Abstract
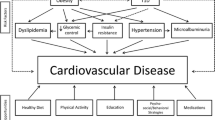
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the most frequent cause of death in people with type 1 diabetes (T1D), despite modern advances in glycemic control and CVD risk factor modification. CVD risk identification is essential in this high-risk population, yet remains poorly understood. This review discusses the risk factors for CVD in young people with T1D, including hyperglycemia, traditional CVD risk factors (dyslipidemia, smoking, physical activity, hypertension), as well as novel risk factors such as insulin resistance, inflammation, and hypoglycemia. We present evidence that adverse changes in cardiovascular function, arterial compliance, and atherosclerosis are present even during adolescence in people with T1D, highlighting the need for earlier intervention. The methods for investigating cardiovascular risk are discussed and reviewed. Finally, we discuss the observational studies and clinical trials which have thus far attempted to elucidate the best targets for early intervention in order to reduce the burden of CVD in people with T1D.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laing, S. P., Swerdlow, A. J., Slater, S. D., Burden, A. C., Morris, A., Waugh, N. R., Gatling, W., Bingley, P. J., & Patterson, C. C. (2003). Mortality from heart disease in a cohort of 23,000 patients with insulin-treated diabetes. Diabetologia, 46(6), 760–765. doi:10.1007/s00125-003-1116-6.
Dorman, J. S., Laporte, R. E., Kuller, L. H., Cruickshanks, K. J., Orchard, T. J., Wagener, D. K., Becker, D. J., Cavender, D. E., & Drash, A. L. (1984). The Pittsburgh insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) morbidity and mortality study. Mortality results. Diabetes, 33(3), 271–276.
Rewers, M. (2008). Why do people with diabetes die too soon? More questions than answers. Diabetes Care, 31(4), 830–832. doi:10.2337/dc08-0245.
Soedamah-Muthu, S. S., Fuller, J. H., Mulnier, H. E., Raleigh, V. S., Lawrenson, R. A., & Colhoun, H. M. (2006). All-cause mortality rates in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus compared with a non-diabetic population from the UK general practice research database, 1992–1999. Diabetologia, 49(4), 660–666. doi:10.1007/s00125-005-0120-4.
Dabelea, D., Bell, R. A., D'Agostino, R. B., Jr., Imperatore, G., Johansen, J. M., Linder, B., Liu, L. L., Loots, B., Marcovina, S., Mayer-Davis, E. J., Pettitt, D. J., & Waitzfelder, B. (2007). Incidence of diabetes in youth in the United States. Journal of the American Medical Association, 297(24), 2716–2724. doi:10.1001/jama.297.24.2716.
Narayan, K. M., Boyle, J. P., Thompson, T. J., Sorensen, S. W., & Williamson, D. F. (2003). Lifetime risk for diabetes mellitus in the United States. JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association, 290(14), 1884–1890.
Secrest, A.M., Becker, D.J., Kelsey, S.F., LaPorte, R.E., & Orchard, T.J. All-cause mortality trends in a large population-based cohort with long-standing childhood-onset type 1 diabetes: the Allegheny County type 1 diabetes registry. Diabetes Care, 33(12), 2573–2579. doi:10.2337/dc10-1170
Harjutsalo, V., Forsblom, C., & Groop, P.H. Time trends in mortality in patients with type 1 diabetes: nationwide population based cohort study. BMJ, 343, d5364
Jarvisalo, M. J., Putto-Laurila, A., Jartti, L., Lehtimaki, T., Solakivi, T., Ronnemaa, T., & Raitakari, O. T. (2002). Carotid artery intima-media thickness in children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes, 51(2), 493–498.
Krantz, J. S., Mack, W. J., Hodis, H. N., Liu, C. R., Liu, C. H., & Kaufman, F. R. (2004). Early onset of subclinical atherosclerosis in young persons with type 1 diabetes. Journal of Pediatrics, 145(4), 452–457. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2004.06.042.
Kostraba, J. N., Dorman, J. S., Orchard, T. J., Becker, D. J., Ohki, Y., Ellis, D., Doft, B. H., Lobes, L. A., LaPorte, R. E., & Drash, A. L. (1989). Contribution of diabetes duration before puberty to development of microvascular complications in IDDM subjects. Diabetes Care, 12(10), 686–693.
Lawson, M. L., Sochett, E. B., Chait, P. G., Balfe, J. W., & Daneman, D. (1996). Effect of puberty on markers of glomerular hypertrophy and hypertension in IDDM. Diabetes, 45(1), 51–55.
Nadeau, K.J., Regensteiner, J.G., Bauer, T.A., Brown, M.S., Dorosz, J.L., Hull, A., Zeitler, P., Draznin, B., & Reusch, J.E. (2010, in press) Insulin resistance in adolescents with type 1 diabetes and its relationship to cardiovascular function. Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism, 95(2), 513–521. doi:10.1210/jc.2009-1756
Snell-Bergeon, J. K., West, N. A., Mayer-Davis, E. J., Liese, A. D., Marcovina, S. M., D'Agostino, R. B., Jr., Hamman, R. F., & Dabelea, D. (2010). Inflammatory markers are increased in youth with type 1 diabetes: the SEARCH case–control study. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 95(6), 2868–2876. doi:10.1210/jc.2009-1993.
Brown, T., Snell-Bergeon, J.k.K., Maahs, D.M., & Wadwa, R.P. (2011) Loss of cardiovascular protection in women with type 1 diabetes may begin in adolescence. Diabetes Suppl, 267OR, July 2011
Nadeau, K., Draznin, B., Reusch, J., & Regensteiner, J. G. (2008). Gender differences in insulin sensitivity among youth with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Journal of Investigative Medicine, 56(1), 136.
