Abstract
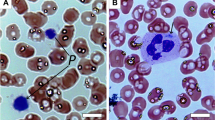
Bernard-Soulier Syndrome (BSS) is an autosomal recessive bleeding disorder due to quantitative or qualitative abnormalities in the glycoprotein (GP) Ib/IX/V complex, the platelet receptor for von Willebrand factor. BSS is characterized by giant platelets, thrombocytopenia, and prolonged bleeding time, and the hallmark of this disorder is the absence of ristocetininduced platelet agglutination. In the last 10 years, the molecular and genetic bases of many GPIb/IX/V defects have been elucidated, providing a better understanding of primary hemostasis and structure-function relations of the complex. Thus far, more than 30 mutations of the GPIbα, GPIbβ, or GPIX genes have been described in BSS. Recent studies also have shown that the phenotypes caused by mutations in the subunits of the GPIb/IX/V span a wide spectrum, from the normal phenotype, to isolated giant platelet disorders/macrothrombocytopenia, to full-blown BSS and platelet-type von Willebrand disease. Although recent progress in molecular biology has clarified the genotype-phenotype relationships of the GPIb/IX/V disorders, a close examination of platelet morphology on blood smears is still indispensable for a proper diagnosis. In this review, we summarize recent advances in the molecular basis of BSS with special emphasis on giant platelets and the genetic characteristics of Japanese BSS.Int J Hematol. 2002; 76: 319-327.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernard J, Soulier JP. Sur une nouvelle variete de dystrophie thrombocytaire-hemorragipare congenitale.Semi Hop Paris. 1948; 24: 3217–3223.
Lopez JA, Andrews RK, Afshar-Kharghan V, Berndt MC. Bernard-Soulier syndrome.Blood. 1998; 91: 4397–4418.
Lopez JA. The platelet glycoprotein Ib-IX complex.Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1994; 5: 97–119.
Berndt MC, Shen Y, Dopheide SM, Gardiner EE, Andrews RK. The vascular biology of the glycoprotein Ib-IX-V complex.Thromb Haemost. 2001; 86: 178–188.
Kroll MH, Harris TS, Moake JL, Handin RI, Schafer AI. von Willebrand factor binding to platelet GpIb initiates signals for platelet activation.J Clin Invest. 1991; 88: 1568–1573.
Ikeda Y, Handa M, Kamata T, et al. Transmembrane calcium influx associated with von Willebrand factor binding to GPIb in the initiation of shear-induced platelet aggregation.Thromb Haemost. 1993; 69: 496–502.
Savage B, Saldivar E, Ruggeri ZM. Initiation of platelet adhesion by arrest onto fibrinogen or translocation on von Willebrand factor.Cell. 1996; 84: 289–297.
Kulkarni S, Dopheide SM, Yap CL, et al. A revised model of platelet aggregation.J Clin Invest. 2000; 105: 783–791.
Ikeda Y, Handa M, Kawano K, et al. The role of von Willebrand factor and fibrinogen in platelet aggregation under varying shear stress.J Clin Invest. 1991; 87: 1234–1240.
Savage B, Almus-Jacobs F, Ruggeri ZM. Specific synergy of multiple substrate-receptor interactions in platelet thrombus formation under flow.Cell. 1998; 94: 657–666.
Wu YP, Vink T, Schiphorst M, et al. Platelet thrombus formation on collagen at high shear rates is mediated by von Willebrand factorglycoprotein Ib interaction and inhibited by von Willebrand factorglycoprotein IIb/IIIa interaction.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000; 20: 1661–1667.
Cunningham JG, Meyer SC, Fox JE. The cytoplasmic domain of the a-subunit of glycoprotein (GP) Ib mediates attachment of the entire GP Ib-IX complex to the cytoskeleton and regulates von Willebrand factor-induced changes in cell morphology.J Biol Chem. 1996; 271: 11581–11587.
Mistry N, Cranmer SL, Yuan Y, et al. Cytoskeletal regulation of the platelet glycoprotein Ib/V/IX-von Willebrand factor interaction.Blood. 2000; 96: 3480–3489.
Englund GD, Bodnar RJ, Li Z, Ruggeri ZM, Du X. Regulation of von Willebrand factor binding to the platelet glycoprotein Ib-IX by a membrane skeleton-dependent inside-out signal.J Biol Chem. 2001; 276: 16952–16959.
