Abstract
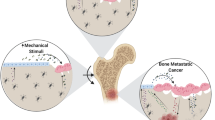
Certain tumors, such as breast, frequently metastasize to bone where they can induce bone destruction. Currently, it is well-accepted that the tumor cells are influenced by other cells and growth factors present in the bone microenvironment that lead to tumor-induced bone disease. Over the past 20 years, many groups have studied this process and determined the major contributing factors; however, these results do not fully explain the changes in gene expression and cell behavior that occur when tumor cells metastasize to bone. More recently, groups studying metastasis from soft tissue sites have determined that the rigidity of the microenvironment, which increases during tumor progression in soft tissue, can regulate tumor cell behavior and gene expression. Therefore, we began to investigate the role of the rigid bone extracellular matrix in the regulation of genes that stimulate tumor-induced bone disease. We found that the rigidity of bone specifically regulates parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) and Gli2 expression in a transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) and mechanotransduction-dependent mechanism. In this review, we summarize the mechanotransduction signaling pathway and how this influences TGF-β signaling and osteolytic gene expression.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fizazi K, Carducci M, Smith M, Damiao R, Brown J, Karsh L, Milecki P, Shore N, Rader M, Wang H, Jiang Q, Tadros S, Dansey R, Goessl C (2011) Denosumab versus zoledronic acid for treatment of bone metastases in men with castration-resistant prostate cancer: a randomised, double-blind study. Lancet 377:813–822
Guise TA, Mundy GR (1998) Cancer and bone. Endocr Rev 19:18–54
Yoneda T, Sasaki A, Mundy GR (1994) Osteolytic bone metastasis in breast cancer. Breast Canc Res Treat 32:73–84
Ruppender NS, Merkel AR, Martin TJ, Mundy GR, Sterling JA, Guelcher SA (2010) Matrix rigidity induces osteolytic gene expression of metastatic breast cancer cells. PLoS One 5:e15451
Sterling JA, Edwards JR, Martin TJ, Mundy GR (2011) Advances in the biology of bone metastasis: how the skeleton affects tumor behavior. Bone 48:6–15
Johnson RW, Nguyen MP, Padalecki SS, Grubbs BG, Merkel AR, Oyajobi BO, Matrisian LM, Mundy GR, Sterling JA (2011) Tgf-β promotion of gli2 induced pthrp expression is independent of canonical hedgehog signaling. Cancer Res
Sterling JA, Wu L, Banerji SS (2006) Parp regulates tgf-beta receptor type ii expression in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cell lines. Anticancer Res 26:1893–1901
Ko Y, Koli KM, Banerji SS, Li W, Zborowska E, Willson JK, Brattain MG, Arteaga CL (1998) A kinase-defective transforming growth factor-beta receptor type ii is a dominant-negative regulator for human breast carcinoma mcf-7 cells. Int J Oncol 12:87–94
Ko Y, Banerji SS, Liu Y, Li W, Liang J, Soule HD, Pauley RJ, Willson JK, Zborowska E, Brattain MG (1998) Expression of transforming growth factor-beta receptor type ii and tumorigenicity in human breast adenocarcinoma mcf-7 cells. J Cell Physiol 176:424–434
Guise TA (2000) Molecular mechanisms of osteolytic bone metastases. Cancer 88:2892–2898
Yin JJ, Selander K, Chirgwin JM, Dallas M, Grubbs BG, Wieser R, Massague J, Mundy GR, Guise TA (1999) Tgf-beta signaling blockade inhibits pthrp secretion by breast cancer cells and bone metastases development. J Clin Invest 103:197–206
Kakonen SM, Selander KS, Chirgwin JM, Yin JJ, Burns S, Rankin WA, Grubbs BG, Dallas M, Cui Y, Guise TA (2002) Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates parathyroid hormone-related protein and osteolytic metastases via smad and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 277:24571–24578