Dabelea, D., Kinney, G., Snell-Bergeon, J. K., Hokanson, J. E., Eckel, R. H., Ehrlich, J., Garg, S., Hamman, R. F., & Rewers, M. (2003). Effect of type 1 diabetes on the gender difference in coronary artery calcification: a role for insulin resistance? The Coronary Artery Calcification in Type 1 Diabetes (CACTI) Study. Diabetes, 52(11), 2833–2839.
Colhoun, H. M., Rubens, M. B., Underwood, S. R., & Fuller, J. H. (2000). The effect of type 1 diabetes mellitus on the gender difference in coronary artery calcification. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 36(7), 2160–2167.
Suys, B. E., Katier, N., Rooman, R. P., Matthys, D., Op De Beeck, L., Du Caju, M. V., & De Wolf, D. (2004). Female children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes have more pronounced early echocardiographic signs of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetes Care, 27(8), 1947–1953.
Samara-Boustani, D., Colmenares, A., Elie, C., Dabbas, M., Beltrand, J., Caron, V., Ricour, C., Jacquin, P., Tubiana-Rufi, N., Levy-Marchal, C., Delcroix, C., Martin, D., Benadjaoud, L., Jacqz Aigrain, E., Trivin, C., Laborde, K., Thibaud, E., Robert, J.J., & Polak, M. High prevalence of hirsutism and menstrual disorders in obese adolescent girls and adolescent girls with type 1 diabetes mellitus despite different hormonal profiles. European Journal of Endocrinology, 166(2), 307–316. doi:10.1530/EJE-11-0670
Iniguez, G., Torrealba, I. M., Avila, A., Cassorla, F., & Codner, E. (2008). Adiponectin serum levels and their relationships to androgen concentrations and ovarian volume during puberty in girls with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Hormone Research, 70(2), 112–117. doi:10.1159/000137656.
Krolewski, A. S., Kosinski, E. J., Warram, J. H., Leland, O. S., Busick, E. J., Asmal, A. C., Rand, L. I., Christlieb, A. R., Bradley, R. F., & Kahn, C. R. (1987). Magnitude and determinants of coronary artery disease in juvenile-onset, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. The American Journal of Cardiology, 59(8), 750–755.
Orchard, T. J., Olson, J. C., Erbey, J. R., Williams, K., Forrest, K. Y., Smithline Kinder, L., Ellis, D., & Becker, D. J. (2003). Insulin resistance-related factors, but not glycemia, predict coronary artery disease in type 1 diabetes: 10-year follow-up data from the Pittsburgh Epidemiology of Diabetes Complications Study. Diabetes Care, 26(5), 1374–1379.
Lloyd, C. E., Kuller, L. H., Ellis, D., Becker, D. J., Wing, R. R., & Orchard, T. J. (1996). Coronary artery disease in IDDM. Gender differences in risk factors but not risk. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 16(6), 720–726.
Pambianco, G., Costacou, T., Ellis, D., Becker, D. J., Klein, R., & Orchard, T. J. (2006). The 30-year natural history of type 1 diabetes complications: the Pittsburgh Epidemiology of Diabetes Complications Study experience. Diabetes, 55(5), 1463–1469.
Koivisto, V. A., Stevens, L. K., Mattock, M., Ebeling, P., Muggeo, M., Stephenson, J., & Idzior-Walus, B. (1996). Cardiovascular disease and its risk factors in IDDM in Europe. EURODIAB IDDM Complications Study Group. Diabetes Care, 19(7), 689–697.
Nathan, D. M., Cleary, P. A., Backlund, J. Y., Genuth, S. M., Lachin, J. M., Orchard, T. J., Raskin, P., & Zinman, B. (2005). Intensive diabetes treatment and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 1 diabetes. The New England Journal of Medicine, 353(25), 2643–2653. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa052187.
Bjarnegard, N., Arnqvist, H. J., Lindstrom, T., Jonasson, L., Jonsson, A., & Lanne, T. (2009). Long-term hyperglycaemia impairs vascular smooth muscle cell function in women with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes & Vascular Disease Research: Official Journal of the International Society of Diabetes and Vascular Disease, 6(1), 25–31.
Heilman, K., Zilmer, M., Zilmer, K., Lintrop, M., Kampus, P., Kals, J., & Tillmann, V. (2009). Arterial stiffness, carotid artery intima-media thickness and plasma myeloperoxidase level in children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 84(2), 168–173. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2009.01.014.
Salem, M., El Behery, S., Adly, A., Khalil, D., & El Hadidi, E. (2009). Early predictors of myocardial disease in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Pediatric Diabetes, 10(8), 513–521. doi:10.1111/j.1399-5448.2009.00517.x.
Jenkins, A. J., Lyons, T. J., Zheng, D., Otvos, J. D., Lackland, D. T., McGee, D., Garvey, W. T., & Klein, R. L. (2003). Serum lipoproteins in the diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes intervention and complications cohort: associations with gender and glycemia. Diabetes Care, 26(3), 810–818.
Chait, A., & Bornfeldt, K. E. (2008). Diabetes and atherosclerosis: is there a role for hyperglycemia? Journal of Lipid Research. doi:10.1194/jlr.R800059-JLR200.
Purnell, J. Q., Hokanson, J. E., Marcovina, S. M., Steffes, M. W., Cleary, P. A., & Brunzell, J. D. (1998). Effect of excessive weight gain with intensive therapy of type 1 diabetes on lipid levels and blood pressure: results from the DCCT. Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Journal of the American Medical Association, 280(2), 140–146.