Handa M, Titani K, Holland LZ, Roberts JR, Ruggeri ZM. The von Willebrand factor-binding domain of platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib: characterization by monoclonal antibodies and partial amino acid sequence analysis of proteolytic fragments.J Biol Chem. 1986; 261: 12579–12585.
De Marco L, Mazzucato M, Masotti A, Ruggeri ZM. Localization and characterization of an a-thrombin-binding site on platelet glycoprotein Ibα.J Biol Chem. 1994; 269: 6478–6484.
Du X, Fox JE, Pei S. Identification of a binding sequence for the 14-3-3 protein within the cytoplasmic domain of the adhesion receptor, platelet glycoprotein Ibα.J Biol Chem. 1996; 271: 7362–7367.
Meyer SC, Zuerbig S, Cunningham CC, et al. Identification of the region in actin-binding protein that binds to the cytoplasmic domain of glycoprotein Ibα.J Biol Chem. 1997; 272: 2914–2919.
Lopez JA, Leung B, Reynolds CC, Li CQ, Fox JE. Efficient plasma membrane expression of a functional platelet glycoprotein Ib-IX complex requires the presence of its three subunits.J Biol Chem. 1992; 267: 12851–12859.
Lopez JA, Weisman S, Sanan DA, Sih T, Chambers M, Li CQ. Glycoprotein (GP) Ibβ is the critical subunit linking GPIbα and GPIX in the GPIb-IX complex.J Biol Chem. 1994; 269: 23716–23721.
Dong JF, Sae-Tung G, Lopez JA. Role of glycoprotein V in the formation of the platelet high-affinity thrombin-binding site.Blood. 1997; 89: 4355–4363.
Romo GM, Dong JF, Schade AJ, et al. The glycoprotein Ib-IX-V complex is a platelet counterreceptor for P-selectin.J Exp Med. 1999; 190: 803–814.
Simon DI, Chen Z, Xu H, et al. Platelet glycoprotein Ibα is a counterreceptor for the leukocyte integrin Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18).J Exp Med. 2000; 192: 193–204.
Wenger RH, Kieffer N, Wicki AN, Clemetson KJ. Structure of the human blood platelet membrane glycoprotein Ibα gene.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988; 156: 389–395.
Wenger RH, Wicki AN, Kieffer N, Adolph S, Hameister H, Clemetson KJ. The 5 flanking region and chromosomal localization of the gene encoding human platelet membrane glycoprotein Ibα.Gene. 1989; 85: 517–524.
Yagi M, Edelhoff S, Disteche CM, Roth GJ. Structural characterization and chromosomal location of the gene encoding human platelet glycoprotein Ibβ.J Biol Chem. 1994; 269: 17424–17427.
Hickey MJ, Roth GJ. Characterization of the gene encoding human platelet glycoprotein IX.J Biol Chem. 1993; 268: 3438–3443.
Yagi M, Edelhoff S, Disteche CM, Roth GJ. Human platelet glycoproteins V and IX: mapping of two leucine-rich glycoprotein genes to chromosome 3 and analysis of structures.Biochemistry. 1995; 34: 16132–16137.
Hashimoto Y, Ware J. Identification of essential GATA and Ets binding motifs within the promoter of the platelet glycoprotein Ibα gene.J Biol Chem. 1995; 270: 24532–24539.
Bastian LS, Yagi M, Chan C, Roth GJ. Analysis of the megakaryocyte glycoprotein IX promoter identifies positive and negative regulatory domains and functional GATA and Ets sites.J Biol Chem. 1996; 271: 18554–18560.
Ravanat C, Morales M, Azorsa DO, et al. Gene cloning of rat and mouse platelet glycoprotein V: identification of megakaryocytespecific promoters and demonstration of functional thrombin cleavage.Blood. 1997; 89: 3253–3262.
Yasunaga K. Congenital platelet function disorders: survey findings and pathophysiology.Nippon Ketsueki Gakkai Zasshi. 1986; 49: 1499–1508.
Greinacher A, Potzsch B, Kiefel V, White JG, Muller-Berghaus G, Mueller-Eckhardt C. Evidence that DDAVP transiently improves hemostasis in Bernard-Soulier syndrome independent of von Willebrand-factor.Ann Hematol. 1993; 67: 149–150.
Kemahli S, Canatan D, Uysal Z, Akar N, Cin S, Arcasoy A. DDAVP shortens bleeding time in Bernard-Soulier syndrome.Thromb Haemost. 1994; 71: 675.
