Summary
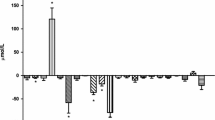
The haemodynamic effects of a meal on the splanchnic and hepatic circulation were evaluated in 30 healthy volunteers, using Doppler ultrasonography. The resistance index (RI) of the superior mesenteric artery and of the left and right intrahepatic arteries, the portal vein blood flow as well as the ratio between maximal velocity in the left and right intrahepatic arteries and the adjacent portal vein were measured initially, then 15, 30, 45, and 60 min after the ingestion of a standard balanced liquid meal. Postprandial haemodynamic changes were maximal 30 min after the meal; at that time, mesenteric artery RI decreased significantly [mean −11% (SEM 14%)] whereas portal vein blood flow increased markedly [mean +79% (SEM 14%)]; a significant increase in hepatic artery RI was observed in both liver lobes. The ratio between maximal velocities of the intrahepatic artery and the intrahepatic portal vein was reduced significantly; this ratio decreased more markedly in the right lobe of the liver. These findings would suggest that there was an adaptation of hepatic artery to portal vein blood flow after a meal. The subsequent increase in intrahepatic portal vein flow velocity was found to be greater in the right lobe of the liver.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson SL, Langille BL (1992) Factors determining aortic and umbilical blood flow pulsatility in fetal sheep. Ultrasound Med Biol 18:255–266
Alvarez D, Mastai R, Lennie A, Soifer G, Levi D, Terg R (1991) Noninvasive measurement of portal venous blood flow in patients with cirrhosis: effects of physiological and pharmacological stimuli. Dig Dis Sci 36:82–86
Barbara L (1990) The value of Doppler US in the study of hepatic haemodynamics. Consensus conference. Bologna, Italy, 2 September 1989. J Hepatol 10:353–355
Bendsten F, Simonsen L, Henriksen JH (1992) Effect on haemodynamics of a liquid meal alone and in combination with propranolol in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 102:1017–1023
Brandt JL, Castleman L, Ruskin HD, Greenwald J, Kelly JJ, Jones A (1955) The effect of oral protein and glucose feeding on splanchnic blood flow and oxygen utilization in normal and cirrhotic subjects. J Clin Invest 34:1017–1021
Brown BP, Heistad DD (1986) Capacitance of the rabbit portal vein and inferior vena cave. J Physiol 381:417–425
Burns PN, Jaffe CC (1985) Quantitative flow measurement with Doppler ultrasound: techniques, accuracy, and limitations. Radiol Clin North Am 23:641–657
Chou CC (1983) Splanchnic and overall cardiovascular haemodynamics during eating and digestion. Fed Proc 42:1658–1661
Dauzat M, Pomier-Layrargues G (1989) Portal vein blood flow measurements using pulsed Doppler and electromagnetic flowmetry in dogs: a comparative study. Gastroenterology 96:913–919
De Vries PJ, Van Hattum J, Hoekstra JBL, de Hooge P (1991) Duplex Doppler measurements of portal venous flow in normal subjects. Inter and intra-observer variability. J Hepat 13:358–363
Doi R, Inoue K, Kogire M, Sumi S, Takaori K, Suzuki T, Tobe T (1988) Simultaneous measurement of hepatic arterial and portal venous flows by transit time ultrasonic volume flowmetry. Surg Gynecol Obstet 167:65–69
Gaiani S, Bolondi L, Li Bassi S, Sand V, Zironi G, Barbara L (1989) Effect of meal on portal haemodynamics in healthy humans and in patients with chronic liver disease. Hepatology 9:815–819
Gallavan RH, Chou CC, Kvietys PR, Sit SP (1980) Regional blood flow during digestion in the conscious dog. Am J Physiol 238 [Heart Circ Physiol 7]:H220-H225
Garcia JE, Atkins F (1985) A low right to left hepatic lobe ratio. Is streamlining of ethanol to the right lobe of the liver the cause? Clin Nucl Med 10:807–809
Gates GF, Dore EK (1973) Streamline flow in the human portal vein. J Nucl Med 14:79–83
Gill RW (1982) Accuracy calculations for ultrasonic pulsed Doppler flow measurements. Aust Phys Eng Sci Med 5:237–247
Gill RW (1985) Splanchnic blood flow measurement. In: Altobelli SA, Voyles WIT, Greene ER (eds) Cardiovascular ultrasonic flowmetry. Elsevier, New York, pp 369–389
Goldberg REA, Rada C, Knelson M, Haaga J, Minkin S (1990) The response of the portal vein to an oral glucose load. J Clin Ultrasound 18:691–695
Hernandez LA, Kvietys PR, Granger DN (1986) Postprandial haemodynamics in the conscious rat. Am J Physiol 251 [Gastrointest Liver Physiol 14]:G117-G123
Jäger K, Bollinger A, Valli C, Ammann R (1986) Measurement of mesenteric blood flow by duplex scanning. J Vase Surg 3:462–469
Kawasaki T, Carmichael FJ, Saldivia V, Roldan L, Orrego H (1990) Relationship between portal venous and hepatic arterial blood flows:spectrum of reponse. Am J Physiol 259 (Gastrointest Liver Physiol 22):G1010-G1018
Lafortune M, Madore F, Patriquin H, Breton G (1991) Segmental anatomy of the liver: a sonographic approach to the Couinaud nomenclature. Radiology 181:43–448