Nadeau, K.J., Zeitler, P.S., Bauer, T.A., Brown, M.S., Dorosz, J.L., Draznin, B., Regensteiner, J.G., & Reusch, J.E.B. (2009) Insulin resistance in adolescents with Type 2 diabetes is associated with impaired exercise capacity. JCEM Online, ahead of print
Haller, M. J., Stein, J., Shuster, J., Theriaque, D., Silverstein, J., Schatz, D. A., Earing, M. G., Lerman, A., & Mahmud, F. H. (2007). Peripheral artery tonometry demonstrates altered endothelial function in children with type 1 diabetes. Pediatric Diabetes, 8(4), 193–198.
Gusso, S., Hofman, P., Lalande, S., Cutfield, W., Robinson, E., & Baldi, J. C. (2008). Impaired stroke volume and aerobic capacity in female adolescents with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia, 51(7), 1317–1320. doi:10.1007/s00125-008-1012-1.
Schauer, I. E., Snell-Bergeon, J. K., Bergman, B. C., Maahs, D. M., Kretowski, A., Eckel, R. H., & Rewers, M. (2011). Insulin resistance, defective insulin-mediated fatty acid suppression, and coronary artery calcification in subjects with and without type 1 diabetes: The CACTI study. Diabetes, 60(1), 306–314. doi:10.2337/db10-0328.
Nadeau, K.J., Regensteiner, J.G., Bauer, T.A., Brown, M.S., Dorosz, J.L., Hull, A., Zeitler, P., Draznin, B., & Reusch, J.E. Insulin resistance in adolescents with type 1 diabetes and its relationship to cardiovascular function. Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism, 95(2), 513–521. doi:10.1210/jc.2009-1756
Dabelea, D., D'Agostino, R.B., Jr., Mason, C.C., West, N., Hamman, R.F., Mayer-Davis, E.J., Maahs, D., Klingensmith, G., Knowler, W.C., & Nadeau, K. Development, validation and use of an insulin sensitivity score in youths with diabetes: the SEARCH for diabetes in youth study. Diabetologia, 54(1), 78–86. doi:10.1007/s00125-010-1911-9
Specht, B.J., Wadwa, R.P., Snell-Bergeon, J.K., Bishop, F.K., & Maahs, D.M. (2012) Estimated insulin sensitivity and cardiovascular disease risk factors in adolescents with and without type 1 diabetes submitted to ADA meeting, 2012
Bishop, F. K., Maahs, D. M., Snell-Bergeon, J. K., Ogden, L. G., Kinney, G. L., & Rewers, M. (2009). Lifestyle risk factors for atherosclerosis in adults with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes & Vascular Disease Research: Official Journal of the International Society of Diabetes and Vascular Disease, 6(4), 269–275. doi:10.1177/1479164109346359.
Schauer, I.E., Snell-Bergeon, J.K., Bergman, B.C., Maahs, D.M., Kretowski, A., Eckel, R.H., & Rewers, M. (2010, in press) Insulin resistance, defective insulin-mediated fatty acid suppression, and coronary artery calcification in subjects with and without type 1 diabetes: The CACTI study. Diabetes. doi:10.2337/db10-0328
Maahs, D. M., Hokanson, J. E., Wang, H., Kinney, G. L., Snell-Bergeon, J. K., East, A., Bergman, B. C., Schauer, I. E., Rewers, M., & Eckel, R. H. (2010). Lipoprotein subfraction cholesterol distribution is proatherogenic in women with type 1 diabetes and insulin resistance. Diabetes, 59(7), 1771–1779. doi:10.2337/db09-1626.
Farkas, K., Jermendy, G., Herold, M., Ruzicska, E., Sasvari, M., & Somogyi, A. (2004). Impairment of the NO/cGMP pathway in the fasting and postprandial state in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes, 112(5), 258–263. doi:10.1055/s-2004-817973.
Horoz, O. O., Yuksel, B., Bayazit, A. K., Attila, G., Sertdemir, Y., Mungan, N. O., Topaloglu, A. K., & Ozer, G. (2009). Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and serum nitric oxide concentration in type 1 diabetic children. Endocrine Journal, 56(3), 477–485.
Huemer, M., Simma, B., Mayr, D., Muhl, A., Rami, B., Schober, E., Ulmer, H., Zanier, U., & Bodamer, O.A. Low levels of asymmetric dimethylarginine in children with diabetes mellitus type I compared with healthy children. Journal of Pediatric, 158(4), 602–606 e601. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2010.09.058
Battelino, N., Sebestjen, M., Keber, I., Blagus, R., Hovnik, T., Bratina, N., & Battelino, T. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase T(−786)C polymorphism in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes and impaired endothelium-dependent dilatation. Hormone Research Pediatric, 76(4), 248–253. doi:10.1159/000329549
Zineh, I., Beitelshees, A. L., & Haller, M. J. (2007). NOS3 polymorphisms are associated with arterial stiffness in children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care, 30(3), 689–693. doi:10.2337/dc06-1697.
Chan, N. N., Vallance, P., & Colhoun, H. M. (2000). Nitric oxide and vascular responses in type I diabetes. Diabetologia, 43(2), 137–147. doi:10.1007/s001250050022.
