p75 neurotrophin receptor levels in developing hypothyroid rat cerebral cortex are associated with enhanced apoptosis. Endocrinology, 147, 4893–4903.
Kurzchalia, T. V., & Parton, R. G. (1999). Membrane microdomains and caveolae. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 11, 424–431.
Lachyankar, M. B., Condon, P. J., Quesenberry, P. J., Litofsky, N. S., Recht, L. D., & Ross, A. H. (1997). Embryonic precursor cells that express Trk receptors: Induction of different cell fates by NGF, BDNF, NT-3, and CNTF. Experimental Neurology, 144, 350–360.
Lad, S. P., & Neet, K. E. (2003). Activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway through p75NTR: a common mechanism for the neurotrophin family. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 73, 614–626.
Ladiwala, U., Lachance, C., Simoneau, S. J. J., Bhakar, A., Barker, P. A., & Antel, J. P. (1998). p75 neurotrophin receptor expression on adult human oligodendrocytes: signaling without cell death in response to NGF. Journal of Neuroscience, 18, 1297–1304.
Lappe-Siefke, C., Goebbels, S., Gravel, M., et al. (2003). Disruption of Cnp1 uncouples oligodendroglial functions in axonal support and myelination. Nature Genetics, 33, 366–374.
Lee, H., Volonte, D., Galbiati, F., et al. (2000). Constitutive and growth factor-regulated phosphorylation of caveolin-1 occurs at the same site (Tyr-14) in vivo: identification of a c-Src/Cav-1/Grb7 signaling cassette. Molecular Endocrinology, 14, 1750–1775.
Lee, R., Kermani, P., Teng, K. K., & Hempstead, B. L. (2001). Regulation of cell survival by secreted proneurotrophins. Science, 294, 1945–1948.
Lee, X., Yang, Z. S., Shao, Z. H., et al. (2007). NGF regulates the expression of axonal LINGO-1 to inhibit oligodendrocyte differentiation and myelination. Journal of Neuroscience, 27, 220–225.
Lei, L., & Parada, L. F. (2007). Transcriptional regulation of Trk family neurotrophin receptors. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 64, 522–532.
Lessmann, V., Gottmann, K., & Malcangio, M. (2003). Neurotrophin secretion: current facts and future prospects. Progress in Neurobiology, 69, 341–374.
Lorigados, L., Pavon, N., Serrano, T., Robinson, M. A., Fernandez, C. I., & Alvarez, P. (2001). Cambios en los niveles de factor de crecimiento nervioso con el envejecimiento y el tratamiento neurotrofico en primates no humanos. Revista de Neurologia, 33, 417–421.
Lu, B., Pang, P. T., & Woo, N. H. (2005). The Yin and Yang of neurotrophin action. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 6, 603–614.
Lugaro, E. (1907). Sulle funzioni della neuroglia. Rivista di Patologia Nervosa e Mentale, 12, 225–233.
McTigue, D. M., Horner, P. J., Stokes, B. T., & Gage, F. H. (1998). Neurotrophin-3 and brain-derived neurotrophic factor induce oligodendrocyte proliferation and myelination of regenerating axons in the contused adult rat spinal cord. Journal of Neuroscience, 18, 5354–5365.
Mi, S., Lee, X., Shao, Z., et al. (2004). LINGO-1 is a component of the Nogo-66 receptor/p75 signaling complex. Nature Neuroscience, 7, 221–228.
Micera, A., Lambiase, A., Rama, P., & Aloe, L. (1999). Altered nerve growth factor level in the optic nerve of patients affected by multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis, 5, 389–394.
Miron, V. E., Rajasekharan, S., Jarjour, A. A., Zamvil, S. S., Kennedy, T. E., & Antel, J. P. (2007). Simvastatin regulates oligodendroglial process dynamis and survival. Glia, 55, 130–143.
Mowla, S. J., Pareek, S., Farhadi, H. F., et al. (1999). Differential sorting of nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in hippocampal neurons. Journal of Neuroscience, 19, 2069–2080.
Mowla, S. J., Farhadi, H. F., Pareek, S., et al. (2001). Biosynthesis and post-translational processing of the precursor to brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276, 12660–12666.
Nakamura, K., Namekata, K., Harada, C., & Harada, T. (2007). Intracellular sortilin expression pattern regulates proNGF-induced maturally occurring cell death during development. Cell Death and Differentiation, 14, 1552–1554.
Nakayama, K. (1997). Furin: a mammalian subtilisin/Kex2p-like endoprotease involved in processing of a wide variety of precursor proteins. Biochemical Journal, 327, 625–635.
