Summary
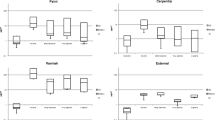
Biological exposure indices (BEIs) of toluene, perchloroethylene (PCE) and methyl ethyl ketone (MEK) for Korean workers were studied respectively. Exposure in workplace to organic solvents were measured by personal sampling. Blood toluene, blood PCE, urinary trichloroacetic acid and urinary MEK were determined by headspace GC. Urinary hippuric acid was determined by HPLC and corrected for creatinine. BEIs for Korean workers were calculated with the levels of the determinants corresponding to permissible exposure limits in Korea which were the same with TLV of ACGIH. Blood toluene level of 2.2 mg/l and urinary hippuric acid level of 1.7 g/g creatinine corresponded to exposure of 100 ppm toluene. Blood PCE concentration of 1.6 mg/l and urinary trichloroacetic acid concentration of 2.9 mg/l corresponded to exposure to 50 ppm PCE. Urinary MEK concentration of 1.4 mg/l corresponded to exposure to 200 ppm of MEK. In conclusion, BEIs for Korean workers determined in this study were different to ACGIH's BEI as urinary determinants were lower and blood determinants were higher than ACGIH's BEI.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ACGIH (1991) Threshold limit values of chemical substances and physical agents and biological exposure Indices. American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists, Cincinnati, pp 62–69
Breimer DD, Ketelaars CH, Van Rossum MJ (1974) Gas chromatographic determination of chloral, hydrate, trichloroethanol and trichloroacetic acid in blood and in urine employing headspace analysis. J Chromat 88:55–63
Fiserova-Bergerova V, Vlach J, Cassady JC (1980) Predictable ‘individual differences’ in uptake and excretion of gases and lipid vapour simulation study. Br J Ind Med 37: 42–49
Fiserova-Bergerova V (1990) Application of toxicokinetic models to establish biological exposure indicators. Ann Occup Hyg 34:639–651
Goedde HW, Singh S, Agarwal DP, Fritze G, Stapel K, Paik YK (1989) Genotyping of mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase in blood samples using Allele-specific oligonucleotides: Comparison with phenotyping in hair roots. Hum Genet 81:305–307
Inoue O, Seiji K, Nakatsuka H, Kasahara M, Watanabe T, Lee BK, Lee SH, Lee KM, Cho KS, Ikeda M (1988) Relationship between exposure to toluene and excretion of urinary metabolites in Korean female solvent workers. Ind Health 26:147–152
Jang JY, Chun HS (1991) Status of usage of organic solvent in manufacture. Institute of occupational disease, Korea Labour Wealfare Corporation, Inchon, pp 23–24
Jang JY, Chun HS, Chunb HK (1990) Biological monitoring of occupational toluene exposure. Institute of occupational disease, Korea Labour Wealfare Corporation, Inchon
Lee SH, Kim HA, Lee BK, Lee KM (1988) Urinary excretion of hippuric acid and o-cresol and subjective symptoms among occupational exposed to toluene. Korean J Occup Health 27:4–11
Miyasaka M, Kumai M, Koizumi A, Watanabe T, Kurasako K, Sato K, Ikeda M (1982) Biological monitoring of occupational exposure to methyl ethyl ketone by means of urinanalysis for methyl ethyl ketone itself. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 50:131–137
NIOSH (1984) NIOSH manual of analytical methods, 3rd Ed., Method 1501, 8301, 8002, U.S. Department of Health and human services, Cincinnati
Ramsey JD, Flanagan RJ (1982) Detection and identification of volatile organic compounds in blood by headspace gas chromatography as an aid to the diagnosis of solvent abuse. J Chromat 240:423–444
Yoo KY, Park BY, Ahn YO (1988) Seroepidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection in healthy Korean adults in Seoul. Kor J Prevent Med 21:89–98
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, JY., Kang, SK. & Chung, H.K. Biological exposure indices of organic solvents for Korean workers. Int. Arch Occup Environ Heath 65 (Suppl 1), S219–S222 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00381345
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00381345