Powell GJ, Southby J, Danks JA, Stillwell RG, Hayman JA, Henderson MA, Bennett RC, Martin TJ (1991) Localization of parathyroid hormone-related protein in breast cancer metastases: increased incidence in bone compared with other sites. Cancer Res 51:3059061
Southby J, Kissin MW, Danks JA, Hayman JA, Moseley JM, Henderson MA, Bennett RC, Martin TJ (1990) Immunohistochemical localization of parathyroid hormone-related protein in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 50:7710–7716
Sterling JA, Oyajobi BA (2006) The hedgehog signaling molecule gli2 induces parathyroid hormone-related peptide expression and osteolysis in metastatic human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 66:7548–7553
Guise T, Yin J, Taylor S, Kumagai Y, Dallas M, Boyce B, Yoneda T, Mundy G (1996) Evidence for a causal role of parathyroid hormone-related protein in the pathogenesis of human breast cancer-mediated osteolysis. J Clin Invest 98:1544–1549
Pratap J, Javed A, Languino LR, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Stein GS, Lian JB (2005) The runx2 osteogenic transcription factor regulates matrix metalloproteinase 9 in bone metastatic cancer cells and controls cell invasion. Mol Cell Biol 25:8581–8591
Javed A, Barnes GL, Pratap J, Antkowiak T, Gerstenfeld LC, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Lian JB, Stein GS (2005) Impaired intranuclear trafficking of runx2 (aml3/cbfa1) transcription factors in breast cancer cells inhibits osteolysis in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:1454–1459
Bendre MS, Margulies AG (2005) Tumor-derived interleukin-8 stimulates osteolysis independent of the receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappab ligand pathway. Cancer Res 65:11001–11009
Bendre MS, Montague DC, Peery T, Akel NS, Gaddy D, Suva LJ (2003) Interleukin-8 stimulation of osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption is a mechanism for the increased osteolysis of metastatic bone disease. Bone 33:28–37
Gallwitz WE, Guise TA (2002) Guanosine nucleotides inhibit different syndromes of pthrp excess caused by human cancers in vivo. J Clin Invest 110:1559–1572
Broadus AE, Mangin M, Ikeda K, Insogna KL, Weir EC, Burtis WJ, Stewart AF (1988) Humoral hypercalcemia of cancer. Identification of a novel parathyroid hormone-like peptide. N Engl J Med 319:556–563
Lanske B, Amling M, Neff L, Guiducci J, Baron R, Kronenberg HM (1999) Ablation of the pthrp gene or the pth/pthrp receptor gene leads to distinct abnormalities in bone development. J Clin Invest 104:399–407
Wysolmerski JJ, Philbrick WM, Dunbar ME, Lanske B, Kronenberg H, Broadus AE (1998) Rescue of the parathyroid hormone-related protein knockout mouse demonstrates that parathyroid hormone-related protein is essential for mammary gland development. Development 125:1285–1294
VanHouten JN, Wysolmerski JJ (2003) Low estrogen and high parathyroid hormone-related peptide levels contribute to accelerated bone resorption and bone loss in lactating mice. Endocrinology 144:5521–5529
Yamamoto M, Harm SC, Grasser WA, Thiede MA (1992) Parathyroid hormone-related protein in the rat urinary bladder: a smooth muscle relaxant produced locally in response to mechanical stretch. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:5326–5330
Noda M, Katoh T, Takuwa N, Kumada M, Kurokawa K, Takuwa Y (1994) Synergistic stimulation of parathyroid hormone-related peptide gene expression by mechanical stretch and angiotensin ii in rat aortic smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 269:17911–17917
Pirola CJ, Wang HM, Strgacich MI, Kamyar A, Cercek B, Forrester JS, Clemens TL, Fagin JA (1994) Mechanical stimuli induce vascular parathyroid hormone-related protein gene expression in vivo and in vitro. Endocrinology 134:2230–2236