Nedergaard, M., Ransom, B., & Goldman, S. A. (2003). New roles for astrocytes: redefining the functional architecture of the brain. Trends Neuroscience, 26, 523–530.
Nicolay, D. J., Doucette, J. R., & Nazarali, A. J. (2007). Transcriptional control of oligodendrogenesis. Glia, 55, 1287–1299.
Nistor, G. I., Totoiu, M. O., Haque, N., Carpenter, M. K., & Keirstead, H. S. (2005). Human embryonic stem cells differentiate into oligodendrocytes in high purity and myelinate after spinal cord transplantation. Glia, 49, 385–396.
Noble, M. (2004). The possible role of myelin destruction as a precipitating event in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 25, 25–31.
Notterpek, L. (2003). Neurotrophins in myelination: a new role for a puzzling receptor. Trends Neuroscience, 26, 232–234.
Nykjaer, A., Lee, R., Teng, K. K., et al. (2004). Sortilin is essential for proNGF-induced neuronal cell death. Nature, 427, 843–848.
Nykjaer, A., Willnow, T. E., & Petersen, C. M. (2005). p75NTR-live or let die. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 15, 49–57.
Paratcha, G., & Ibanez, C. F. (2002). Lipid rafts and the control of neurotrophic factor signaling in the nervous system: variation on a theme. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 12, 542–549.
Pawson, T., Olivier, P., Rozakis-Adcock, M., McGlade, J., & Henkemeyer, M. (1993). Proteins with SH2 and SH3 domains couple receptor tyrosine kinases to intracellular signalling pathways. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 340, 279–285.
Pearson, G., Robinson, F., Gibson, T. B., et al. (2001). Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: Regulation and physiological functions. Endocrine Reviews, 22, 153–183.
Peiro, S., Comella, J. X., Enrich, C., Martin-Zanca, D., & Rocamora, N. (2000). PC12 cells have caveolae that contain TrkA. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275, 37846–37852.
Peng, S., Wuu, J., Mufson, E. J., & Fahnestock, M. (2005). Precursor form of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and mature brain-derived neurotrophic factor are decreased in the pre- clinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neurochemistry, 93, 1412–1421.
Pfeiffer, S. E., Warrington, A. E., & Bansal, R. (1993). The oligodendrocyte and its many cellular processes. Trends in Cell Biology, 3, 191–197.
Pierce, S. K. (2004). To cluster or not to cluster: FRETting over rafts. Nature Cell Biology, 6, 180–181.
Rabizadeh, S., Oh, J., Zhong, L. Z., et al. (1993). Induction by apoptosis by low-affinity NGF receptor. Science, 243, 1450–1455.
Reichardt, L. F. (2006). Neurotrophin-regulated signalling pathways. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 361, 1545–1564.
Rice, C., & Scolding, N. (2007). Strategies for achieving and monitoring myelin repair. Journal of Neurology, 254, 275–283.
Richardson, W. D., Kessaris, N., & Pringle, N. (2006). Oligodendrocyte wars. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 7, 11–18.
Richter-Landsberg, C., & Bauer, N. G. (2004). Tau-inclusion body formation in oligodendroglia: the role of stress proteins and proteasome inhibition. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience, 22, 443–451.
Rifkin, J. T., Todd, V. J., Anderson, L. W., & Lefcort, B. (2000). Dynamic expression of neurotrophin receptors during sensory neuron genesis and differentiation. Developmental Biologies, 227, 465–480.
Robinson, S., & Miller, R. (1996). Environmental enhancement of growth factor-mediated oligodendrocyte precursor proliferation. Molecular and Cellular Neurosciences, 8, 38–52.
Rosenberg, S. S., Ng, B. K., & Chan, J. R. (2006). The quest for remyelination: A new role for neurotrophins and their receptors. Brain Pathology, 16, 288–294.
Roux, P. P., & Barker, P. A. (2002). Neurotrophin signalling through the p75 neurotrophin receptor. Progress in Neurobiology, 67, 203–233.
Satoh, J., & Kim, S. U. (1994). Proliferation and differentiation of fetal human oligodendrocytes in culture. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 39, 260–272.
Scarisbrick, I. A., Asakura, K., & Rodriguez, M. (2000). Neurotrophin-4/5 promotes proliferation of oligodendrocyte-type-2 astrocytes (O-2A). Developmental Brain Research, 123, 87–90.
Schmitz, M. (2006). Expression und Funktion von Caveolin bei Gliazellen, insbesondere Oligodendrozyten. PhD thesis, University of Goettingen, Germany.
