Abstract
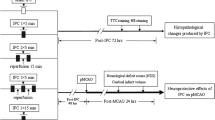
Although the protective mechanisms of delayed ischemic preconditioning have received extensive studies, few have addressed the mechanisms associated with rapid ischemic preconditioning. We investigated whether ischemic tolerance induced by rapid preconditioning is regulated by the Akt survival signaling pathway. Stroke was generated by permanent occlusion of the left distal middle cerebral artery plus 30 min or 1 h occlusion of the bilateral common carotid artery (CCA) in male rats. Rapid preconditioning performed 1 h before stroke onset reduced infarct size by 69% in rats with 30 min CCA occlusion, but by only 19% with 1 h occlusion. After control ischemia with 30 min CCA occlusion, Western blot showed that P-Akt was transiently increased while Akt kinase assay showed that Akt activity was decreased. Although preconditioning did not change P-Akt levels at 1 and 5 h compared with control ischemia, it attenuated reduction in Akt activity at 5 h in the penumbra. However, preconditioning did not change the levels of P-PDK1, P-PTEN, and P-GSK3β in the Akt pathway, all of which were decreased after stroke. At last, the PI3K kinase inhibitor, LY294002, completely reversed the protection from ischemic preconditioning. In conclusion, Akt contributes to the protection of rapid preconditioning against stroke.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alessi DR, Andjelkovic M, Caudwell B, Cron P, Morrice N, Cohen P, Hemmings BA (1996) Mechanism of activation of protein kinase B by insulin and IGF-1. Embo J 15:6541–6551
Bellacosa A, Chan TO, Ahmed NN, Datta K, Malstrom S, Stokoe D, McCormick F, Feng J, Tsichlis P (1998) Akt activation by growth factors is a multiple-step process: the role of the PH domain. Oncogene 17:313–325
Chen ST, Hsu CY, Hogan EL, Maricq H, Balentine JD (1986) A model of focal ischemic stroke in the rat: reproducible extensive cortical infarction. Stroke 17:738–743
Chen R, Kim O, Yang J, Sato K, Eisenmann KM, McCarthy J, Chen H, Qiu Y (2001) Regulation of Akt/PKB activation by tyrosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 276:31858–31862
Dirnagl U, Simon RP, Hallenbeck JM (2003) Ischemic tolerance and endogenous neuroprotection. Trends Neurosci 26:248–254
Franke TF, Hornik CP, Segev L, Shostak GA, Sugimoto C (2003) PI3K/Akt and apoptosis: size matters. Oncogene 22:8983–8998
Fresno Vara JA, Casado E, de Castro J, Cejas P, Belda-Iniesta C, Gonzalez-Baron M (2004) PI3K/Akt signalling pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 30:193–204
Gao X, Ren C, Zhao H (2008) Protective effects of ischemic postconditioning compared with gradual reperfusion or preconditioning. J Neurosci Res 86:2505–2511
Gao G, Zhang H, Takahashi T, Hsieh J, Liao J, Steinberg GK, Zhao H (2008) The Akt signaling pathway contributes to postconditioning's protection against stroke; the protection is associated with the MAPK and PKC pathways. J Neurochem 105:943–955
Garcia L, Burda J, Hrehorovska M, Burda R, Martin ME, Salinas M (2004) Ischaemic preconditioning in the rat brain: effect on the activity of several initiation factors, Akt and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase phosphorylation, and GRP78 and GADD34 expression. J Neurochem 88:136–147
Gidday JM (2006) Cerebral preconditioning and ischaemic tolerance. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:437–448
Hashiguchi A, Yano S, Morioka M, Hamada J, Ushio Y, Takeuchi Y, Fukunaga K (2004) Up-regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway contributes to ischemic tolerance in the CA1 subfield of gerbil hippocampus. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 24:271–279
Hill MM, Andjelkovic M, Brazil DP, Ferrari S, Fabbro D, Hemmings BA (2001) Insulin-stimulated protein kinase B phosphorylation on Ser-473 is independent of its activity and occurs through a staurosporine-insensitive kinase. J Biol Chem 276:25643–25646
Kato H, Araki T, Kogure K (1992) Preserved neurotransmitter receptor binding following ischemia in preconditioned gerbil brain. Brain Res Bull 29:395–400
Kato H, Liu Y, Araki T, Kogure K (1992) MK-801, but not anisomycin, inhibits the induction of tolerance to ischemia in the gerbil hippocampus. Neurosci Lett 139:118–121
Manning BD, Cantley LC (2007) AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream. Cell 129:1261–1274
