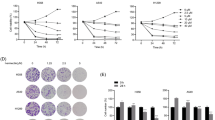
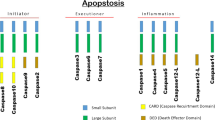
Abstract
Fas-associated death domain (FADD) is a common adaptor molecule which plays an important role in transduction of death receptor mediated apoptosis. The FADD provides DED motif for binding to both procaspase-8 and cFLIP molecules which executes death receptor mediated apoptosis. Dysregulated expression of FADD and cFLIP may contribute to inhibition of apoptosis and promote cell survival in cancer. Moreover elevated intracellular level of cFLIP competitively excludes the binding of procaspase-8 to the death effector domain (DED) of FADD at the DISC to block the activation of death receptor signaling required for apoptosis. Increasing evidence shows that defects in FADD protein expression are associated with progression of malignancies and resistance to apoptosis. Therefore, improved expression and function of FADD may provide new paradigms for regulation of cell proliferation and survival in cancer. In the present study, we have examined the potential of FADD in induction of apoptosis by overexpression of FADD in HEK 293T cells and validated further its consequences on the expression of pro and anti-apoptotic proteins besides initiation of death receptor mediated signaling. We have found deficient expression of FADD and elevated expression of cFLIPL in HEK 293T cells. Our results demonstrate that over expression of FADD attenuates the expression of anti-apoptotic protein cFLIP and activates the cascade of extrinsic caspases to execution of apoptosis in HEK 293T cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DED:
-
Death Effector Domain
- DISC:
-
Death-Inducing Signaling Complex
- cFLIP:
-
Cellular fas-associated death domain-like interleukin-1-β- converting enzyme-inhibitory protein
- CHX:
-
Cycloheximide
- CD 95L:
-
CD 95 ligand
References
Algeciras-Schimnich A, Shen L, Barnhart BC, Murmann AE, Burkhardt JK, Peter ME (2002) Molecular ordering of the initial signaling events of CD95. Mol Cell Biol 22:207–220
Bagnoli M, Ambrogi F, Pilotti S, Alberti P, Ditto A, Barbareschi M, Galligioni E, Biganzoli E, Canevari S, Mezzanzanica D (2009) c-FLIPL expression defines two ovarian cancer patient subsets and is a prognostic factor of adverse outcome. Endocr Relat Canc 16:443–453
Bagnoli M, Canevari S, Mezzanzanica D (2010) Cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein (c-FLIP) signalling: a key regulator of receptor-mediated apoptosis in physiologic context and in cancer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 42:210–213
Beisner DR, Chu IH, Arechiga AF, Hedrick SM, Walsh CM (2003) The requirements for Fas-associated death domain signaling in mature T cell activation and survival. J Immunol 171:247–256
Bell BD, Leverrier S, Weist BM, Newton RH, Arechiga AF, Luhrs KA, Morrissette NS, Walsh CM (2008) FADD and caspase-8 control the outcome of autophagic signaling in proliferating T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:16677–16682
Brumatti G, Yon M, Castro FA, Bueno-da-Silva AE, Jacysyn JF, Brunner T, Amarante-Mendes GP (2008) Conversion of CD95 (Fas) Type II into Type I signaling by sub-lethal doses of cycloheximide. Exp Cell Res 314:554–563
Chang DW, Xing Z, Pan Y, Algeciras-Schimnich A, Barnhart BC, Yaish-Ohad S, Peter ME, Yang X (2002) c-FLIP(L) is a dual function regulator for caspase-8 activation and CD95-mediated apoptosis. EMBO J 21:3704–3714
Chinnaiyan AM, O’Rourke K, Tewari M, Dixit VM (1995) FADD, a novel death domain-containing protein, interacts with the death domain of Fas and initiates apoptosis. Cell 81:505–512
Chinnaiyan AM, Tepper CG, Seldin MF, O’Rourke K, Kischkel FC, Hellbardt S, Krammer PH, Peter ME, Dixit VM (1996) FADD/MORT1 is a common mediator of CD95 (Fas/APO-1) and tumor necrosis factor receptor-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 271:4961–4965
Debatin KM, Krammer PH (2004) Death receptors in chemotherapy and cancer. Oncogene 23:2950–2966
