Abstract
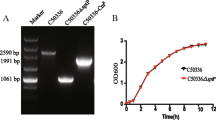
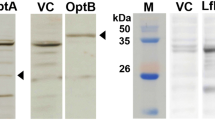
Attenuated bacteria have long been developed as vaccine candidates but can have some disadvantages, such as the potential for damage to immune organs due to insufficient clearance. To minimize these disadvantages, we generated Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium mutants SHJ2104 (asd::cm) and HTSaYA (wzy::km, asd::cm). The wzy gene codes for the O-antigen polymerase, which is involved in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) biosynthesis, and asd codes for aspartate β-semialdehyde dehydrogenase, which participates in cell wall formation. The strains synthesized LPS with a short-chain length, and showed lower cytotoxicity and reduced intracellular proliferation in animal cells compared to wild-type bacteria. After oral infection, the mutants were cleared in immune tissues, including the Peyer’s patch, mesenteric lymph node, and spleen, within 5 days. The LD50 of the mutants in Balb/c mice was estimated to be 106 higher than wild-type bacteria when administered either via an oral or i.p. route, indicating that the two strains are highly attenuated. To compare the immune response to and protective effects of the mutants against wild-type bacterial infection, we inoculated the mutants into mice via an oral (1×1010CFU) or i.p. (1×107 CFU) route once or twice at a two week interval. All immune responses, such as serum IgG and secretory IgA levels, cytokine production, and delayed hypersensitivity, were highly induced by two rounds of immunization. HTSaYA and SHJ2104 induced similar immune responses, and mice immunized with HTSaYA or SHJ2104 via an i.p. route were protected against wild-type Salmonella infection even at 100-fold of the LD50 (5×106 CFU). Taken together, these data indicate that HTSaYA and SHJ2104 could be developed as live attenuated Salmonella vaccine candidates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
al-Hendy, A., P. Toivanen, and M. Skurnik. 1991. Rapid method for isolation and staining of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Microbiol. Immunol. 35, 331–333.
Carter, P.B. and F.M. Collins. 1974. The route of enteric infection in normal mice. J. Exp. Med. 139, 1189–1203.
Collins, L.V., S. Attridge, and J. Hackett. 1991. Mutations at rfc or pmi attenuate Salmonella typhimurium virulence for mice. Infect. Immun. 59, 1079–1085.
Datsenko, K.A. and B.L. Wanner. 2000. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 6640–6645.
Denich, K., P. Borlin, P.D. O’Hanley, M. Howard, and A.W. Heath. 1993. Expression of the murine interleukin-4 gene in an attenuated aroA strain of Salmonella typhimurium: persistence and immune response in BALB/c mice and susceptibility to macrophage killing. Infect. Immun. 61, 4818–4827.
Douce, G., M. Fontana, M. Pizza, R. Rappuoli, and G. Dougan. 1997. Intranasal immunogenicity and adjuvanticity of site-directed mutant derivatives of cholera toxin. Infect. Immun. 65, 2821–2828.
Gahring, L.C., F. Heffron, B.B. Finlay, and S. Falkow. 1990. Invasion and replication of Salmonella typhimurium in animal cells. Infect. Immun. 58, 443–448.
Galan, J.E., K. Nakayama, and R. Curtiss, 3rd. 1990. Cloning and characterization of the asd gene of Salmonella typhimurium: use in stable maintenance of recombinant plasmids in Salmonella vaccine strains. Gene 94, 29–35.
Hoare, A., M. Bittner, J. Carter, S. Alvarez, M. Zaldivar, D. Bravo, M.A. Valvano, and I. Contreras. 2006. The outer core lipopoly-saccharide of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi is required for bacterial entry into epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 74, 1555–1564.
Hone, D.M., A.M. Harris, S. Chatfield, G. Dougan, and M.M. Levine. 1991. Construction of genetically defined double aro mutants of Salmonella typhi. Vaccine 9, 810–816.
Hvalbye, B.K., I.S. Aaberge, M. Lovik, and B. Haneberg. 1999. Intranasal immunization with heat-inactivated Streptococcus pneumoniae protects mice against systemic pneumococcal infection. Infect. Immun. 67, 4320–4325.
Ianaro, A., D. Xu, C.A. O’Donnell, M. Di Rosa, and F.Y. Liew. 1995. Expression of TGF-beta in attenuated Salmonella typhimurium: oral administration leads to the reduction of inflammation, IL-2 and IFN-gamma, but enhancement of IL-10, in carrageenin-induced oedema in mice. Immunology 84, 8–15.
Kang, H.Y. and R. Curtiss, 3rd. 2003. Immune responses dependent on antigen location in recombinant attenuated Salmonella typhimurium vaccines following oral immunization. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 37, 99–104.
Kang, H.Y., J. Srinivasan, and R. Curtiss, 3rd. 2002. Immune responses to recombinant pneumococcal PspA antigen delivered by live attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium vaccine. Infect. Immun. 70, 1739–1749.