Poon MC, d’Oiron R. Recombinant activated factor VII (Novo-Seven) treatment of platelet-related bleeding disorders: International Registry on Recombinant Factor VIIa and Congenital Platelet Disorders Group.Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2000; 11(suppl 1): S55-S68.
Wilcox DA, Olsen JC, Ishizawa L, et al. Megakaryocyte-targeted synthesis of the integrin β3-subunit results in the phenotypic correction of Glanzmann thrombasthenia.Blood. 2000; 95: 3645–3652.
Kunishima S, Lopez JA, Kobayashi S, et al. Missense mutations of the glycoprotein (GP) Ibβ gene impairing the GPIb α/β disulfide linkage in a family with giant platelet disorder.Blood. 1997; 89: 2404–2412.
Kunishima S, Naoe T, Kamiya T, Saito H. A novel heterozygous missense mutation in the platelet glycoprotein Ibβ gene associated with isolated giant platelet disorder.Am J Hematol. 2001; 68: 249–255.
Raccuglia G. Gray platelet syndrome: a variety of qualitative platelet disorders.Am J Med. 1971; 51: 818–828.
May R. Leukozyteneinschlusse.Dtsch Arch Klin Med. 1909; 96: 1–6.
Hegglin R. Gleichzeitige konstitutionelle Veranderungen an Neutrophilen und Thrombocyten.Helv Med Acta. 1945; 12: 439–440.
Kunishima S, Kojima T, Matsushita T, et al. Mutations in the NMMHC-A gene cause autosomal dominant macrothrombocytopenia with leukocyte inclusions (May-Hegglin anomaly/Sebastian syndrome).Blood. 2001; 97: 1147–1149.
Nichols KE, Crispino JD, Poncz M, et al. Familial dyserythropoietic anaemia and thrombocytopenia due to an inherited mutation in GATA1.Nat Genet. 2000; 24: 266–270.
Freson K, Devriendt K, Matthijs G, et al. Platelet characteristics in patients with X-linked macrothrombocytopenia because of a novel GATA1 mutation.Blood. 2001; 98: 85–92.
Stricker RB, Wong D, Saks SR, Corash L, Shuman MA. Acquired Bernard-Soulier syndrome: evidence for the role of a 210,000- molecular weight protein in the interaction of platelets with von Willebrand factor.J Clin Invest. 1985; 76: 1274–1278.
Devine DV, Currie MS, Rosse WF, Greenberg CS. Pseudo-Bernard-Soulier syndrome: thrombocytopenia caused by autoanti- body to platelet glycoprotein Ib.Blood. 1987; 70: 428–431.
Berndt MC, Kabral A, Grimsley P, Watson N, Robertson TI, Bradstock KF. An acquired Bernard-Soulier-like platelet defect associated with juvenile myelodysplastic syndrome.Br J Haematol. 1988; 68: 97–101.
Kunishima S, Miura H, Fukutani H, et al. Bernard-Soulier syndrome Kagoshima: Ser 444—>stop mutation of glycoprotein (GP) Ibα resulting in circulating truncated GPIbα and surface expression of GPIbβ and GPIX.Blood. 1994; 84: 3356–3362.
Wright SD, Michaelides K, Johnson DJ, West NC, Tuddenham EG. Double heterozygosity for mutations in the platelet glycoprotein IX gene in three siblings with Bernard-Soulier syndrome.Blood. 1993; 81: 2339–2347.
Frojmovic MM, Milton JG, Caen JP, Tobelem G. Platelets from “giant platelet syndrome (BSS)” are discocytes and normal sized.J Lab Clin Med. 1978; 91: 109–116.
White JG, Burris SM, Hasegawa D, Johnson M. Micropipette aspiration of human blood platelets: a defect in Bernard-Soulier’s syndrome.Blood. 1984; 63: 1249–1252.
Hourdille P, Pico M, Jandrot-Perrus M, Lacaze D, Lozano M, Nurden AT. Studies on the megakaryocytes of a patient with the Bernard-Soulier syndrome.Br J Haematol. 1990; 76: 521–530.
Tomer A, Scharf RE, McMillan R, Ruggeri ZM, Harker LA. Bernard-Soulier syndrome: quantitative characterization of megakaryocytes and platelets by flow cytometric and platelet kinetic measurements.Eur J Haematol. 1994; 52: 193–200.