Lautt WW (1985) Mechanism and role of intrinsic regulation of hepatic arterial blood flow: hepatic arterial buffer response. Am Physiol (Gastrointest Liver Physiol 12) 249:G549-G556
Lautt WW, Legare DJ, Ezzatt WR (1991) Quantitation of the hepatic arterial buffer response to graded changes in portal blood flow. Gastroenterology 100:1024–1028
Lee SS, Hadengue A, Moreau R, Sayegh R, Hillon P, Lebrec D (1988) Postprandial haemodynamic responses in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 8:647–651
Legarth J, Thorup E (1989) Characteristics of Doppler bloodvelocity waveforms in a cardiovascular in vitro model. II. The influence of peripheral resistance, perfusion pressure and blood flow. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 49:459–464
Lilly MP, Harward RS, Flinn WR, Blackburn DR, Astleford PM, Yao JST (1989) Duplex ultrasound measurement of changes in mesenteric flow velocity with pharmacologic and physiologic alteration of intestinal blood flow in man. J Vase Surg 9:18–25
Maulik D, Arbeille P, Kadado T (1992) Haemodynamic foundation of umbilical arterial Doppler waveform analysis. Biol Neonate 62:280–289
Meifort R, Vogel HM, Henning H (1990) Duplexsonographische Pfortaderfllußmessungen bei Lebergesunden und Patienten mit chronnischer Hepatitis nach Verabreichung einer vollresorbierbaren Testmahlzeit. Z Gastroenterol 28:291–294
Moneta GL, Taylor DC, Helton WS, Mulholland MW, Strandness DE (1988) Duplex ultrasound measurement of postprandial intestinal blood flow:effect of meal composition. Gastroenterology 95:1294–1301
Norryd C, Dencker H, Lunderquist A, Lin T, Tylen U (1975) Superior mesenteric blood flow during digestion in man. Acta Chir Scand 141:197–202
O'Brien S, Keogan M, Patchett S, McCormick PA, Afdhal N, Hegarty JE (1992) Postprandial changes in portal haemodynamics in patients with cirrhosis. Gut 33:364–367
Okazaki K, Miyazaki M, Ohnishi S, Ito K (1986) Effects of food intake and various extrinsic hormones on portal blood flow in patients with liver cirrhosis demonstrated by pulsed Doppler with the Octoson. Scand J Gastroenterol 21:1029–1038
Orrego H, Mena I, Baraona E, Palma R (1965) Modifications in hepatic blood flow and portal pressure produced by different diets. New Series 10:239–248
Payen DM, Fratacci MD, Dupuy P, Gatecel C, Vigouroux C, Ozier Y, Houssin D, Chapuis Y (1990) Portal and hepatic arterial blood flow measurements of human transplanted liver by implanted Doppler probes: interest for early complication and nutrition. Surgery 107:417–427
Pourcelot L (1976) Diagnostic ultrasound for cerebral vascular diseases. In: Donald I, Levi S (eds) Present and future of diagnostic ultrasound. Kooyker Science, Rotterdam, pp 141–147
Premen AJ, Kvietys PR, Granger DN (1985) Postprandial regulation of intestinal blood flow: role of gastrointestinal hormones. Am J Physiol 249 [Gastrointest Liver Physiol 12]:G250-G255
Pugliese D, Ohnishi K, Tsunoda T, Sabba C, Albano O (1987) Portal hemodynamics after meal in normal subjects and in patients with chronic liver disease studied by echo-Doppler flowmeter. Am J Gastroenterol 82:1052–1056
Qamar MI, Read AE, Mountford R, Skidmore R, Wells PNT (1984) Effects of carbohydrate, fat and protein on superior mesenteric artery blood flow in man. Gut 25:A1154
Qamar MI, Read AE, Skidmore R, Evans JM, Wells PNT (1986) Pulsatility index of superior mesenteric artery blood velocity waveforms.Ultrasound Med Biol 12:773–776
Shreiner DP, Barlai-Kovach M (1981) Diagnosis of alcoholic cirrhosis with the right-to-left hepatic lobe ratio: concise communication. J Nucl Med 22:116–120
Siregar H, Chou CC (1981) Relative contribution of fat, protein, carbohydrate, and ethanol to intestinal hyperaemia. Am J Physiol [Gastrointest Liver Physiol 5]:G27–G31
Spencer JA, Giussani DA, Moore PJ, Hanson MA (1991) In vitro validation of Doppler indices using blood and water. J Ultrasound Med 10:305–308
Svensson CK, Mauriello PM, Baarde SH, Middleton E, Lalka D (1984) Effects of carbohydrates on estimated hepatic blood flow. Clin Pharmacol Ther 35:660–665
Tsunoda T, Ohnishi K, Tanaka H (1988) Portal hemodynamic responses after oral intake of glucose in patients with cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol 83:398–403
Vatner SF, Patrick TA, Higgins CB, Franklin D (1974) Regional circulatory adjustments to eating and digestion in conscious unrestrained primates. J Appl Physiol 36:524–529
Webster J, Osuji PO, White F, Ingram JF (1975) The influence of food intake on portal blood flow and heat production in the digestive tract of sheep. Br J Nutr 34:125–139
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dauzat, M., Lafortune, M., Patriquin, H. et al. Meal induced changes in hepatic and splanchnic circulation: a noninvasive Doppler study in normal humans. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 68, 373–380 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00843732
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00843732