Karem, K.L., S. Chatfield, N. Kuklin, and B.T. Rouse. 1995. Differential induction of carrier antigen-specific immunity by Salmonella typhimurium live-vaccine strains after single mucosal or intravenous immunization of BALB/c mice. Infect. Immun. 63, 4557–4563.
Kihlstrom, E. and L. Edebo. 1976. Association of viable and inactivated Salmonella typhimurium 395 MS and MR 10 with HeLa cells. Infect. Immun. 14, 851–857.
Kim, H.J., E.Y. Kim, Y. Hong, J.H. Rhee, and H.E. Choy. 2006. Alternative methods to limit extracellular bacterial activity for enumeration of intracellular bacteria. J. Microbiol. Methods 64, 17–26.
Lesse, A.J., A.A. Campagnari, W.E. Bittner, and M.A. Apicella. 1990. Increased resolution of lipopolysaccharides and lipooligosaccharides utilizing tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J. Immunol. Methods 126, 109–117.
Levine, M.M., C. Ferreccio, R.E. Black, and R. Germanier. 1987. Large-scale field trial of Ty21a live oral typhoid vaccine in enteric-coated capsule formulation. Lancet 1, 1049–1052.
Li, Y., S. Wang, W. Xin, G. Scarpellini, Z. Shi, B. Gunn, K.L. Roland, and R. Curtiss, 3rd. 2008. A sopB deletion mutation enhances the immunogenicity and protective efficacy of a heterologous antigen delivered by live attenuated Salmonella enterica vaccines. Infect. Immun. 76, 5238–5246.
McFarland, W.C. and B.A. Stocker. 1987. Effect of different purine auxotrophic mutations on mouse-virulence of a Vi-positive strain of Salmonella dublin and of two strains of Salmonella typhimurium. Microb. Pathog. 3, 129–141.
Miller, I., D. Maskell, C. Hormaeche, K. Johnson, D. Pickard, and G. Dougan. 1989. Isolation of orally attenuated Salmonella typhimurium following TnphoA mutagenesis. Infect. Immun. 57, 2758–2763.
Murray, G.L., S.R. Attridge, and R. Morona. 2003. Regulation of Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharide O antigen chain length is required for virulence; identification of FepE as a second Wzz. Mol. Microbiol. 47, 1395–1406.
Na, H.S., H.J. Kim, H.C. Lee, Y. Hong, J.H. Rhee, and H.E. Choy. 2006. Immune response induced by Salmonella typhimurium defective in ppGpp synthesis. Vaccine 24, 2027–2034.
Nevola, J.J., B.A. Stocker, D.C. Laux, and P.S. Cohen. 1985. Colonization of the mouse intestine by an avirulent Salmonella typhimurium strain and its lipopolysaccharide-defective mutants. Infect. Immun. 50, 152–159.
O’Callaghan, D., D. Maskell, F.Y. Liew, C.S. Easmon, and G. Dougan. 1988. Characterization of aromatic- and purine-dependent Salmonella typhimurium: attention, persistence, and ability to induce protective immunity in BALB/c mice. Infect. Immun. 56, 419–423.
Pang, T., M.M. Levine, B. Ivanoff, J. Wain, and B.B. Finlay. 1998. Typhoid fever—important issues still remain. Trends Microbiol. 6, 131–133.
Raetz, C.R. and C. Whitfield. 2002. Lipopolysaccharide endotoxins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71, 635–700.
Reed, L.J. and H. Muench. 1938. A simple method of estimating fifty percent end points. Am. J. Hyg. 27, 493–497.
Schleifer, K.H. and O. Kandler. 1972. Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol. Rev. 36, 407–477.
Song, M., H.J. Kim, E.Y. Kim, M. Shin, H.C. Lee, Y. Hong, J.H. Rhee, H. Yoon, S. Ryu, S. Lim, and H.E. Choy. 2004. ppGpp-dependent stationary phase induction of genes on Salmonella pathogenicity island 1. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 34183–34190.
Stuhl, L., R. Benda, and N. Frey. 1964. A controlled field trial of the effectiveness of acetone-dried and inactivated and heat-phenol-inactivated typhoid vaccines in Yugoslavia. Bull World Health Organ. 30, 623–630.
Zhang, X., S.M. Kelly, W.S. Bollen, and R. Curtiss, 3rd. 1997. Characterization and immunogenicity of Salmonella typhimurium SL1344 and UK-1 delta crp and delta cdt deletion mutants. Infect. Immun. 65, 5381–5387.
Zychlinsky, A., C. Fitting, J.M. Cavaillon, and P.J. Sansonetti. 1994. Interleukin 1 is released by murine macrophages during apoptosis induced by Shigella flexneri. J. Clin. Invest. 94, 1328–1332.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piao, H.H., Tam, V.T.M., Na, H.S. et al. Immunological responses induced by asd and wzy/asd mutant strains of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in BALB/c mice. J Microbiol. 48, 486–495 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-010-0023-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-010-0023-z