Summary
In acute and subacute inhalation studies rats and dogs were exposed to N,N-dimethylformamide. In addition dogs were subjected to subchronic inhalation tests.
The rats were subjected to N,N-dimethylformamide concentrations of 21, 146 or 2005 ppm during the 3-hr trial. During the 6-hr exposure they were subjected to 29 or 170 ppm.
In the case of repeated exposures on rats the average concentration was 350 ppm.
In the 6-hr test dogs were exposed to 20, 32, 143 or 172 ppm. In the 5-day test (6 hrs/day) they were exposed to 23 or 59 ppm, and in the 4-week test (6 hrs/day) the concentration was 20 ppm (MAC).
The metabolisation of N,N-dimethylformamide was studied in rats and dogs. Methods for the analytical determination of the unchanged active substance and its metabolites (N-methylformamide and formamide) in blood and urine were developed.
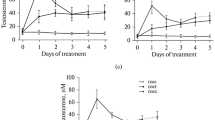
In addition to the already known metabolite N-methylformamide, a further metabolite, formamide, was found in the urine of rats and dogs. The elimination rate of N-methylformamide and formamide differed in dogs and rats. The elimination rate in dogs was much slower. In the group of dogs subjected to repeated inhalation of 59 ppm an accumulation of N-methylformamide was determined in the blood and urine. In the case of rats exposed to substantially higher subacute N,N-dimethylformamide concentration (350 ppm) this phenomenon was not observed.
In the MAC-range (20 ppm) the dogs of the subacute and subchronic group showed no signs of accumulation.
The results of the liver and kidney function studies in dogs exposed to 20 ppm N,N-dimethylformamide for 4 weeks were normal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes,I.R., Ranta,K.E.: The metabolism of dimethylformamide and dimethylacetamide. Toxicol.appl.Pharmacol. 23, 271 (1972)
Chanh,P.H., Dat Xuong,N., Azum-Gelade,M.C.: Etude toxicologique de la formamide et de ses dérivés N. méthyles et N. éthyles. Therapie 26, 409 (1971)
Clayton.,I.W., Barnes,I.R., Hood,D.B., Schepers.,G.W.H.: The inhalation toxicity of dimethylformamide (DMF). Amer.ind.Hyg.Assoc.J. 24, 144 (1963)
Druckrey,H., Preu\mann,R., Ivankovic,D., SchmÄhl,D.: Organotrope carcinogene Wirkung von 65 verschiedenen N-Nitroso-Verbindungen an BD-Ratten. Z.Krebsforschung 69, 103 (1967)
Henry,R.J.: Clinical chemistry. Philadelphia: Hoeber 1964
Hofmann,H.T.: Zur Frage der hepatotoxischen Wirkung von Dimethylformamid. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch.Exper.Pathol.Pharmakol. 240, 38 (1960)
Hofmann,H.T.: Gewerbetoxikologische Grundlagen des MAK-Wertes für Dimethylformamid (DMF). Medichem. Internationales Symposium der WerksÄrzte der chemischen Industrie, Ludwigshafen, 27.–29. April 1972, S. 415
Kimmerle,G., Eben,A.: Metabolism, excretion and toxicology of trichloroethyl ene after inhalation. 1. Experimental exposure on rats. Arch.Toxikol. 30, 115 (1973)
Kutzsche,A.: Zur Toxikologie des Dimethylformamids. Arzneimittelforschung 15, 618 (1965)
Massmann,W.: Toxicological investigations of dimethylformamide. Brit.J.Ind.Med. 13, 51 (1956)
Parke,D.V.: The biochemistry of foreign compounds, pp. 50–52. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1958
Popper,H., Mandel,E., Mayer,H.: Zur Kreatininbestimmung im Blut. Biochem.Z. 291, 354 (1937)
Reitman,St., Frankel,S.: A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxalacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminase. Amer.J.clin.Pathol. 28, 56 (1957)
Smyth,H.F., Carpenter,C.P.: Further experience with the range finding test in the industrial toxicology laboratory. J.ind.Hyg. 30, 63 (1948)
Tanaka,Ken-Ichi: Toxicity of dimethylformamide (DMF) to the young female rat. Int.Arch.Arbeitsmed. 28, 95 (1971)
Tudisco,R.: Toxicity of N,N-dimethylformamide. Rass.Med.Sper. 12, 139 (1965)
Wiles,J.S., Narcisse,J.K.: The acute toxicity of dimethylamides in several animal species. Amer.ind.Hyg.Assoc.J. 32, 539 (1971)
With,T.K.: Bestimmung von Bilirubin in kleinen Blutmengen (Cutanblut). Hoppe-Seyler's Z.physiol.Chem. 278, 129 (1943)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kimmerle, G., Eben, A. Metabolism studies of N,N-dimethylformamide. Int. Arch. Arbeitsmed 34, 109–126 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00539129
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00539129