Thiede MA, Daifotis AG, Weir EC, Brines ML, Burtis WJ, Ikeda K, Dreyer BE, Garfield RE, Broadus AE (1990) Intrauterine occupancy controls expression of the parathyroid hormone-related peptide gene in preterm rat myometrium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:6969–6973
Ito M, Ohtsuru A, Enomoto H, Ozeki S, Nakashima M, Nakayama T, Shichijo K, Sekine I, Yamashita S (1994) Expression of parathyroid hormone-related peptide in relation to perturbations of gastric motility in the rat. Endocrinology 134:1936–1942
Tanaka N, Ohno S, Honda K, Tanimoto K, Doi T, Ohno-Nakahara M, Tafolla E, Kapila S, Tanne K (2005) Cyclic mechanical strain regulates the pthrp expression in cultured chondrocytes via activation of the ca2+ channel. J Dent Res 84:64–68
Chen X, Macica CM, Ng KW, Broadus AE (2005) Stretch-induced pth-related protein gene expression in osteoblasts. J Bone Miner Res 20:1454–1461
Dallas SL, Miyazono K, Skerry TM, Mundy GR, Bonewald LF (1995) Dual role for the latent transforming growth factor-beta binding protein in storage of latent tgf-beta in the extracellular matrix and as a structural matrix protein. J Cell Biol 131:539–549
Young MF (2003) Bone matrix proteins: their function, regulation, and relationship to osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int 14(Suppl 3):S35–S42
Yoneda T (2000) Cellular and molecular basis of preferential metastasis of breast cancer to bone. J Orthop Sci 5:75–81
van der P, Vloedgraven H, Papapoulos S, Lowick C, Grzesik W, Kerr J, Robey PG (1997) Attachment characteristics and involvement of integrins in adhesion of breast cancer cell lines to extracellular bone matrix components. Lab Invest 77:665–675
Liapis H, Flath A, Kitazawa S (1996) Integrin alpha v beta 3 expression by bone-residing breast cancer metastases. Diagn Mol Pathol 5:127–135
McCabe NP, De S, Vasanji A, Brainard J, Byzova TV (2007) Prostate cancer specific integrin alphavbeta3 modulates bone metastatic growth and tissue remodeling. Oncogene 26:6238–6243
Townsend PA, Villanova I, Uhlmann E, Peyman A, Knolle J, Baron R, Teti A, Horton MA (2000) An antisense oligonucleotide targeting the alphav integrin gene inhibits adhesion and induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Eur J Cancer 36:397–409
Gillespie MT, Thomas RJ, Pu ZY, Zhou H, Martin TJ, Findlay DM (1997) Calcitonin receptors, bone sialoprotein and osteopontin are expressed in primary breast cancers. Int J Canc 73:812–815
Schneider JG, Amend SR, Weilbaecher KN (2011) Integrins and bone metastasis: integrating tumor cell and stromal cell interactions. Bone 48:54–65
Nakamura I, le Duong T, Rodan SB, Rodan GA (2007) Involvement of alpha(v)beta3 integrins in osteoclast function. J Bone Miner Metab 25:337–344
Pecheur I, Peyruchaud O, Serre CM, Guglielmi J, Voland C, Bourre F, Margue C, Cohen-Solal M, Buffet A, Kieffer N, Clezardin P (2002) Integrin alpha(v)beta3 expression confers on tumor cells a greater propensity to metastasize to bone. FASEB J 16:1266–1268
Sloan EK, Pouliot N, Stanley KL, Chia J, Moseley JM, Hards DK, Anderson RL (2006) Tumor-specific expression of alphavbeta3 integrin promotes spontaneous metastasis of breast cancer to bone. Breast Canc Res 8:R20
Zhao Y, Bachelier R, Treilleux I, Pujuguet P, Peyruchaud O, Baron R, Clement-Lacroix P, Clezardin P (2007) Tumor alphavbeta3 integrin is a therapeutic target for breast cancer bone metastases. Cancer Res 67:5821–5830
Sterling JA, Guelcher SA (2011) Bone structural components regulating sites of tumor metastasis. Curr Osteoporos Rep
Van der Velde-Zimmermann D, Verdaasdonk MA, Rademakers LH, De Weger RA, Van den Tweel JG, Joling P (1997) Fibronectin distribution in human bone marrow stroma: matrix assembly and tumor cell adhesion via alpha5 beta1 integrin. Exp Cell Res 230:111–120