Ware J, Russell S, Ruggeri ZM. Generation and rescue of a murine model of platelet dysfunction: the Bernard-Soulier syndrome.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000; 97: 2803–2808.
Miller JL, Lyle VA, Cunningham D. Mutation of leucine-57 to phenylalanine in a platelet glycoprotein Ibα leucine tandem repeat occurring in patients with an autosomal dominant variant of Bernard-Soulier disease.Blood. 1992; 79: 439–446.
Ware J, Russell SR, Marchese P, et al. Point mutation in a leucinerich repeat of platelet glycoprotein Ibα resulting in the Bernard- Soulier syndrome.J Clin Invest. 1993; 92: 1213–1220.
Miller JL. Platelet-type von Willebrand disease.Thromb Haemost. 1996; 75: 865–869.
Nurden P, Chretien F, Poujol C, Winckler J, Borel-Derlon A, Nurden A. Platelet ultrastructural abnormalities in three patients with type 2B von Willebrand disease.Br J Haematol. 2000; 110: 704–714.
Takahashi R, Sekine N, Nakatake T. Influence of monoclonal antiplatelet glycoprotein antibodies on in vitro human megakaryocyte colony formation and proplatelet formation.Blood. 1999; 93: 1951–1958.
Feng S, Christodoulides N, Kroll MH. The glycoprotein Ib/IX complex regulates cell proliferation.Blood. 1999; 93: 4256–4263.
Feng S, Christodoulides N, Resendiz JC, Berndt MC, Kroll MH. Cytoplasmic domains of GPIbα and GPIbβ regulate 14-3-3ζ binding to GPIb/IX/V.Blood. 2000; 95: 551–557.
Ludlow LB, Schick BP, Budarf ML, et al. Identification of a mutation in a GATA binding site of the platelet glycoprotein Ibβ promoter resulting in the Bernard-Soulier syndrome.J Biol Chem. 1996; 271: 22076–22080.
DiGeorge AM. Congenital absence of the thymus and its immunologic consequences: concurrence with congenital hypoparathyroidism.Birth Defects Orig Art Ser. 1968; 4: 116–121.
Van Geet C, Devriendt K, Eyskens B, Vermylen J, Hoylaerts MF. Velocardiofacial syndrome patients with a heterozygous chromosome 22q11 deletion have giant platelets.Pediatr Res. 1998; 44: 607–611.
Budarf ML, Konkle BA, Ludlow LB, et al. Identification of a patient with Bernard-Soulier syndrome and a deletion in the DiGeorge/velo-cardio-facial chromosomal region in 22q11.2.Hum Mol Genet. 1995; 4: 763–766.
Kenny D, Morateck PA, Gill JC, Montgomery RR. The critical interaction of glycoprotein (GP) Ibβ with GPIX: a genetic cause of Bernard-Soulier syndrome.Blood. 1999; 93: 2968–2975.
Nakagawa M, Okuno M, Okamoto N, Fujino H, Kato H. Bernard- Soulier syndrome associated with 22q11.2 microdeletion.Am J Med Genet. 2001; 99: 286–288.
Lascone MR, Sacchelli M, Vittorini S, Giusti S. Complex conotruncal heart defect, severe bleeding disorder and 22q11 deletion: a new case of Bernard-Soulier syndrome and of 22q11 deletion syndrome?Ital Heart J. 2001; 2: 475–477.
De Marco L, Mazzucato M, Fabris F, et al. Variant Bernard-Soulier syndrome type bolzano: a congenital bleeding disorder due to a structural and functional abnormality of the platelet glycoprotein Ib-IX complex.J Clin Invest. 1990; 86: 25–31.
de la Salle C, Baas MJ, Lanza F, et al. A three-base deletion remov ing a leucine residue in a leucine-rich repeat of platelet glycoprotein Ibα associated with a variant of Bernard-Soulier syndrome (Nancy I).Br J Haematol. 1995; 89: 386–396.
Ulsemer P, Lanza F, Baas MJ, et al. Role of the leucine-rich domain of platelet GPIbα in correct post-translational processing: the Nancy I Bernard-Soulier mutation expressed on CHO cells.Thromb Haemost. 2000; 84: 104–111.
Sadler JE. A revised classification of von Willebrand disease.Thromb Haemost. 1994; 71: 520–525.
Miller JL, Cunningham D, Lyle VA, Finch CN. Mutation in the gene encoding the a chain of platelet glycoprotein Ib in platelet- type von Willebrand disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991; 88: 4761–4765.
