Abstract
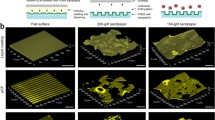
Concentration gradients of ECM proteins play active roles in many areas of cell biology including wound healing and metastasis. They may also form the basis of tissue engineering scaffolds, as these can direct cell adhesion and migration and promote new matrix synthesis. To better understand cell–matrix interactions on attractive gradients, we have used multiphoton excited (MPE) photochemistry to fabricate covalently linked micro-structured gradients from fibronectin (FN). The gradient design is comprised of a parallel series of individual linear gradients with overall dimensions of approximately 800 × 800 µm, where a linear dynamic range of nearly 10-fold in concentration was achieved. The adhesion dynamics of 3T3 fibroblasts were investigated, where the cell morphology and actin cytoskeleton became increasingly elongated and aligned with the direction of the gradient at increasing protein concentration. Moreover, the cell morphologies are distinct when adhered to regions of differing FN concentration but with similar topography. These results show that the fabrication approach allows investigating the roles of contact guidance and ECM cues on the cell–matrix interactions. We suggest this design overcomes some of the limitations with other fabrication methods, especially in terms of 3D patterning capabilities, and will serve as a new tool to study cell–matrix interactions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basu, S., and P. J. Campagnola. Properties of crosslinked protein matrices for tissue engineering applications synthesized by multiphoton excitation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 71A(2):359–368, 2004.
Basu, S., L. P. Cunningham, G. Pins, K. Bush, R. Toboada, A. R. Howell, J. Wang, and P. J. Campagnola. Multi-photon excited fabrication of collagen matrices crosslinked by a modified benzophenone dimer: bioactivity and enzymatic degradation. Biomacromolecules 6:1465–1474, 2005.
Basu, S., C. W. Wolgemuth, and P. J. Campagnola. Measurement of normal and anomalous diffusion of dyes within protein structures fabricated via multi-photon excited crosslinking. Biomacromolecules 5:2347–2357, 2004.
Belisle, J. M., J. P. Correia, P. W. Wiseman, T. E. Kennedy, and S. Costantino. Patterning protein concentration using laser-assisted adsorption by photobleaching, LAPAP. Lab Chip 8(12):2164–2167, 2008.
Brandley, B. K., and R. L. Schnaar. Tumor cell haptotaxis on covalently immobilized linear and exponential gradients of a cell adhesion peptide. Dev. Biol. 135(1):74–86, 1989.
Burdick, J. A., A. Khademhosseini, and R. Langer. Fabrication of gradient hydrogels using a microfluidics/photopolymerization process. Langmuir 20(13):5153–5156, 2004.
Campagnola, P. J., A. R. Howell, D. Delguidas, G. A. Epling, J. D. Pitts, and S. L. Goodman. 3-Dimensional sub-micron polymerization of acrylamide by multi-photon excitation of xanthene dyes. Macromolecules 33:1511–1513, 2000.
Chen, X., M. A. Brewer, C. Zou, and P. J. Campagnola. Adhesion and migration of ovarian cancer cells on crosslinked laminin fibers nanofabricated by multiphoton excited photochemistry. Integr. Biol. 1:469–476, 2009.
Cunningham, L. P., M. P. Veilleux, and P. J. Campagnola. Freeform multiphoton excited microfabrication for biological applications using a rapid prototyping CAD-based approach. Opt. Express 14:8613–8621, 2006.
Dalby, M. J., M. O. Riehle, D. S. Sutherland, H. Agheli, and A. S. Curtis. Fibroblast response to a controlled nanoenvironment produced by colloidal lithography. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 69A(2):314–322, 2004.
DeLong, S. A., A. S. Gobin, and J. L. West. Covalent immobilization of RGDS on hydrogel surfaces to direct cell alignment and migration. J. Controlled Release 109(1–3):139–148, 2005.
DeLong, S. A., J. J. Moon, and J. L. West. Covalently immobilized gradients of bFGF on hydrogel scaffolds for directed cell migration. Biomaterials 26(16):3227–3234, 2005.
Dertinger, S. K., X. Jiang, Z. Li, V. N. Murthy, and G. M. Whitesides. Gradients of substrate-bound laminin orient axonal specification of neurons. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99(20):12542–12547, 2002.
Doyle, A. D., F. W. Wang, K. Matsumoto, and K. M. Yamada. One-dimensional topography underlies three-dimensional fibrillar cell migration. J. Cell Biol. 184(4):481–490, 2009.
Fricke, R., P. D. Zentis, L. T. Rajappa, B. Hofmann, M. Banzet, A. Offenhausser, and S. H. Meffert. Axon guidance of rat cortical neurons by microcontact printed gradients. Biomaterials 32(8):2070–2076, 2011.
Gallant, N. D., K. E. Michael, and A. J. Garcia. Cell adhesion strengthening: contributions of adhesive area, integrin binding, and focal adhesion assembly. Mol. Biol. Cell 16(9):4329–4340, 2005.
Garcia, A. J., and N. D. Gallant. Stick and grip: measurement systems and quantitative analyses of integrin-mediated cell adhesion strength. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 39(1):61–73, 2003.
Gunawan, R. C., E. R. Choban, J. E. Conour, J. Silvestre, L. B. Schook, H. R. Gaskins, D. E. Leckband, and P. J. Kenis. Regiospecific control of protein expression in cells cultured on two-component counter gradients of extracellular matrix proteins. Langmuir 21(7):3061–3068, 2005.