Takayama S, Ishii S, Ikeda T, Masamura S, Doi M, Kitajima M (2005) The relationship between bone metastasis from human breast cancer and integrin alpha(v)beta3 expression. Anticancer Res 25:79–83
Geiger B, Bershaksky A (2002) Exploring the neighborhood: adhesion-coupled cell mechanotransducers. Cell 110:139–143
Moore SW, Roca-Cusachs P, Sheetz MP (2010) Stretchy proteins on stretchy substrates: the important elements of integrin-mediated rigidity sensing. Dev Cell 19:194–206
Paszek MJ, Zahir N, Johnson KR, Lakins JN, Rozenberg GI, Gefen A, Reinhart-King CA, Margulies SS, Dembo M, Boettiger D, Hammer DA, Weaver VM (2005) Tensional homeostasis and the malignant phenotype. Cancer Cell 8:241–254
Paszek MJ, Weaver VM (2004) The tension mounts: mechanics meets morphogenesis and malignancy. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 9:325–342
Huang SJ, Ingber DE (2005) Cell tension, matrix mechanics, and cancer development. Cancer Cell 8:175–176
Reijnders CM, Bravenboer N, Tromp AM, Blankenstein MA, Lips P (2007) Effect of mechanical loading on insulin-like growth factor-i gene expression in rat tibia. J Endocrinol 192:131–140
Mantila Roosa SM, Liu Y, Turner CH (2011) Gene expression patterns in bone following mechanical loading. J Bone Miner Res 26:100–112
Hochmuth RM (2000) Micropipette aspiration of living cells. J Biomech 33:15–22
Jiang G, Huang AH, Cai Y, Tanase M, Sheetz MP (2006) Rigidity sensing at the leading edge through alphavbeta3 integrins and rptpalpha. Biophys J 90:1804–1809
Saez A, Buguin A, Silberzan P, Ladoux B (2005) Is the mechanical activity of epithelial cells controlled by deformations or forces? Biophys J 89:L52–L54
Discher DE, Janmey P, Wang YL (2005) Tissue cells feel and respond to the stiffness of their substrate. Science 310:1139–1143
Katsumi A, Orr AW, Tzima E, Schwartz MA (2004) Integrins in mechanotransduction. J Biol Chem 279:12001–12004
Harjanto D, Zaman MH (2010) Matrix mechanics and receptor-ligand interactions in cell adhesion. Org Biomol Chem 8:299–304
Luo BH, Carman CV, Springer TA (2007) Structural basis of integrin regulation and signaling. Annu Rev Immunol 25:619–647
Humphries JD, Byron A, Humphries MJ (2006) Integrin ligands at a glance. J Cell Sci 119:3901–3903
Berrier AL, Yamada KM (2007) Cell-matrix adhesion. J Cell Physiol 213:565–573
den Hertog J, Pals CE, Peppelenbosch MP, Tertoolen LG, de Laat SW, Kruijer W (1993) Receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase alpha activates pp 60c-src and is involved in neuronal differentiation. EMBO J 12:3789–3798
Na S, Collin O, Chowdhury F, Tay B, Ouyang M, Wang Y, Wang N (2008) Rapid signal transduction in living cells is a unique feature of mechanotransduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:6626–6631
Zheng XM, Resnick RJ, Shalloway D (2000) A phosphotyrosine displacement mechanism for activation of src by ptpalpha. EMBO J 19:964–978
Schmidt C, Pommerenke H, Durr F, Nebe B, Rychly J (1998) Mechanical stressing of integrin receptors induces enhanced tyrosine phosphorylation of cytoskeletally anchored proteins. J Biol Chem 273:5081–5085
Kakonen ea SM (2005) Transforming growth factor beta stimulates parathyroid hormone related protein an dosteolytic metastases via smad and mapk signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 227
Wang N, Butler JP, Ingber DE (1993) Mechanotransduction across the cell surface and through the cytoskeleton. Science 260:1124–1127
Galbraith CG, Yamada KM, Sheetz MP (2002) The relationship between force and focal complex development. J Cell Biol 159:695–705
Giannone G, Jiang G, Sutton DH, Critchley DR, Sheetz MP (2003) Talin1 is critical for force-dependent reinforcement of initial integrin-cytoskeleton bonds but not tyrosine kinase activation. J Cell Biol 163:409–419