Russell SD, Roth GJ. Pseudo-von Willebrand disease: a mutation in the platelet glycoprotein Ibα gene associated with a hyperactive surface receptor.Blood. 1993; 81: 1787–1791.
Takahashi H, Murata M, Moriki T, et al. Substitution of Val for Met at residue 239 of platelet glycoprotein Ibα in Japanese patients with platelet-type von Willebrand disease.Blood. 1995; 85: 727–733.
Kunishima S, Heaton DC, Naoe T, et al. De novo mutation of the platelet glycoprotein Ibα gene in a patient with pseudo-von Willebrand disease.Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1997; 8: 311–315.
Noris P, Simsek S, Stibbe J, von dem Borne AE. A phenylalanine- 55 to serine amino-acid substitution in the human glycoprotein IX leucine-rich repeat is associated with Bernard-Soulier syndrome.Br J Haematol. 1997; 97: 312–320.
Suzuki K, Hayashi T, Yahagi A, et al. Novel point mutation in the leucine-rich motif of the platelet glycoprotein IX associated with Bernard-Soulier syndrome.Br J Haematol. 1997; 99: 794–800.
Noda M, Fujimura K, Takafuta T, et al. A point mutation in glycoprotein IX coding sequence (Cys73 (TGT) to Tyr(TAT)) causes impaired surface expression of GPIb/IX/V complex in two families with Bernard-Soulier syndrome.Thromb Haemost. 1996; 76: 874–878.
Kanaji T, Okamura T, Kurolwa M, et al. Molecular and genetic analysis of two patients with Bernard-Soulier syndrome: identification of new mutations in glycoprotein Ibα gene.Thromb Haemost. 1997; 77: 1055–1061.
Mitsui T, Yokoyama S, Yazaki N, et al. Severe bleeding tendency in a patient with Bernard-Soulier syndrome associated with a homozygous single base pair deletion in the gene coding for the human platelet glycoprotein Ibα.J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1998; 20: 246–251.
Noda M, Fujimura K, Takafuta T, et al. Heterogeneous expression of glycoprotein Ib, IX and V in platelets from two patients with Bernard-Soulier syndrome caused by different genetic abnormalities.Thromb Haemost. 1995; 74: 1411–1415.
Iwanaga M, Kunishima S, Ikeda S, Tomonaga M, Naoe T. Vulnerable mutation Trp126—>stop of glycoprotein IX in Japanese Bernard-Soulier syndrome.Eur J Haematol. 1998; 60: 264–266.
Kurokawa Y, Ishida F, Kamijo T, et al. A missense mutation (Tyr88 to Cys) in the platelet membrane glycoprotein Ibβ gene affects GPIb/IX complex expression: Bernard-Soulier syndrome in the homozygous form and giant platelets in the heterozygous form.Thromb Haemost. 2001; 86: 1249–1256.
Kunishima S, Tomiyama Y, Honda S, et al. Cys97—>Tyr mutation in the glycoprotein IX gene associated with Bernard-Soulier syndrome.Br J Haematol. 1999; 107: 539–545.
Kunishima S, Tomiyama Y, Honda S, et al. Homozygous Pro74—>Arg mutation in the platelet glycoprotein Ibβ gene associated with Bernard-Soulier syndrome.Thromb Haemost. 2000; 84: 112–117.
Savoia A, Balduini CL, Savino M, et al. Autosomal dominant macrothrombocytopenia in Italy is most frequently a type of heterozygous Bernard-Soulier syndrome.Blood. 2001; 97: 1330–1335.
Li C, Martin SE, Roth GJ. The genetic defect in two well-studied cases of Bernard-Soulier syndrome: a point mutation in the fifth leucine-rich repeat of platelet glycoprotein Ibα.Blood. 1995; 86: 3805–3814.
Koskela S, Partanen J, Salmi TT, Kekomaki R. Molecular characterization of two mutations in platelet glycoprotein (GP) Ibα in two Finnish Bernard-Soulier syndrome families.Eur J Haematol. 1999; 62: 160–168.
Antonucci JV, Martin ES, Hulick PJ, Joseph A, Martin SE. Bernard-Soulier syndrome: common ancestry in two African American families with the GPIbα Leu129Pro mutation.Am J Hematol. 2000; 65: 141–148.