MacKenzie, K. E., Wiltshire, E. J., Pena, A. S., Gent, R., Hirte, C., Piotto, L., & Couper, J. J. (2009). Hs-CRP is associated with weight, BMI, and female sex but not with endothelial function in children with type 1 diabetes. Pediatric Diabetes, 10(1), 44–51. doi:10.1111/j.1399-5448.2008.00456.x.
Polonsky, W. H., Anderson, B. J., Lohrer, P. A., Aponte, J. E., Jacobson, A. M., & Cole, C. F. (1994). Insulin omission in women with IDDM. Diabetes Care, 17(10), 1178–1185.
Olmsted, M. P., Colton, P. A., Daneman, D., Rydall, A. C., & Rodin, G. M. (2008). Prediction of the onset of disturbed eating behavior in adolescent girls with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care, 31(10), 1978–1982.
Margeirsdottir, H.D., Stensaeth, K.H., Larsen, J.R., Brunborg, C., & Dahl-Jorgensen, K. (2010, In Press) Early signs of atherosclerosis in diabetic children on intensive insulin treatment: a population-based study. Diabetes Care, 33(9), 2043–2048. doi: 10.2337/dc10-0505
Taskinen, M. R., & Nikkila, E. A. (1979). Lipoprotein lipase activity of adipose tissue and skeletal muscle in insulin-deficient human diabetes. Relation to high-density and very-low-density lipoproteins and response to treatment. Diabetologia, 17(6), 351–356.
Maahs, D. M., Wadwa, R. P., McFann, K., Nadeau, K., Williams, M. R., Eckel, R. H., & Klingensmith, G. J. (2007). Longitudinal lipid screening and use of lipid-lowering medications in pediatric type 1 diabetes. Journal of Pediatrics, 150(2), 146–150. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2006.10.054. 150 e141-142.
Schwab, K.O., Doerfer, J., Marg, W., Schober, E., & Holl, R.W. (2010, in press) Characterization of 33 488 children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes based on the gender-specific increase of cardiovascular risk factors. Pediatric Diabetes, 11(5), 357–363. doi:10.1111/j.1399-5448.2010.00665.x
Petitti, D. B., Imperatore, G., Palla, S. L., Daniels, S. R., Dolan, L. M., Kershnar, A. K., Marcovina, S., Pettitt, D. J., & Pihoker, C. (2007). Serum lipids and glucose control: the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, 161(2), 159–165. doi:10.1001/archpedi.161.2.159.
Groop, P. H., Thomas, M. C., Rosengard-Barlund, M., Mills, V., Ronnback, M., Thomas, S., Forsblom, C., Taskinen, M. R., & Viberti, G. (2007). HDL composition predicts new-onset cardiovascular disease in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care, 30(10), 2706–2707. doi:10.2337/dc07-0030.
Jarvisalo, M. J., Raitakari, M., Toikka, J. O., Putto-Laurila, A., Rontu, R., Laine, S., Lehtimaki, T., Ronnemaa, T., Viikari, J., & Raitakari, O. T. (2004). Endothelial dysfunction and increased arterial intima-media thickness in children with type 1 diabetes. Circulation, 109(14), 1750–1755. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000124725.46165.2C.
Singh, T. P., Groehn, H., & Kazmers, A. (2003). Vascular function and carotid intimal-medial thickness in children with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 41(4), 661–665.
Harrington, J., Pena, A.S., Gent, R., Hirte, C., & Couper, J. (2010, in press) Aortic intima media thickness is an early marker of atherosclerosis in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Journal of Pediatrics, 156(2), 237–241. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.08.036
Collado-Mesa, F., Colhoun, H. M., Stevens, L. K., Boavida, J., Ferriss, J. B., Karamanos, B., Kempler, P., Michel, G., Roglic, G., & Fuller, J. H. (1999). Prevalence and management of hypertension in type 1 diabetes mellitus in Europe: the EURODIAB IDDM Complications Study. Diabetic Medicine: A Journal of the British Diabetic Association, 16(1), 41–48.
Lee, S. H., Kim, J. H., Kang, M. J., Lee, Y. A., Won Yang, S., & Shin, C. H. (2011). Implications of nocturnal hypertension in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care, 34(10), 2180–2185.
Perrin, N. E., Torbjornsdotter, T., Jaremko, G. A., & Berg, U. B. (2010). Risk markers of future microalbuminuria and hypertension based on clinical and morphological parameters in young type 1 diabetes patients. Pediatric Diabetes, 11(5), 305–313.
Rossing, P., Hougaard, P., Borch-Johnsen, K., & Parving, H. H. (1996). Predictors of mortality in insulin dependent diabetes: 10 year observational follow up study. BMJ, 313(7060), 779–784.
Gay, E. C., Cai, Y., Gale, S. M., Baron, A., Cruickshanks, K. J., Kostraba, J. N., & Hamman, R. F. (1992). Smokers with IDDM experience excess morbidity. The Colorado IDDM Registry. Diabetes Care, 15(8), 947–952.