von Wichert G, Jiang G, Kostic A, De Vos K, Sap J, Sheetz MP (2003) Rptp-alpha acts as a transducer of mechanical force on alphav/beta3-integrin-cytoskeleton linkages. J Cell Biol 161:143–153
Choquet D, Felsenfeld DP, Sheetz MP (1997) Extracellular matrix rigidity causes strengthening of integrin-cytoskeleton linkages. Cell 88:39–48
Zhao XH, Laschinger C, Arora P, Szaszi K, Kapus A, McCulloch CA (2007) Force activates smooth muscle alpha-actin promoter activity through the rho signaling pathway. J Cell Sci 120:1801–1809
Yeung T, Georges PC, Flanagan LA, Marg B, Ortiz M, Funaki M, Zahir N, Ming W, Weaver V, Janmey PA (2005) Effects of substrate stiffness on cell morphology, cytoskeletal structure, and adhesion. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 60:24–34
Zaman MH, Trapani LM, Sieminski A, MacKellar D, Gong H, Kamm RD, Wells A, Lauffenburger DA, Matsudaira P (2006) Migration of tumor cells in 3d matrices is governed by matrix stiffness along with cell-matrix adhesion and proteolysis. PNAS 103:10889–10894
Alexander NR, Branch KM, Iwueke IC, Guelcher SA, Weaver AM (2008) Extracellular matrix rigidity promotes invadopodia activity. Curr Biol 18:1295–1299
Engler AJ, Sen S, Sweeney HL, Discher DE (2006) Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell 126:677–689
Enderling H, Alexander NR, Clark E, Branch KM, Estrada L, Crooke C, Jourquin J, Lobdell N, Zaman MH, Guelcher SA, Anderson A, Weaver AM (2008) Dependence of invadopodia function on collagen fiber spacing and crosslinking: computational modeling and experimental evidence. Biophys J 95:2203–2218
Smith KE, Hyzy SL, Sunwoo M, Gall KA, Schwartz Z, Boyan BD (2010) The dependence of mg63 osteoblast responses to (meth)acrylate-based networks on chemical structure and stiffness. Biomaterials 31:6131–6141
Khatiwala CB, Kim PD, Peyton SR, Putnam AJ (2009) Ecm compliance regulates osteogenesis by influencing mapk signaling downstream of rhoa and rock. J Bone Miner Res 24:886–898
Butcher DT, Alliston T, Weaver VM (2009) A tense situation: forcing tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer 9:108–122
Guelcher SA, Dumas J, Srinivasan A, Didier JE, Hollinger JO (2008) Synthesis, mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and biodegradation of polyurethane networks from lysine polyisocyanates. Biomaterials 29:1762–1775
Gibson LJ, Ashby MF (1997) Cellular solids: structure and properties. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kang Y, Siegel PM, Shu W, Drobnjak M, Kakonen SM, Cordón-Cardo C, Guise TA, Massague J (2003) A multigenic program mediating breast cancer metastasis to bone. Cancer Cell 3:537–549
Huang JH, Peng XL, Xiong CY, Fang J (2011) Influence of substrate stiffness on cell–substrate interfacial adhesion and spreading: a mechano-chemical coupling model. J Coll Interfac Sci 355:503–508
Bell GI (1978) Models for the specific adhesion of cells to cells. Science 200:618–627
Bershadsky AD, Balaban NQ, Geiger B (2003) Adhesion-dependent cell mechanosensitivity. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 19:677–695
Desgrosellier JS, Cheresh DA Integrins in cancer: biological implications and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer 10:9–22
Engleman VW, Nickols GA, Ross FP, Horton MA, Griggs DW, Settle SL, Ruminski PG, Teitelbaum SL (1997) A peptidomimetic antagonist of the alpha(v)beta3 integrin inhibits bone resorption in vitro and prevents osteoporosis in vivo. J Clin Invest 99:2284–2292
Galliher AJ, Schiemann WP (2006) Beta3 integrin and src facilitate transforming growth factor-beta mediated induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in mammary epithelial cells. Breast Canc Res 8:R42
Matthews BD, Overby DR, Mannix R, Ingber DE (2006) Cellular adaptation to mechanical stress: role of integrins, rho, cytoskeletal tension and mechanosensitive ion channels. J Cell Sci 119:508–518