Meller R, Thompson SJ, Lusardi TA, Ordonez AN, Ashley MD, Jessick V, Wang W, Torrey DJ, Henshall DC, Gafken PR, Saugstad JA, Xiong ZG, Simon RP (2008) Ubiquitin proteasome-mediated synaptic reorganization: a novel mechanism underlying rapid ischemic tolerance. J Neurosci 28:50–59
Nakamura M, Nakakimura K, Matsumoto M, Sakabe T (2002) Rapid tolerance to focal cerebral ischemia in rats is attenuated by adenosine A1 receptor antagonist. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22:161–170
Namura S, Nagata I, Kikuchi H, Andreucci M, Alessandrini A (2000) Serine-threonine protein kinase Akt does not mediate ischemic tolerance after global ischemia in the gerbil. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20:1301–1305
Noshita N, Lewen A, Sugawara T, Chan PH (2001) Evidence of phosphorylation of Akt and neuronal survival after transient focal cerebral ischemia in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21:1442–1450
Nusse R (2003) Wnts and Hedgehogs: lipid-modified proteins and similarities in signaling mechanisms at the cell surface. Development 130:5297–5305
Ostrowski RP, Graupner G, Titova E, Zhang J, Chiu J, Dach N, Corleone D, Tang J, Zhang JH (2008) The hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning-induced brain protection is mediated by a reduction of early apoptosis after transient global cerebral ischemia. Neurobiol Dis 29:1–13
Perez-Pinzon MA (2004) Neuroprotective effects of ischemic preconditioning in brain mitochondria following cerebral ischemia. J Bioenerg Biomembranes 36:323–327
Perez-Pinzon MA, Xu GP, Dietrich WD, Rosenthal M, Sick TJ (1997) Rapid preconditioning protects rats against ischemic neuronal damage after 3 but not 7 days of reperfusion following global cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 17:175–182
Ren C, Gao X, Steinberg G, Zhao H (2008) Limb remote-preconditioning protects against focal ischemia in rats and contradicts the dogma of therapeutic time windows for preconditioning. Neuroscience 151:1099–1103
Wang Q, Xiong L, Chen S, Liu Y, Zhu X (2005) Rapid tolerance to focal cerebral ischemia in rats is induced by preconditioning with electroacupuncture: window of protection and the role of adenosine. Neurosci Lett 381:158–162
Yano S, Morioka M, Fukunaga K, Kawano T, Hara T, Kai Y, Hamada J, Miyamoto E, Ushio Y (2001) Activation of Akt/protein kinase B contributes to induction of ischemic tolerance in the CA1 subfield of gerbil hippocampus. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21:351–360
Yin XH, Zhang QG, Miao B, Zhang GY (2005) Neuroprotective effects of preconditioning ischaemia on ischaemic brain injury through inhibition of mixed-lineage kinase 3 via NMDA receptor-mediated Akt1 activation. J Neurochem 93:1021–1029
Zhang H, Gao X, Yan Z, Ren C, Shimohata T, Steinberg GK, Zhao H (2008) Inhibiting caspase-3 activity blocks beta-catenin degradation after focal ischemia in rat. NeuroReport 19:821–824
Zhang H, Ren C, Gao X, Takahashi T, Sapolsky RM, Steinberg GK, Zhao H (2008) Hypothermia blocks beta-catenin degradation after focal ischemia in rats. Brain Res 1198:182–187
Zhao H, Sapolsky RM, Steinberg GK (2006) Phosphoinositide-3-kinase/akt survival signal pathways are implicated in neuronal survival after stroke. Mol Neurobiol 34:249–270
Zhao H, Shimohata T, Wang JQ, Sun G, Schaal DW, Sapolsky RM, Steinberg GK (2005) Akt contributes to neuroprotection by hypothermia against cerebral ischemia in rats. J Neurosci 25:9794–9806
Zhao H, Yenari MA, Cheng D, Barreto-Chang OL, Sapolsky RM, Steinberg GK (2004) Bcl-2 transfection via herpes simplex virus blocks apoptosis-inducing factor translocation after focal ischemia in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 24:681–692
Zhao H, Yenari MA, Cheng D, Sapolsky RM, Steinberg GK (2003) Bcl-2 overexpression protects against neuron loss within the ischemic margin following experimental stroke and inhibits cytochrome c translocation and caspase-3 activity. J Neurochem 85:1026–1036
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Ms. Felicia F. Beppu for manuscript assistance and Ms. Elizabeth Hoyte for figure preparations. This study was supported by AHA grant SDG 0730113N (HZ) and NIH grant 1R21NS057750-01A2 (HZ), and NINDS grants R01 NS27292 (GKS) and P01 NS37520 (GKS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, X., Zhang, H., Steinberg, G. et al. The Akt Pathway Is Involved in Rapid Ischemic Tolerance in Focal Ischemia in Rats. Transl. Stroke Res. 1, 202–209 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-010-0017-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-010-0017-5