Abstract
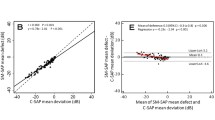
• Purpose: The purpose of this study was to develop software that allows the performance of routine static threshold perimetry using the scanning laser ophthalmoscope (SLO) and the comparison of the results with conventional computerized cupola perimetry. The original software does not allow performance of static threshold perimetry within a reasonable examination time. • Methods: Static perimetry was performed in random order on 50 healthy eyes using our SLO staircase threshold perimetry technique and the Octopus 500 (program 38). We compared the relative sensitivities for each of 25 corresponding visual field locations. • Results: Mean sensitivity in the SLO perimetry amounted to 32.7 dB (range 25–37 dB) while it was 28.7 dB in the Octopus. For all test locations the SLO showed higher dB values on average. The mean difference between both methods was 3.7±0.8 dB (range 1.4–5.8 dB) when the test locations at the blind spot were excluded (linear regression between the two methods: r=0.843, P<0.0001). The mean time interval between two stimulus presentations was 2.5 s with the SLO perimetry. • Conclusion: With the Heidelberg software, automated static threshold perimetry using the SLO is possible within reasonably short examination times. The mean time interval between two test point presentations is about one tenth of that necessary using the original Rodenstock software. There is a systematic difference between SLO and Octopus fields of about 4 dB which was not very much influenced by the stimulus locations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta F, Lashkari K, Reynaud X, Jalkh AE, Van de Velde F, Chedid N (1991) Characterization of functional changes in macular holes and cysts. Ophthalmology 98:1820–1823
Alexandridis E (1970) Rümliche und zeitliche Summation pupillomotorisch wirksamer Lichtreize beim Menschen. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 180:12–19
Barlow HB (1958) Temporal and spatial summation in human vision at different background intensities. J Physiol (Lond) 141:337–350
Bebie H, Fankhauser F, Spahr J (1976) Static perimetry: strategies. Acta Ophthalmol 54:325–338
Burk ROW, Rohrschneider K, Völcker HE (1992) Dreidimensionale Biomorphometrie der Papille mittels der Laser-Scanning-Tomographie. In: Kampik A (ed) Jahrbuch der Augenheilkunde. Laser. Biermann, Zülpich, pp 55–67
Enoch JM (1978) Quantitative layer by-layer perimetry. Proctor lecture. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 17:208–257
Gloor B (1993) Perimetrie mit besonderer Berücksichtigung der automatischen Perimetrie. Enke, Stuttgart
Hart WMJ (1992) Adler's physiology of the eye. Clinical application. Mosby, St. Louis
Heijl A (1977) Computer test logics for automatic perimetry. Acta Ophthalmol 55: 837–853
Kani K, Ogita Y (1978) Fundus controlled perimetry. Doc Ophthalmol Proc Ser 19:341–350
Krastel H, Grimm H, Götz ML, Bergdolt K (1981) Der Grauglastest am Perimeter. Gesichtsfeldbefunde bei herabgesetzter Beleuchtung. Ber Dtsch Ophthalmol Ges 78:1041–1047
Krastel H, Jaeger W, Zimmermann S, Heckmann B, Krystek M (1991) Systematics of human photopic spectral sensitivity. Doc Ophthalmol Proc Ser 54:323–339
Nasemann JE (1991) Scanning-Laser-Ophthalmoskopie. Prinzip und klinische Anwendung. Augenarztl Fortbildung 14:14–19
Plesch A, Klingbeil U (1989) Optical characteristics of a scanning laser ophthalmoscope. In: Wampler JE (ed) New methods in microscopy and low light imaging. SPIE Int Soc Optical Engineering, Bellingham, pp 390–398 (Proc SPIEE 1161)
Ring TM, Mueller AJ, Schaumberger MM, Lachenmayr BJ (1992) Static fundus perimetry with the scanning laser ophthalmoscope. German J Ophthalmol 1:249
Rohrschneider K, Becker M, Fendrich T, Weber J, Kruse FE, Burk ROW, Vö1cker HE (1994) Fundus perimetry using a Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscope (SLO) with an automated threshold-strategy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 35:2189