Wang Y, Botvinick EL, Zhao Y, Berns MW, Usami S, Tsien RY, Chien S (2005) Visualizing the mechanical activation of src. Nature 434:1040–1045
Sawada Y, Tamada M, Dubin-Thaler BJ, Cherniavskaya O, Sakai R, Tanaka S, Sheetz MP (2006) Force sensing by mechanical extension of the src family kinase substrate p130cas. Cell 127:1015–1026
Huveneers S, Danen EH (2009) Adhesion signaling - crosstalk between integrins, src and rho. J Cell Sci 122:1059–1069
Harms ea (2004) A small molecule antagonist of the alphavbeta3 integrin suppresses mda-mb-435 skeletal metastasis. Clin Exp Met 21:119–128
Zhao YBR, Treilleux I, Pujuguet P, Peyruchaud O, Baron R (2007) Tumor alphavbeta3 integrin is a therapeutic target for breast cancer bone metastases. Cancer Res 67:5821–5830
Myoui ANR, Williams PJ, Hiraga T, Tamura D, Michigami T et al (2003) C-src tyrosine kinase activity is associated with tumor colonization in bone and lung in an animal model of human breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res 63:5028–5033
Duband JL, Nuckolls GH, Ishihara A, Hasegawa T, Yamada KM, Thiery JP, Jacobson K (1988) Fibronectin receptor exhibits high lateral mobility in embryonic locomoting cells but is immobile in focal contacts and fibrillar streaks in stationary cells. J Cell Biol 107:1385–1396
Felsenfeld DP, Schwartzberg PL, Venegas A, Tse R, Sheetz MP (1999) Selective regulation of integrin–cytoskeleton interactions by the tyrosine kinase src. Nat Cell Biol 1:200–206
Zhang X, Jiang G, Cai Y, Monkley SJ, Critchley DR, Sheetz MP (2008) Talin depletion reveals independence of initial cell spreading from integrin activation and traction. Nat Cell Biol 10:1062–1068
Galliher AJSW (2006) Beta3 integrin and src facilitate transforming growth factor beta mediated induction of epithelial-mesenchumal transition in mammary epithelial cells. Breast Cancer Res 8:R42
Gui GP, Wells CA, Yeomans P, Jordan SE, Vinson GP, Carpenter R (1996) Integrin expression in breast cancer cytology: a novel predictor of axillary metastasis. Eur J Surg Oncol 22:254–258
Mizejewski GJ (1999) Role of integrins in cancer: survey of expression patterns. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 222:124–138
Shane E Evolving data about subtrochanteric fractures and bisphosphonates. N Engl J Med 362:1825–1827
Coleman R, Woodward E, Brown J, Cameron D, Bell R, Dodwell D, Keane M, Gil M, Davies C, Burkinshaw R, Houston SJ, Grieve RJ, Barrett-Lee PJ, Thorpe H (2011) Safety of zoledronic acid and incidence of osteonecrosis of the jaw (onj) during adjuvant therapy in a randomised phase iii trial (azure: Big 01-04) for women with stage ii/iii breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat
Black DM, Kelly MP, Genant HK, Palermo L, Eastell R, Bucci-Rechtweg C, Cauley J, Leung PC, Boonen S, Santora A, de Papp A, Bauer DC (2010) Bisphosphonates and fractures of the subtrochanteric or diaphyseal femur. N Engl J Med 362:1761–1771
McClung MR (2006) Inhibition of rankl as a treatment for osteoporosis: preclinical and early clinical studies. Curr Osteoporos Rep 4:28–33
Gonzalez-Suarez E, Jacob AP, Jones J, Miller R, Roudier-Meyer MP, Erwert R, Pinkas J, Branstetter D, Dougall WC (2010) Rank ligand mediates progestin-induced mammary epithelial proliferation and carcinogenesis. Nature 468:103–107
Biswas S, Guix M, Rinehart C, Dugger TC, Chytil A, Moses HL, Freeman ML, Arteaga CL (2007) Inhibition of tgf-beta with neutralizing antibodies prevents radiation-induced acceleration of metastatic cancer progression. J Clin Invest 117:1305–1313
Ganapathy V, Ge R, Grazioli A, Xie W, Banach-Petrosky W, Kang Y, Lonning S, McPherson J, Yingling JM, Biswas S, Mundy GR, Reiss M (2010) Targeting the transforming growth factor-beta pathway inhibits human basal-like breast cancer metastasis. Mol Cancer 9:122