Afshar-Kharghan V, Lopez JA. Bernard-Soulier syndrome caused by a dinucleotide deletion and reading frameshift in the region encoding the glycoprotein Ibα transmembrane domain.Blood. 1997; 90: 2634–2643.
Afshar-Kharghan V, Craig FE, Lopez JA. Bernard-Soulier syndrome in a patient doubly heterozygous for two frameshift mutations in the glycoprotein Ibα gene.Br J Haematol. 2000; 110: 919–924.
Donner M, Karpman D, Kristoffersson AC, Winqvist I, Holmberg L. Recurrent mutation Asn45—>Ser of glycoprotein IX in Bernard-Soulier syndrome.Eur J Haematol. 1996; 57: 178–179.
Koskela S, Javela K, Jouppila J, et al. Variant Bernard-Soulier syndrome due to homozygous Asn45Ser mutation in the platelet glycoprotein (GP) IX in seven patients of five unrelated Finnish families.Eur J Haematol. 1999; 62: 256–264.
Vanhoorelbeke K, Schlammadinger A, Delville JP, et al. Occurrence of the Asn45Ser mutation in the GPIX gene in a Belgian patient with Bernard Soulier syndrome.Platelets. 2001; 12: 114–120.
Li C, Pasquale DN, Roth GJ. Bernard-Soulier syndrome with severe bleeding: absent platelet glycoprotein Ibα due to a homozygous one-base deletion.Thromb Haemost. 1996; 76: 670–674.
Kenny D, Jonsson OG, Morateck PA, Montgomery RR. Naturally occurring mutations in glycoprotein Ibα that result in defective ligand binding and synthesis of a truncated protein.Blood. 1998; 92: 175–183.
Simsek S, Admiraal LG, Modderman PW, van-der-Schoot CE, von-dem-Borne AE. Identification of a homozygous single base pair deletion in the gene coding for the human platelet glycoprotein Ibα causing Bernard-Soulier syndrome.Thromb Haemost. 1994; 72: 444–449.
Margaglione M, DAndrea G, Grandone E, Brancaccio V, Amoriello A, Di Minno G. Compound heterozygosity (554-589 del, C515-T transition) in the platelet glycoprotein Ibα gene in a patient with a severe bleeding tendency.Thromb Haemost. 1999; 81: 486–492.
Simsek S, Noris P, Lozano M, et al. Cys209 Ser mutation in the platelet membrane glycoprotein Ibα gene is associated with Bernard-Soulier syndrome.Br J Haematol. 1994; 88: 839–844.
Gonzalez-Manchon C, Larrucea S, Pastor AL, et al. Compound heterozygosity of the GPIbα gene associated with Bernard-Soulier syndrome.Thromb Haemost. 2001; 86: 1385–1391.
Ware J, Russell SR, Vicente V, et al. Nonsense mutation in the glycoprotein Ibα coding sequence associated with Bernard-Soulier syndrome.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990; 87: 2026–2030.
Holmberg L, Karpman D, Nilsson I, Olofsson T. Bernard-Soulier syndrome Karlstad: Trp 498—>Stop mutation resulting in a truncated glycoprotein Ibα that contains part of the transmembranous domain.Br J Haematol. 1997; 98: 57–63.
Moran N, Morateck PA, Deering A, et al. Surface expression of glycoprotein Ibα is dependent on glycoprotein Ibβ: evidence from a novel mutation causing Bernard-Soulier syndrome.Blood. 2000; 96: 532–539.
Rivera CE, Villagra J, Riordan M, Williams S, Lindstrom KJ, Rick ME. Identification of a new mutation in platelet glycoprotein IX (GPIX) in a patient with Bernard-Soulier syndrome.Br J Haematol. 2001; 112: 105–108.
Noris P, Arbustini E, Spedini P, Belletti S, Balduini CL. A new variant of Bernard-Soulier syndrome characterized by dysfunctional glycoprotein (GP) Ib and severely reduced amounts of GPIX and GPV.Br J Haematol. 1998; 103: 1004–1013.
Arai M, Yamamoto N, Akamatsu N, et al. Substantial expression of glycoproteins IX and V on the platelet surface from a patient with Bernard-Soulier syndrome.Br J Haematol. 1994; 87: 185–188.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kunishima, S., Kamiya, T. & Saito, H. Genetic Abnormalities of Bernard-Soulier Syndrome. Int J Hematol 76, 319–327 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02982690
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02982690