Fischer-Posovszky P, Keuper M, Nagel S, Hesse D, Schurmann A, Debatin KM, Strauss G, Wabitsch M (2011) Downregulation of FLIP by cycloheximide sensitizes human fat cells to CD95-induced apoptosis. Exp Cell Res 317:2200–2209
Foger N, Bulfone-Paus S, Chan AC, Lee KH (2009) Subcellular compartmentalization of FADD as a new level of regulation in death receptor signaling. FEBS J 276:4256–4265
Fulda S, Meyer E, Debatin KM (2000) Metabolic inhibitors sensitize for CD95 (APO-1/Fas)-induced apoptosis by down-regulating Fas-associated death domain-like interleukin 1-converting enzyme inhibitory protein expression. Cancer Res 60:3947–3956
Golks A, Brenner D, Fritsch C, Krammer PH, Lavrik IN (2005) c-FLIPR, a new regulator of death receptor-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 280:14507–14513
Golks A, Brenner D, Krammer PH, Lavrik IN (2006) The c-FLIP-NH2 terminus (p22-FLIP) induces NF-kappaB activation. J Exp Med 203:1295–1305
Gomez-Angelats M, Cidlowski JA (2003) Molecular evidence for the nuclear localization of FADD. Cell Death Differ 10:791–797
Holler N, Tardivel A, Kovacsovics-Bankowski M, Hertig S, Gaide O, Martinon F, Tinel A, Deperthes D, Calderara S, Schulthess T, Engel J, Schneider P, Tschopp J (2003) Two adjacent trimeric Fas ligands are required for Fas signaling and formation of a death-inducing signaling complex. Mol Cell Biol 23:1428–1440
Irmler M, Thome M, Hahne M, Schneider P, Hofmann K, Steiner V, Bodmer JL, Schroter M, Burns K, Mattmann C, Rimoldi D, French LE, Tschopp J (1997) Inhibition of death receptor signals by cellular FLIP. Nature 388:190–195
Kavuri SM, Geserick P, Berg D, Dimitrova DP, Feoktistova M, Siegmund D, Gollnick H, Neumann M, Wajant H, Leverkus M (2011) Cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein (cFLIP) isoforms block CD95- and TRAIL death receptor-induced gene induction irrespective of processing of caspase-8 or cFLIP in the death-inducing signaling complex. J Biol Chem 286:16631–16646
Krammer PH (1999) CD95(APO-1/Fas)-mediated apoptosis: live and let die. Adv Immunol 71:163–210
Krueger A, Baumann S, Krammer PH, Kirchhoff S (2001) FLICE-inhibitory proteins: regulators of death receptor-mediated apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 21:8247–8254
Lavrik IN, Golks A, Riess D, Bentele M, Eils R, Krammer PH (2007) Analysis of CD95 threshold signaling: triggering of CD95 (FAS/APO-1) at low concentrations primarily results in survival signaling. J Biol Chem 282:13664–13671
Lavrik IN, Mock T, Golks A, Hoffmann JC, Baumann S, Krammer PH (2008) CD95 stimulation results in the formation of a novel death effector domain protein-containing complex. J Biol Chem 283:26401–26408
Longley DB, Wilson TR, McEwan M, Allen WL, McDermott U, Galligan L, Johnston PG (2006) c-FLIP inhibits chemotherapy-induced colorectal cancer cell death. Oncogene 25:838–848
Matsuda F, Inoue N, Goto Y, Maeda A, Cheng Y, Sakamaki K, Manabe N (2008) cFLIP regulates death receptor-mediated apoptosis in an ovarian granulosa cell line by inhibiting procaspase-8 cleavage. J Reprod Dev 54:314–320
Osborn SL, Diehl G, Han SJ, Xue L, Kurd N, Hsieh K, Cado D, Robey EA, Winoto A (2010) Fas-associated death domain (FADD) is a negative regulator of T-cell receptor-mediated necroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:13034–13039
Peter ME, Krammer PH (2003) The CD95(APO-1/Fas) DISC and beyond. Cell Death Differ 10:26–35
Peter ME, Legembre P, Barnhart BC (2005) Does CD95 have tumor promoting activities? Biochim Biophys Acta 1755:25–36
Rogers KM, Thomas M, Galligan L, Wilson TR, Allen WL, Sakai H, Johnston PG, Longley DB (2007) Cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein regulates chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 6:1544–1551
Ryu BK, Lee MG, Chi SG, Kim YW, Park JH (2001) Increased expression of cFLIP(L) in colonic adenocarcinoma. J Pathol 194:15–19
Safa AR, Day TW, Wu CH (2008) Cellular FLICE-like inhibitory protein (C-FLIP): a novel target for cancer therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 8:37–46
Scaffidi C, Schmitz I, Krammer PH, Peter ME (1999) The role of c-FLIP in modulation of CD95-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 274:1541–1548