Polak, J.F., Backlund, J.Y., Cleary, P.A., Harrington, A.P., O’Leary, D.H., Lachin, J.M., & Nathan, D.M. Progression of carotid artery intima-media thickness during 12 years in the diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications (DCCT/EDIC) study. Diabetes, 60(2), 607–613. doi:10.2337/db10-0296
Prince, C.T., Secrest, A.M., Mackey, R.H., Arena, V.C., Kingsley, L.A., & Orchard, T.J. Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy, HDL cholesterol, and smoking correlate with arterial stiffness markers determined 18 years later in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care, 33(3), 652–657. doi:10.2337/dc09-1936
Salem, M., Moneir, I., Adly, A.M., & Esmat, K. Study of coronary artery calcification risk in Egyptian adolescents with type-1 diabetes. Acta Diabetologica, 48(1), 41–53. doi:10.1007/s00592-010-0214-4
Reynolds, K., Liese, A.D., Anderson, A.M., Dabelea, D., Standiford, D., Daniels, S.R., Waitzfelder, B., Case, D., Loots, B., Imperatore, G., & Lawrence, J.M. Prevalence of tobacco use and association between cardiometabolic risk factors and cigarette smoking in youth with type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus. Journal of Pediatric, 158(4), 594–601 e591. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2010.10.011
Schwab, K. O., Doerfer, J., Hecker, W., Grulich-Henn, J., Wiemann, D., Kordonouri, O., Beyer, P., & Holl, R. W. (2006). Spectrum and prevalence of atherogenic risk factors in 27,358 children, adolescents, and young adults with type 1 diabetes: cross-sectional data from the German diabetes documentation and quality management system (DPV). Diabetes Care, 29(2), 218–225.
Borch-Johnsen, K., & Kreiner, S. (1987). Proteinuria: value as predictor of cardiovascular mortality in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. British Medical Journal (Clinical Research Ed.), 294(6588), 1651–1654.
Gale, E. A. (1999). Prevention studies in type 1 diabetes. Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes, 107(Suppl 3), S101.
Gibb, D. M., Dunger, D., Levin, M., Shah, V., Smith, C., & Barratt, T. M. (1989). Early markers of the renal complications of insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Archives of Disease in Childhood, 64(7), 984–991.
Mortensen, H. B., Marinelli, K., Norgaard, K., Main, K., Kastrup, K. W., Ibsen, K. K., Villumsen, J., & Parving, H. H. (1990). A nation-wide cross-sectional study of urinary albumin excretion rate, arterial blood pressure and blood glucose control in Danish children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Danish Study Group of Diabetes in Childhood. Diabetic Medicine: A Journal of the British Diabetic Association, 7(10), 887–897.
Quattrin, T., Waz, W. R., Duffy, L. C., Sheldon, M. W., Campos, S. P., Albini, C. H., & Feld, L. G. (1995). Microalbuminuria in an adolescent cohort with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Clinical Pediatrics (Phila), 34(1), 12–17.
Salardi, S., Cacciari, E., Pascucci, M. G., Giambiasi, E., Tacconi, M., Tazzari, R., Cicognani, A., Boriani, F., Puglioli, R., Mantovani, W., et al. (1990). Microalbuminuria in diabetic children and adolescents. Relationship with puberty and growth hormone. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica, 79(4), 437–443.
Schultz, C. J., Neil, H. A., Dalton, R. N., Konopelska Bahu, T., & Dunger, D. B. (2001). Blood pressure does not rise before the onset of microalbuminuria in children followed from diagnosis of type 1 diabetes. Oxford Regional Prospective Study Group. Diabetes Care, 24(3), 555–560.
Abraha, A., Schultz, C., Konopelska-Bahu, T., James, T., Watts, A., Stratton, I. M., Matthews, D. R., & Dunger, D. B. (1999). Glycaemic control and familial factors determine hyperlipidaemia in early childhood diabetes. Oxford Regional Prospective Study of Childhood Diabetes. Diabetic Medicine: A Journal of the British Diabetic Association, 16(7), 598–604.
Orchard, T. J., Forrest, K. Y., Kuller, L. H., & Becker, D. J. (2001). Lipid and blood pressure treatment goals for type 1 diabetes: 10-year incidence data from the Pittsburgh Epidemiology of Diabetes Complications Study. Diabetes Care, 24(6), 1053–1059.
Groop, P. H., Elliott, T., Ekstrand, A., Franssila-Kallunki, A., Friedman, R., Viberti, G. C., & Taskinen, M. R. (1996). Multiple lipoprotein abnormalities in type I diabetic patients with renal disease. Diabetes, 45(7), 974–979.
Deckert, T., Feldt-Rasmussen, B., Borch-Johnsen, K., Jensen, T., & Kofoed-Enevoldsen, A. (1989). Albuminuria reflects widespread vascular damage. The Steno hypothesis. Diabetologia, 32(4), 219–226.
Tuomilehto, J., Borch-Johnsen, K., Molarius, A., Forsen, T., Rastenyte, D., Sarti, C., & Reunanen, A. (1998). Incidence of cardiovascular disease in Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic subjects with and without diabetic nephropathy in Finland. Diabetologia, 41(7), 784–790.
Chaturvedi, N., Fuller, J. H., & Taskinen, M. R. (2001). Differing associations of lipid and lipoprotein disturbances with the macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care, 24(12), 2071–2077.
Thorn, L. M., Forsblom, C., Fagerudd, J., Thomas, M. C., Pettersson-Fernholm, K., Saraheimo, M., Waden, J., Ronnback, M., Rosengard-Barlund, M., Bjorkesten, C. G., Taskinen, M. R., & Groop, P. H. (2005). Metabolic syndrome in type 1 diabetes: association with diabetic nephropathy and glycemic control (the FinnDiane study). Diabetes Care, 28(8), 2019–2024.
Schweiger, B., Klingensmith, G., & Snell-Bergeon, J. K. (2010). Physical activity in adolescent females with type 1 diabetes. International Journal of Pediatrics, 2010, 328318. doi:10.1155/2010/328318.