Schor, N. F. (2005). The p75 neurotrophin receptor in human development and disease. Progress in Neurobiology, 77, 201–214.
Schuldiner, M., Yanuka, O., Itskovitz-Eldor, J., Melton, D. A., & Benvenisty, N. (2000). Effects of eight growth factors on the differentiation of cells derived from human emryonicstem cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97, 11307–11312.
Schwartz, P. H., Nethercott, H., Kirov, I. I., Ziaeian, B., Young, M. J., & Klassen, H. (2005). Expression of neurodevelopmental markers by cultured porcine neural precursor cells. Stem Cells, 23, 1286–1294.
Scolding, N. J., Rayner, P. J., Sussman, J., Shaw, C., & Compston, D. A. S. (1995). A proliferative adult human oligodendrocyte progenitor. NeuroReport, 6, 441–445.
Seidah, N. G., Benjannet, S., Pareek, S., et al. (1996). Cellular processing of the nerve growth factor precursor by the mammalian pro-protein convertase. Biochemical Journal, 314, 951–960.
Seidah, N. G., Mowla, S. J., Hamelin, J., et al. (1999). Mammalian subtilisin/kexin isozyme SKI- 1: a widely expressed proprotein convertases with a unique cleavage specificity and cellular localization. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 96, 1321–1326.
Shalizi, A., Lehtinen, M., Gaudilliere, B., et al. (2003). Characterization of a neurotrophin signalling mechanism that mediates neuron survival in a temporally specific pattern. Journal of Neuroscience, 23, 7326–7336.
Simons, K., & van Meer, G. (1988). Lipid sorting in epithelial cells. Biochemistry, 27, 6197–6202.
Simons, K., & Toomre, D. (2000). Lipid rafts and signal transduction. Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology, 1, 31–39.
Sofroniew, M. V., Howe, C. L., & Mobley, W. C. (2001). Nerve growth factor signalling, neuroprotection, and neural repair. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 24, 1217–1281.
Soilu-Hänninen, M., Epa, R., Shipham, K., Butzkueven, H., Bucci, T., Barrett, G., et al. (2000). Treatment of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis with antisense oligonucleotides against the low affinity neurotrophin receptor. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 59, 712–721.
Soliven, B. (2001). Calcium signalling in cells of oligodendroglial lineage. Microscopy Research and Technique, 52, 672–679.
Song, S. K., Li, S., Okamoto, T., Quilliam, L. A., Sargiacomo, L. A., & Lisanti, M. P. (1996). Co- purification and direct interaction of Ras with caveolin, an integral membrane protein of caveolae microdomains. Detergent-free purification of caveolae microdomains. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 271, 9690–9697.
Song, L., Ge, S. J., & Pachter, J. S. (2007). Caveolin-1 regulates expression of junction-associated proteins in brain microvascular endothelial cells. Blood, 109, 1515–1523.
Srinivasan, B., Roque, C. H., Hempstead, B. L., Al-Ubaidi, M. R., & Roque, R. S. (2004). Microglia- derived pronerve growth factor promotes photoreceptor cell death via p75 neurotrophin receptor. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 41839–41845.
Stariha, R. L., & Kim, S. U. (2001). Protein kinase C and mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling in oligodendrocytes. Microscopy Research and Technique, 52, 680–688.
Starkey, G. D., Petratos, S., Shipham, K. A., et al. (2001). Neurotrophin receptor expression and responsiveness by postnatal cerebral oligodendroglia. NeuroReport, 12, 4081–4086.
Takano, R., Hisahara, S., Namikawa, K., Kijama, H., Okano, H., & Miura, M. (2000). Nerve growth factor protects oligodendrocytes from TNF-a-induced injury through Akt-mediated signaling mechanisms. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275, 16360–16365.
Taylor, S., Srinivasan, B., Wordinger, R. J., & Roque, R. S. (2003). Glutamate stimulates neurotrophin expression in cultured Müller cells. Molecular Brain Research, 111, 189–197.
Teng, K. K., & Hempstead, B. L. (2004). Neurotrophins and their receptors: signaling trios in complex biological systems. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 61, 35–48.
Thomas, G. (2002). Furin at the cutting edge: from protein traffic to embryogenesis and disease. Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology, 3, 753–766.
Tominaga, M., Honda, S., Okada, A., Ikeda, A., Kinoshita, S., & Tomooka, Y. (2005). A bipotent neural progenitor cell line cloned from a cerebellum of an adult p53-deficient mouse generates both neurons and oligodendrocytes. European Journal of Neuroscience, 21, 2903–2911.