Mohammad KS, Javelaud D, Fournier PG, Niewolna M, McKenna CR, Peng XH, Duong V, Dunn LK, Mauviel A, Guise TA (2010) The transforming growth factor-{beta} receptor i kinase inhibitor sd-208 reduces the development and progression of melanoma bone metastases. Cancer Res
Edwards JR, Nyman JS, Lwin ST, Moore MM, Esparza J, O’Quinn EC, Hart AJ, Biswas S, Patil CA, Lonning S, Mahadevan-Jansen A, Mundy GR (2010) Inhibition of tgf-β signaling by 1d11 antibody treatment increases bone mass and quality in vivo. J Bone Miner Res 25:2419–2426
Mohammad KS, Chen CG, Balooch G, Stebbins E, McKenna CR, Davis H, Niewolna M, Peng XH, Nguyen DH, Ionova-Martin SS, Bracey JW, Hogue WR, Wong DH, Ritchie RO, Suva LJ, Derynck R, Guise TA, Alliston T (2009) Pharmacologic inhibition of the tgf-beta type i receptor kinase has anabolic and anti-catabolic effects on bone. PLoS One 4:e5275
Tan AR, Alexe G, Reiss M (2009) Transforming growth factor-beta signaling: emerging stem cell target in metastatic breast cancer? Breast Canc Res Treat 115:453–495
Barman SA, Zhu S, White RE (2009) Rhoa/rho-kinase signaling: a therapeutic target in pulmonary hypertension. Vasc Health Risk Manag 5:663–671
Olson MF (2008) Applications for rock kinase inhibition. Curr Opin Cell Biol 20:242–248
Summy JM, Gallick GE (2006) Treatment for advanced tumors: Src reclaims center stage. Clin Canc Res 12:1398–1401
Boyce BF, Xing L, Yao Z, Yamashita T, Shakespeare WC, Wang Y, Metcalf CA 3rd, Sundaramoorthi R, Dalgarno DC, Iuliucci JD, Sawyer TK (2006) Src inhibitors in metastatic bone disease. Clin Canc Res 12:6291s–6295s
Desgrosellier JSCD (2010) Integrins in cancer: biological implications and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer 10:9–22
Ruppender NS, Merkel AR, Guelcher SA (Submitted) Bone matrix rigidity stimulates signaling through αvβ3, src and mapk to induce the expression of pthrp in osteolytic tumor cells
Brooks PC, Stromblad S, Klemke R, Visscher D, Sarkar FH, Cheresh DA (1995) Antiintegrin alpha v beta 3 blocks human breast cancer growth and angiogenesis in human skin. J Clin Invest 96:1815–1822
Moschos SJ, Sander CA, Wang W, Reppert SL, Drogowski LM, Jukic DM, Rao UN, Athanassiou C, Buzoianu M, Mandic M, Richman L, McKinney L, Leininger J, Tice DA, Hammershaimb L, Kirkwood JM (2010) Pharmacodynamic (phase 0) study using etaracizumab in advanced melanoma. J Immunother 33:316–325
O’Day SJ, Pavlick AC, Albertini MR, Hamid O, Schalch H, Lang Z, Ling J, Mata M, Reddy M, Foster B (2011) Clinical and pharmacologic evaluation of two dose levels of intetumumab (cnto 95) in patients with melanoma or angiosarcoma. Invest New Drugs
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Neyns B, Goldbrunner R, Schlegel U, Clement PM, Grabenbauer GG, Ochsenbein AF, Simon M, Dietrich PY, Pietsch T, Hicking C, Tonn JC, Diserens AC, Pica A, Hermisson M, Krueger S, Picard M, Weller M (2010) Phase i/iia study of cilengitide and temozolomide with concomitant radiotherapy followed by cilengitide and temozolomide maintenance therapy in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 28:2712–2718
Lauth M, Bergstrom A, Shimokawa T, Toftgard R (2007) Inhibition of gli-mediated transcription and tumor cell growth by small-molecule antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:8455–8460
Galliher AJ, Schiemann WP (2007) Src phosphorylates tyr284 in tgf-beta type ii receptor and regulates tgf-beta stimulation of p38 mapk during breast cancer cell proliferation and invasion. Cancer Res 67:3752–3758
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guelcher, S.A., Sterling, J.A. Contribution of Bone Tissue Modulus to Breast Cancer Metastasis to Bone. Cancer Microenvironment 4, 247–259 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12307-011-0078-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12307-011-0078-3