Rohrschneider K, Glück R, Burk ROW, Kruse FE, Völcker HE (1994) The real size of the optic nerve head — telecentricity and magnification curves of different fundus cameras. German J Ophthalmol 3:316
Rohrschneider K, Becker M, Kruse FE, Fendrich T, Völcker HE (1995) Stability of fixation — results of fundus-controlled examination using the Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscope. German J Ophthalmol 4:197–202
Schuchard RA (1993) Validity and interpretation of Amsler grid reports. Arch Ophthalmol 111:776–780
Sjaarda RN, Frank DA, Glaser BM, Thompson JT, Murphy RP (1993) Assessment of vision in idiopathic macular holes with macular microperimetry using the scanning laser ophthalmoscope. Ophthalmology 100: 1513–1518
Sjaarda RN, Frank DA, Glaser BM, Thompson JT, Murphy RP (1993) Resolution of an absolute scotoma and improvement of relative scotoma after successful macular hole surgery. Am J Ophthalmol 116:129–139
Stürmer J (1993) Fundusperimetrie. In: Gloor B (ed) Perimetrie. Enke, Stuttgart, pp 149–158
Stürmer J, Schrödel C, Rappl W (1990) Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscope for static fundus-controlled perimetry. In: Nasemann JE, Burk ROW (eds) Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy and tomography. Quintessenz, Munich, pp 133–146
Stürmer J, Schrödel C, Rappl W (1991) Scanning laser ophthalmoscope for static fundus perimetry in glaucomatous nerve-fiber bundle defects. In: Mills RP, Heijl A (eds) Perimetry update 1990/91. Kugler, Amsterdam, pp 85–92
Sunness JS, Bressler NM, Maguire MG (1994) The pattern of visual loss in the geographic atrophy (GA) form of age-related macular degeneration: a scanning laser ophthalmoscope (SLO) analysis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 35:2146
The Laser Institute of America (1986) American national standard for the safe use of lasers. ANSI Z 136.1.1986, Laser Institute of America, Toledo, Ohio
Timberlake GT, Mainster MA, Webb RH, Hughes GW, Trempe CL (1982) Retinal localization of scotomata by scanning laser ophthalmoscopy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 22:91–97
Timberlake GT, Van de Velde FJ, Jalkh AE (1989) Clinical use of scanning laser ophthalmoscope retinal function maps in macular disease. Lasers Light Ophthalmol 2:211–222
Van de Velde FJ, Jalkh AE, Katsumi O, Hirose T, Timberlake GT, Schepens CL (1990) Clinical Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscope applications: an overview. In: Nasemann JE, Burk ROW (eds) Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy and tomography. Quintessenz, Munich, pp 35–47
Van de Velde FJ, Timberlake GT, Jalkh AE, Schepens CL (1990) La micropérimétrie statique avec l'ophthalmoscope à balayage laser. Ophtalmologie 4:291–294
Van de Velde FJ, Jalkh AE, Elsner AE (1991) Microperimetry with the Scanning Laser Opththalmoscope. In: Mills RP, Heijl A (eds) Perimetry update 1990/91. Kugler, Amsterdam, pp 93–101
Webb RH, Hughes GW, Delori FC (1987) Confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope. Appl Optics 26:1492–1499
Weber J (1993) Atlas der Computerperimetrie. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Wolf S, Toonen F, Schaaf A, Arend O, Remky A, Reim M (1994) Light sensitivity and fixation stability in patients with subretinal neovascularisation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 35:1504
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Presented in part at the ARVO Meeting in Sarasota, Florida, 1–6 May 1994
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rohrschneider, K., Becker, M., Krastel, H. et al. Static fundus perimetry using the scanning laser ophthalmoscope with an automated threshold strategy. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 233, 743–749 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00184084
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00184084