Tsuruda, A., Suzuki, S., Maekawa, T., & Oka, S. (2004). Constitutively active Src facilitates NGF- induced phosphorylation of TrkA and causes enhancement of the MAPK signalling in SK-N- MC cells. FEBS Letters, 560, 215–220.
Twiss, J. L., Chang, J. H., & Schanen, N. C. (2006). Pathophysiological mechanisms for actions of the neurotrophins. Brain Pathology, 16, 320–332.
Valdo, P., Stegagno, C., Mazzucco, S., et al. (2002). Enhanced expression of NGF receptors in multiple scleosis lesions. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, 61, 91–98.
van der Geer, P., & Pawson, T. (1995). The PZB domain: a new protein module implicated in signal transduction. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 20, 277–280.
Villoslada, P., & Genain, C. P. (2004). Role of nerve growth factor and other trophic factors in brain inflammation. Progress in Brain Research, 146, 403–414).
Weston, C. R., & Davis, R. J. (2007). The JNK signal transduction pathway. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 19, 142–149.
Wilkins, A., Majed, H., Layfield, R., Compston, A., & Chandran, S. (2003). Oligodendrocytes promote neuronal survival and axonal length by distinct intracellular mechanisms: A novel role for oligodendrocyte-derived glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. Journal of Neuroscience, 23, 4967–4974.
Willerth, S. M., Faxel, T. E., Gottlieb, D. L., & Sakiyama-Elbert, S. (2007). The effects of soluble growth factors on embryonic stem cell differentiation inside of fibrin scaffolds. Stem Cells, 25, 2235–2244.
Williams, B. P., Read, J., & Price, J. (1991). The generation of neurons and oligodendrocytes from a common precursor cell. Neuron, 7, 685–693.
Wilson, H. C., Onischke, C., & Raine, C. S. (2003). Human oligodendrocyte precursor cells in vitro: Phenotypic analysis and differential response to growth factors. Glia, 44, 153–165.
Xin, M., Yue, T., Ma, Z., Wu, F.-F., Gow, A., & Lu, Q. R. (2005). Myelinogenesis and axonal recognition by oligodendrocytes in brain are uncoupled in Olig1-null mice. Journal of Neuroscience, 25, 1354–1365.
Yamashita, T., & Tohyama, M. (2003). The p75 receptor acts as a displacement factor that releases Rho from Rho-GDI. Nature Neuroscience, 6, 461–467.
Yoon, S. O., Casaccia-Bonnefil, P., Carter, B. D., & Chao, M. V. (1998). Competitive signalling between TrkA and p75 nerve growth factor receptors determines cell survival. Journal of Neuroscience, 18, 3273–3281.
Yune, T. Y., Lee, J. Y., Jung, G. Y., et al. (2007). Minocycline alleviates death of oligodendrocytes by inhibiting pro-nerve growth factor production in microglia after spinal cord injury. Journal of Neuroscience, 27, 7751–7761.
Zampieri, N., & Chao, M. V. (2006). Mechanisms of neurotrophin receptor signalling. Biochemical Society Transactions, 34, 607–611.
Zhang, Y. W., Denham, J., & Thies, R. S. (2006). Oligodendrocyte progenitor cells derived from human embryonic stem cells express neurotrophic factors. Stem Cells Develop., 15, 943–952.
Zhang, Y.-Z., Moheban, D. B., Conway, B. R., Bhattacharyya, A., & Segal, R. A. (2000). Cell surface Trk receptors mediate NGF-induced survival while internalized receptors regulate NGF- induced differentiation. Journal of Neuroscience, 20, 5671–5678.
Zhang, S. C., Wernig, M., Duncan, I. D., Brüstle, O., & Thomson, J. A. (2001). In vitro differentiation of transplantable neural precursors from human embryonic stem cells. Nature Biotechnology, 19, 1129–1133.
Zhou, Q., & Anderson, D. J. (2002). The bHLH transcription factors OLIG2 and OLIG1 couple neuronal and glial subtype specification. Cell, 109, 61–73.
Zhou, X.-F., Song, X.-Y., Zhong, J.-H., et al. (2004). Distribution and localization of pro-brain derived neurotrophic factor-like immunoreactivity in the peripheral and central nervous system of the adult rat. Journal of Neurochemistry, 91, 704–713.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Althaus, H.H., Klöppner, S., Klopfleisch, S. et al. Oligodendroglial Cells and Neurotrophins: A Polyphonic Cantata in Major and Minor. J Mol Neurosci 35, 65–79 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-008-9053-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-008-9053-y