Aman, J., Skinner, T. C., de Beaufort, C. E., Swift, P. G., Aanstoot, H. J., & Cameron, F. (2009). Associations between physical activity, sedentary behavior, and glycemic control in a large cohort of adolescents with type 1 diabetes: the Hvidoere Study Group on Childhood Diabetes. Pediatric Diabetes, 10(4), 234–239. doi:10.1111/j.1399-5448.2008.00495.x.
Tattersall, R. B., & Gill, G. V. (1991). Unexplained deaths of type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetic Medicine: A Journal of the British Diabetic Association, 8(1), 49–58.
Sartor, G., & Dahlquist, G. (1995). Short-term mortality in childhood onset insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: a high frequency of unexpected deaths in bed. Diabetic Medicine: A Journal of the British Diabetic Association, 12(7), 607–611.
Thordarson, H., & Sovik, O. (1995). Dead in bed syndrome in young diabetic patients in Norway. Diabetic Medicine: A Journal of the British Diabetic Association, 12(9), 782–787.
Gill, G. V., Woodward, A., Casson, I. F., & Weston, P. J. (2009). Cardiac arrhythmia and nocturnal hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetes–the ‘dead in bed’ syndrome revisited. Diabetologia, 52(1), 42–45.
Rothenbuhler, A., Bibal, C. P., Le Fur, S., & Bougneres, P. (2008). Effects of a controlled hypoglycaemia test on QTc in adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetic Medicine: A Journal of the British Diabetic Association, 25(12), 1483–1485.
Vallance, P., Calver, A., & Collier, J. (1992). The vascular endothelium in diabetes and hypertension. Journal of Hypertension Supplement, 10(1), S25–S29.
Pena, A. S., Wiltshire, E., MacKenzie, K., Gent, R., Piotto, L., Hirte, C., & Couper, J. (2006). Vascular endothelial and smooth muscle function relates to body mass index and glucose in obese and nonobese children. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 91(11), 4467–4471. doi:10.1210/jc.2006-0863.
Trigona, B., Aggoun, Y., Maggio, A., Martin, X.E., Marchand, L.M., & Beghetti, M., Farpour-Lambert NJ (2010, In press) Preclinical noninvasive markers of atherosclerosis in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes are influenced by physical activity. Journal of Pediatric, 157(4), 533–539. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2010.04.023
Vazquez, B.Y., Vazquez, M.A., Jaquez, M.G., Huemoeller, A.H., Intaglietta, M., & Cabrales, P. (2010, In Press) Blood pressure directly correlates with blood viscosity in diabetes type 1 children but not in normals. Clinical Hemorheology and Microcirculation, 44(1), 55–61. doi:10.3233/CH-2010-1252
Prince, C.T., Secrest, A.M., Mackey, R.H., Arena, V.C., Kingsley, L.A.,& Orchard, T.J. (2010, in press) Pulse wave analysis and prevalent cardiovascular disease in type 1 diabetes. Atherosclerosis. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.08.080
Ahlgren, A. R., Astrand, H., Sundkvist, G., & Lanne, T. (2005). Increased aortic stiffness is persistent in type 1 diabetic women: a follow-up study. Diabetologia, 48(4), 780–783. doi:10.1007/s00125-005-1685-7.
Prince, C. T., Secrest, A. M., Mackey, R. H., Arena, V. C., Kingsley, L. A., & Orchard, T. J. (2010). Pulse wave analysis and prevalent cardiovascular disease in type 1 diabetes. Atherosclerosis, 213(2), 469–474.
Wilhelm, B., Weber, M. M., Kreisselmeier, H. P., Kugler, M., Ries, C., Pfutzner, A., Kann, P. H., & Forst, T. (2007). Endothelial function and arterial stiffness in uncomplicated type 1 diabetes and healthy controls and the impact of insulin on these parameters during an euglycemic clamp. Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology, 1(4), 582–589.
Haller, M. J., Samyn, M., Nichols, W. W., Brusko, T., Wasserfall, C., Schwartz, R. F., Atkinson, M., Shuster, J. J., Pierce, G. L., & Silverstein, J. H. (2004). Radial artery tonometry demonstrates arterial stiffness in children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care, 27(12), 2911–2917.
Stakos, D. A., Schuster, D. P., Sparks, E. A., Wooley, C. F., Osei, K., & Boudoulas, H. (2005). Cardiovascular effects of type 1 diabetes mellitus in children. Angiology, 56(3), 311–317.
Urbina, E.M., Wadwa, R.P., Davis, C., Snively, B.M., Dolan, L.M., Daniels, S.R., Hamman, R.F., & Dabelea, D. (2010, In Press) Prevalence of increased arterial stiffness in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus differs by measurement site and sex: the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. Journal of Pediatric, 156(5), 731–737, 737 e731. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.11.011
Wadwa, R.P., Urbina, E.M., Anderson, A.M., Hamman, R.F., Dolan, L.M., Rodriguez, B.L., Daniels, S.R., & Dabelea, D. (2010, In Press) Measures of arterial stiffness in youth with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: the SEARCH for diabetes in youth study. Diabetes Care, 33(4), 881–886. doi:10.2337/dc09-0747
Gallo, L.M., Silverstein, J.H., Shuster, J.J., & Haller, M.J. (2010, In Press) Arterial stiffness, lipoprotein particle size, and lipoprotein particle concentration in children with type 1 diabetes. Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism, 23(7), 661–667
Godsland, I.F., Pavitt, D., Okoturo, O., Edwards, R.J., Rubens, M.B., Feher, M.D., Flather, M.D., & Elkeles, R.S. (2010, In Press) Can protein biomarkers provide an index of coronary artery calcification in patients with type 2 diabetes? Atherosclerosis. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.09.002
Jarvisalo, M. J., Jartti, L., Nanto-Salonen, K., Irjala, K., Ronnemaa, T., Hartiala, J. J., Celermajer, D. S., & Raitakari, O. T. (2001). Increased aortic intima-media thickness: a marker of preclinical atherosclerosis in high-risk children. Circulation, 104(24), 2943–2947.