Scaffidi C, Volkland J, Blomberg I, Hoffmann I, Krammer PH, Peter ME (2000) Phosphorylation of FADD/MORT1 at serine 194 and association with a 70-kDa cell cycle-regulated protein kinase. J Immunol 164:1236–1242
Schulze-Osthoff K, Ferrari D, Los M, Wesselborg S, Peter ME (1998) Apoptosis signaling by death receptors. Eur J Biochem/FEBS 254:439–459
Screaton RA, Kiessling S, Sansom OJ, Millar CB, Maddison K, Bird A, Clarke AR, Frisch SM (2003) Fas-associated death domain protein interacts with methyl-CpG binding domain protein 4: a potential link between genome surveillance and apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:5211–5216
Shirley S, Micheau O (2010) Targeting c-FLIP in cancer. Cancer Lett. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2010.10.009
Song W, Lahiri DK (1995) Efficient transfection of DNA by mixing cells in suspension with calcium phosphate. Nucleic Acids Res 23:3609–3611
Taylor RC, Cullen SP, Martin SJ (2008) Apoptosis: controlled demolition at the cellular level. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:231–241
Tourneur L, Chiocchia G (2010) FADD: a regulator of life and death. Trends Immunol 31:260–269
Tourneur L, Mistou S, Michiels FM, Devauchelle V, Renia L, Feunteun J, Chiocchia G (2003) Loss of FADD protein expression results in a biased Fas-signaling pathway and correlates with the development of tumoral status in thyroid follicular cells. Oncogene 22:2795–2804
Tourneur L, Delluc S, Levy V, Valensi F, Radford-Weiss I, Legrand O, Vargaftig J, Boix C, Macintyre EA, Varet B, Chiocchia G, Buzyn A (2004) Absence or low expression of fas-associated protein with death domain in acute myeloid leukemia cells predicts resistance to chemotherapy and poor outcome. Cancer Res 64:8101–8108
Tourneur L, Buzyn A, Chiocchia G (2005) FADD adaptor in cancer. Med Immunol 4:1
Vaux DL, Haecker G, Strasser A (1994) An evolutionary perspective on apoptosis. Cell 76:777–779
Wajant H, Haas E, Schwenzer R, Muhlenbeck F, Kreuz S, Schubert G, Grell M, Smith C, Scheurich P (2000) Inhibition of death receptor-mediated gene induction by a cycloheximide-sensitive factor occurs at the level of or upstream of Fas-associated death domain protein (FADD). J Biol Chem 275:24357–24366
Yeh WC, Pompa JL, McCurrach ME, Shu HB, Elia AJ, Shahinian A, Ng M, Wakeham A, Khoo W, Mitchell K, El-Deiry WS, Lowe SW, Goeddel DV, Mak TW (1998) FADD: essential for embryo development and signaling from some, but not all, inducers of apoptosis. Science 279:1954–1958
Yu JW, Jeffrey PD, Shi Y (2009) Mechanism of procaspase-8 activation by c-FLIPL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:8169–8174
Zhang J, Cado D, Chen A, Kabra NH, Winoto A (1998) Fas-mediated apoptosis and activation-induced T-cell proliferation are defective in mice lacking FADD/Mort1. Nature 392:296–300
Zhang J, Kabra NH, Cado D, Kang C, Winoto A (2001) FADD-deficient T cells exhibit a disaccord in regulation of the cell cycle machinery. J Biol Chem 276:29815–29818
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Dr. Andrew Thorburn, University of Colorado Denver, Aurora for providing the construct of full length FADD and Puri Foundation for education and research in India for providing existing facility and supports. This work was supported by grants from the Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science & Technology, Government of India under Rapid Grant for Young Investigator Scheme 2011 (BT/PR15083/GBD/27/306/2011) and J. C. Bose fellowship of Department of Science & Technology to AS.
Conflicts of interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranjan, K., Surolia, A. & Pathak, C. Apoptotic potential of Fas-associated death domain on regulation of cell death regulatory protein cFLIP and death receptor mediated apoptosis in HEK 293T cells. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 6, 155–168 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-012-0166-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-012-0166-2