Gunawan, R. C., J. Silvestre, H. R. Gaskins, P. J. Kenis, and D. E. Leckband. Cell migration and polarity on microfabricated gradients of extracellular matrix proteins. Langmuir 22(9):4250–4258, 2006.
Isenberg, B. C., P. A. Dimilla, M. Walker, S. Kim, and J. Y. Wong. Vascular smooth muscle cell durotaxis depends on substrate stiffness gradient strength. Biophys. J. 97(5):1313–1322, 2009.
Jeon, N. L., S. K. W. Dertinger, D. T. Chiu, I. S. Choi, A. D. Stroock, and G. M. Whitesides. Generation of solution and surface gradients using microfluidic systems. Langmuir 16(22):8311–8316, 2000.
Kaehr, B., R. Allen, D. J. Javier, J. Currie, and J. B. Shear. Guiding neuronal development with in situ microfabrication. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101(46):16104–16108, 2004.
Kaunas, R., P. Nguyen, S. Usami, and S. Chien. Cooperative effects of Rho and mechanical stretch on stress fiber organization. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 102(44):15895–15900, 2005.
LaFratta, C. N., D. Lim, K. O’Malley, T. Baldacchini, and J. T. Fourkas. Direct laser patterning of conductive wires on three-dimensional polymeric microstructures. Chem. Mater. 18(8):2038–2042, 2006.
Mai, J., L. Fok, H. Gao, X. Zhang, and M. M. Poo. Axon initiation and growth cone turning on bound protein gradients. J. Neurosci. 29(23):7450–7458, 2009.
Maruo, S., O. Nakamura, and S. Kawata. Three-dimensional microfabrication with two-photon-absorbed photopolymerization. Opt. Lett. 22:132–134, 1997.
Mooney, J. F., A. J. Hunt, J. R. McIntosh, C. A. Liberko, D. M. Walba, and C. T. Rogers. Patterning of functional antibodies and other proteins by photolithography of silane monolayers. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93(22):12287–12291, 1996.
Neckers, D. C. Rose Bengal. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 47:1–29, 1989.
Pins, G. D., K. A. Bush, L. P. Cunningham, and P. J. Campagnola. Multiphoton excited fabricated nano and micropatterned extracellular matrix proteins direct cellular morphology. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 78A:194–204, 2006.
Pitts, J. D., P. J. Campagnola, G. A. Epling, and S. L. Goodman. Reaction efficiencies for sub-micron multi-photon freeform fabrications of proteins and polymers with applications in sustained release. Macromolecules 33:1514–1523, 2000.
Pitts, J. D., A. R. Howell, R. Taboada, I. Banerjee, J. Wang, S. L. Goodman, and P. J. Campagnola. New photoactivators for multiphoton excited three-dimensional submicron cross-linking of proteins: bovine serum albumin and type 1 collagen. Photochem. Photobiol. 76(2):135–144, 2002.
Plummer, S. T., Q. Wang, P. W. Bohn, R. Stockton, and M. A. Schwartz. Electrochemically derived gradients of the extracellular matrix protein fibronectin on gold. Langmuir 19(18):7528–7536, 2003.
Rhoads, D. S., and J. L. Guan. Analysis of directional cell migration on defined FN gradients: role of intracellular signaling molecules. Exp. Cell Res. 313(18):3859–3867, 2007.
Slater, J. H., and W. Frey. Nanopatterning of fibronectin and the influence of integrin clustering on endothelial cell spreading and proliferation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 87A(1):176–195, 2008.
Sridhar, M., S. Basu, V. L. Scranton, and P. J. Campagnola. Construction of a laser scanning microscope for multiphoton excited optical fabrication. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 74(7):3474–3477, 2003.
Swartz, M. A. Signaling in morphogenesis: transport cues in morphogenesis. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 14(5):547–550, 2003.
Teixeira, A. I., G. A. Abrams, P. J. Bertics, C. J. Murphy, and P. F. Nealey. Epithelial contact guidance on well-defined micro- and nanostructured substrates. J. Cell Sci. 116:1881–1892, 2003.
Teixeira, A. I., P. F. Nealey, and C. J. Murphy. Responses of human keratocytes to micro- and nanostructured substrates. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 71A(3):369–376, 2004.
von Philipsborn, A. C., S. Lang, J. Loeschinger, A. Bernard, C. David, D. Lehnert, F. Bonhoeffer, and M. Bastmeyer. Growth cone navigation in substrate-bound ephrin gradients. Development 133(13):2487–2495, 2006.
Wang, S., C. Wong Po Foo, A. Warrier, M. M. Poo, S. C. Heilshorn, and X. Zhang. Gradient lithography of engineered proteins to fabricate 2D and 3D cell culture microenvironments. Biomed. Microdevices 11(5):1127–1134, 2009.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge support under NIH 1U54-RR022232 and NSF CBET--1057766. Y.-D. Su and S.-J. Chen acknowledge support from National Cheng Kung University. We also thank Prof. Vladimir Rodionov for the use of the imaging system for live cell studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Joyce Wong oversaw the review of this article.
Xiyi Chen and Yuan-Deng Su contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Su, YD., Ajeti, V. et al. Cell Adhesion on Micro-Structured Fibronectin Gradients Fabricated by Multiphoton Excited Photochemistry. Cel. Mol. Bioeng. 5, 307–319 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-012-0237-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-012-0237-8