Atabek, M. E., Pirgon, O., Kurtoglu, S., & Imamoglu, H. (2006). Evidence for an association between type 1 diabetes and premature carotid atherosclerosis in childhood. Pediatric Cardiology, 27(4), 428–433.
Peppa-Patrikiou, M., Scordili, M., Antoniou, A., Giannaki, M., Dracopoulou, M., & Dacou-Voutetakis, C. (1998). Carotid atherosclerosis in adolescents and young adults with IDDM. Relation to urinary endothelin, albumin, free cortisol, and other factors. Diabetes Care, 21(6), 1004–1007.
Zarich, S. W., Arbuckle, B. E., Cohen, L. R., Roberts, M., & Nesto, R. W. (1988). Diastolic abnormalities in young asymptomatic diabetic patients assessed by pulsed Doppler echocardiography. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 12(1), 114–120.
Muranaka, A., Yuda, S., Tsuchihashi, K., Hashimoto, A., Nakata, T., Miura, T., Tsuzuki, M., Wakabayashi, C., Watanabe, N., & Shimamoto, K. (2009). Quantitative assessment of left ventricular and left atrial functions by strain rate imaging in diabetic patients with and without hypertension. Echocardiography, 26(3), 262–271. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8175.2008.00805.x.
Karavanaki, K., Kazianis, G., Konstantopoulos, I., Tsouvalas, E., & Karayianni, C. (2008). Early signs of left ventricular dysfunction in adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus: the importance of impaired circadian modulation of blood pressure and heart rate. Journal of Endocrinological Investigation, 31(4), 289–296.
Shen, X., Zheng, S., Thongboonkerd, V., Xu, M., Pierce, W. M., Jr., Klein, J. B., & Epstein, P. N. (2004). Cardiac mitochondrial damage and biogenesis in a chronic model of type 1 diabetes. American Journal of Physiology, Endocrinology and Metabolism, 287(5), E896–E905. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00047.2004.
Hassouna, A., Loubani, M., Matata, B. M., Fowler, A., Standen, N. B., & Galinanes, M. (2006). Mitochondrial dysfunction as the cause of the failure to precondition the diabetic human myocardium. Cardiovascular Research, 69(2), 450–458. doi:10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.11.004.
Baldi, J.C., Cassuto, N.A., Foxx-Lupo, W.T., Wheatley, C.M., & Snyder, E.M. (2010, in press) Glycemic status affects cardiopulmonary exercise response in athletes with type I diabetes. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 42(8), 1454–1459. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181d1fdb3
Rowland, T. W., Martha, P. M., Jr., Reiter, E. O., & Cunningham, L. N. (1992). The influence of diabetes mellitus on cardiovascular function in children and adolescents. International Journal of Sports Medicine, 13(5), 431–435.
Kimball, T. R., Daniels, S. R., Khoury, P. R., Magnotti, R. A., Turner, A. M., & Dolan, L. M. (1994). Cardiovascular status in young patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Circulation, 90(1), 357–361.
Lucini, D., Zuccotti, G., Malacarne, M., Scaramuzza, A., Riboni, S., Palombo, C., & Pagani, M. (2009). Early progression of the autonomic dysfunction observed in pediatric type 1 diabetes mellitus. Hypertension, 54(5), 987–994. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.140103.
Dorosz, J.L., Salcedo, E.E., Regensteiner, J.G., & Nadeau, K.J. (2009) Sub-clinical cardiac dysfunction in adolescents with T1DM detected by tissue velocities as measured by tissue tracking. American Society of Echocardiography Annual Scientific Sessions.
Lopes-Virella, M. F., McHenry, M. B., Lipsitz, S., Yim, E., Wilson, P. F., Lackland, D. T., Lyons, T., Jenkins, A. J., & Virella, G. (2007). Immune complexes containing modified lipoproteins are related to the progression of internal carotid intima-media thickness in patients with type 1 diabetes. Atherosclerosis, 190(2), 359–369. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2006.02.007.
Klein, R.L., Carter, R.E., Jenkins, A.J., Lyons, T.J., Baker, N.L., Gilbert, G.E., Virella, G., & Lopes-Virella, M.F. (2010, In Press) LDL-containing immune complexes in the DCCT/EDIC cohort: associations with lipoprotein subclasses. Journal of Diabetic Complications. doi:10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2010.03.001
DiMeglio, L.A., Tosh, A., Saha, C., Estes, M., Mund, J., Mead, L.E., Lien, I., Ingram, D.A., & Haneline, L.S. (2010, In Press) Endothelial abnormalities in adolescents with type 1 diabetes: a biomarker for vascular sequelae? Journal of Pediatric, 157(4):540–546. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2010.04.050
McKittrick, I. B., Bogaert, Y., Nadeau, K., Snell-Bergeon, J., Hull, A., Jiang, T., Wang, X., Levi, M., & Moulton, K. S. (2011). Urinary matrix metalloproteinase activities: biomarkers for plaque angiogenesis and nephropathy in diabetes. American Journal of Physiology. Renal Physiology, 301(6), F1326–F1333.
D'hooge, R., Hellinckx, T., Van Laethem, C., Stegen, S., De Schepper, J., Van Aken, S., Dewolf, D., & Calders, P. (2011). Influence of combined aerobic and resistance training on metabolic control, cardiovascular fitness and quality of life in adolescents with type 1 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation, 25(4), 349–359.
Lehmann, R., Kaplan, V., Bingisser, R., Bloch, K. E., & Spinas, G. A. (1997). Impact of physical activity on cardiovascular risk factors in IDDM. Diabetes Care, 20(10), 1603–1611.
Aouadi, R., Khalifa, R., Aouidet, A., Ben Mansour, A., Ben Rayana, M., Mdini, F., Bahri, S., & Stratton, G. (2011). Aerobic training programs and glycemic control in diabetic children in relation to exercise frequency. The Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness, 51(3), 393–400.
Salem, M. A., Aboelasrar, M. A., Elbarbary, N. S., Elhilaly, R. A., & Refaat, Y. M. (2010). Is exercise a therapeutic tool for improvement of cardiovascular risk factors in adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus? A randomised controlled trial. Diabetology and Metabolic Syndrome, 2(1), 47.
MacKenzie, K. E., Wiltshire, E. J., Gent, R., Hirte, C., Piotto, L., & Couper, J. J. (2006). Folate and vitamin B6 rapidly normalize endothelial dysfunction in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Pediatrics, 118(1), 242–253. doi:10.1542/peds.2005-2143.
Pena, A. S., Wiltshire, E., Gent, R., Hirte, C., & Couper, J. (2004). Folic acid improves endothelial function in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Journal of Pediatrics, 144(4), 500–504. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2003.12.049.
Jehlicka, P., Stozicky, F., Mayer, O., Jr., Varvarovska, J., Racek, J., Trefil, L., & Siala, K. (2009). Asymmetric dimethylarginine and the effect of folate substitution in children with familial hypercholesterolemia and diabetes mellitus type 1. Physiological Research, 58(2), 179–184.
Pena, A. S., Wiltshire, E., Gent, R., Piotto, L., Hirte, C., & Couper, J. (2007). Folic acid does not improve endothelial function in obese children and adolescents. Diabetes Care, 30(8), 2122–2127. doi:10.2337/dc06-2505.
Mullen, M. J., Wright, D., Donald, A. E., Thorne, S., Thomson, H., & Deanfield, J. E. (2000). Atorvastatin but not l-arginine improves endothelial function in type I diabetes mellitus: a double-blind study. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 36(2), 410–416.
Haller, M. J., Stein, J. M., Shuster, J. J., Theriaque, D., Samyn, M. M., Pepine, C., & Silverstein, J. H. (2009). Pediatric Atorvastatin in Diabetes Trial (PADIT): a pilot study to determine the effect of atorvastatin on arterial stiffness and endothelial function in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism, 22(1), 65–68.
Adolescent type 1 Diabetes cardio-renal Intervention Trial Research G. (2009). Adolescent type 1 Diabetes Cardio-renal Intervention Trial (AdDIT). BMC Pediatrics, 9, 79. doi:10.1186/1471-2431-9-79.
Wiernsperger, N. F., & Bailey, C. J. (1999). The antihyperglycaemic effect of metformin: therapeutic and cellular mechanisms. Drugs, 58(Suppl 1), 31–39. discussion 75–82.
Hamilton, J., Cummings, E., Zdravkovic, V., Finegood, D., & Daneman, D. (2003). Metformin as an adjunct therapy in adolescents with type 1 diabetes and insulin resistance: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care, 26(1), 138–143.
Sarnblad, S., Kroon, M., & Aman, J. (2003). Metformin as additional therapy in adolescents with poorly controlled type 1 diabetes: randomised placebo-controlled trial with aspects on insulin sensitivity. European Journal of Endocrinology/European Federation of Endocrine Societies, 149(4), 323–329.
Abdelghaffar, S., & Attia, A.M. (2009) Metformin added to insulin therapy for type 1 diabetes mellitus in adolescents. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (1):CD006691
Moon, R. J., Bascombe, L. A., & Holt, R. I. (2007). The addition of metformin in type 1 diabetes improves insulin sensitivity, diabetic control, body composition and patient well-being. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism, 9(1), 143–145.
Walravens, P., Chase, P., Klingensmith, G., Ellison, M., Cornell, C., & Monohan, K. (2000) Low dose metformin in adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus: a double blind controlled study. Diabetes Suppl, 510P, July 2000
Vella, S., Buetow, L., Royle, P., Livingstone, S., Colhoun, H. M., & Petrie, J. R. (2010). The use of metformin in type 1 diabetes: a systematic review of efficacy. Diabetologia, 53(5), 809–820.
Acknowledgments
Dr. Janet Snell-Bergeon is supported by an American Diabetes Association Junior Faculty Award (1-10-JF-50), and Dr. Kristen Nadeau is supported by ADA 7-11-CD-08, JDRF 11-2010-343, and NIH/NIDDK 1R56DK088971-01. Support for this study was provided by the National Institutes of Health National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute grants R01 HL61753 and R01 HL079611, and Diabetes Endocrinology Research Center Clinical Investigation Core P30 DK57516. Support was also provided by the Adult and Pediatric Clinical Translational Research Centers at the University of Colorado Denver Anschutz Medical Center supported by the NIH M01 RR000051, and the Barbara Davis Center for Childhood Diabetes in Aurora, CO.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Snell-Bergeon, J.K., Nadeau, K. Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Young People with Type 1 Diabetes. J. of Cardiovasc. Trans. Res. 5, 446–462 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-012-9363-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-012-9363-x